-
抗体試薬
- フローサイトメトリー用試薬
-
ウェスタンブロッティング抗体試薬
- イムノアッセイ試薬
-
シングルセル試薬
- BD® AbSeq Assay | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits | シングルセル試薬
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Profiling Assays (VDJ Assays) | シングルセル試薬
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
-
細胞機能評価のための試薬
-
顕微鏡・イメージング用試薬
-
細胞調製・分離試薬
-
- BD® AbSeq Assay | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits | シングルセル試薬
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Profiling Assays (VDJ Assays) | シングルセル試薬
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- Japan (Japanese)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


.png)

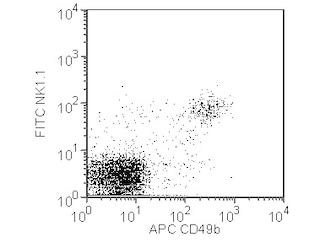
Multicolor flow cytometric analysis of CD314/NKG2D expression on mouse splenocytes. BALB/c splenocytes were stained with APC Rat Anti-Mouse CD49b (Cat. No. 560628) and either BD Horizon™ PE-CF594 Rat IgG1 isotype control (Cat. No. 562309, Left Panel) or BD Horizon™ PE-CF594 Rat Anti-Mouse CD314/NKD2D mAb (Cat. No. 562614, Right Panel), in the presence of Mouse BD Fc Block™ Purified Rat Anti-CD16/CD32 mAb 2.4G2 (Cat. No. 553141/553142). Two-color flow cytometric dot plots showing CD314 (or Ig isotype control staining) versus CD49b expression were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable cells. Flow cytometry was performed on a BD™ LSR II Flow Cytometer System.
.png)

BD Horizon™ PE-CF594 Rat Anti-Mouse CD314
.png)
Regulatory Statusの凡例
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation and Storage
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Please observe the following precautions: Absorption of visible light can significantly alter the energy transfer occurring in any tandem fluorochrome conjugate; therefore, we recommend that special precautions be taken (such as wrapping vials, tubes, or racks in aluminum foil) to prevent exposure of conjugated reagents, including cells stained with those reagents, to room illumination.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Texas Red is a registered trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, OR.
- CF™ is a trademark of Biotium, Inc.
- When excited by the yellow-green (561-nm) laser, the fluorescence may be brighter than when excited by the blue (488-nm) laser.
- This product is provided under an Agreement between BIOTIUM and BD Biosciences. The manufacture, use, sale, offer for sale, or import of this product is subject to one or more patents or pending applications owned or licensed by Biotium, Inc. This product, and only in the amount purchased by buyer, may be used solely for buyer’s own internal research, in a manner consistent with the accompanying product literature. No other right to use, sell or otherwise transfer (a) this product, or (b) its components is hereby granted expressly, by implication or by estoppel. This product is for research use only. Diagnostic uses require a separate license from Biotium, Inc. For information on purchasing a license to this product including for purposes other than research, contact Biotium, Inc., 3159 Corporate Place, Hayward, CA 94545, Tel: (510) 265-1027. Fax: (510) 265-1352. Email: btinfo@biotium.com.
- Because of the broad absorption spectrum of the tandem fluorochrome, extra care must be taken when using multi-laser cytometers, which may directly excite both PE and CF™594.
関連製品



.png?imwidth=320)
The CX5 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to NKG2D, also known as CD314. NKG2D is a lectin-like receptor that is detected on resting and IL-2-activated NK cells, activated CD8-positive T lymphocytes, and LPS-activated macrophages, but not on resting T cells or unstimulated macrophages. NKG2D has little homology to the other members of the NKG2 family, NKG2A, C, and E, and does not form heterodimers with CD94. On NK cells, NKG2D is an activating receptor that associates with DAP10, an adapter protein that stimulates the PI3 kinase pathway. An isoform of mouse NKG2D can also associate with the signaling adapter protein DAP12, also known as KARAP (Killer cell-Associated Receptor-Associated Polypeptide), that activates the Syk and ZAP70 tyrosine kinases. On cytotoxic T cells, NKG2D is a co-stimulatory receptor that associates with DAP10. The ligands for NKG2D include the minor histocompatibility antigen H60, MULT1 (Murine UL16-binding protein-Like Transcript 1), and the five retinoic acid-inducible proteins Rae-1α, β, γ, δ and ε. Interactions of NKG2D with its ligands are involved in the regulation of innate and immune cytotoxic responses to tumor and pathogen-infected cells and in diabetes progression in the NOD mouse. The CX5 mAb blocks the binding of NKG2D to its ligands.
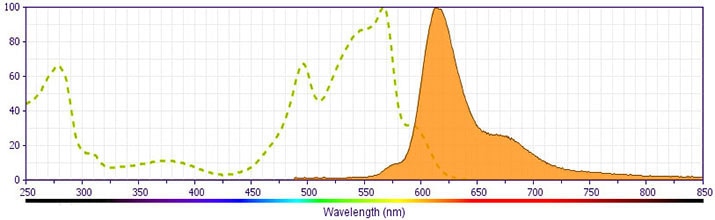
This antibody is conjugated to BD Horizon™ PE-CF594, which has been developed exclusively by BD Biosciences as a better alternative to PE-Texas Red®. PE-CF594 excites and emits at similar wavelengths to PE-Texas Red® yet exhibits improved brightness and spectral characteristics. Due to PE having maximal absorption peaks at 496 nm and 564 nm, PE-CF594 can be excited by the blue (488-nm), green (532-nm) and yellow-green (561-nm) lasers and can be detected with the same filter set as PE-Texas Red® (eg 610/20-nm filter).
Development References (8)
-
Carayannopoulos LN, Naidenko OV, Fremont DH, Yokoyama WM. Murine UL16–binding protein–like transcript 1: A newly described transcript encoding a high–affinity ligand for murine NKG2D . J Immunol. 2002; 169(8):4079-4083. (Biology). View Reference
-
Cerwenka A, Bakker AB, McClanahan T, et al. Retinoic acid early inducible genes define a ligand family for the activating NKG2D receptor in mice. Immunity. 2000; 12(6):721-727. (Biology). View Reference
-
Diefenbach A, Jamieson AM, Liu SD, Shastri N, Raulet DH. Ligands for the murine NKG2D receptor: expression by tumor cells and activation of NK cells and macrophages. Nat Immunol. 2000; 1(2):119-126. (Biology). View Reference
-
Diefenbach A, Tomasello E, Lucas M, et al. Selective associations with signaling proteins determine stimulatory versus costimulatory activity of NKG2D. Nat Immunol. 2002; 3(12):1142-1149. (Biology). View Reference
-
Gilfillan S, Ho EL, Cella M, Yokoyama WM, Colonna M. NKG2D recruits two distinct adapters to trigger NK cell activation and costimulation . Nat Immunol. 2002; 3(12):1150-1155. (Biology). View Reference
-
Ogasawara K, Hamerman JA, Ehrlich LR, et al. NKG2D blockade prevents autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice. Immunity. 2004; 20(6):757-767. (Clone-specific: Blocking). View Reference
-
Ogasawara K, Hamerman JA, Hsin H, et al. Impairment of NK cell function by NKG2D modulation in NOD mice. Immunity. 2003; 18(1):41-51. (Immunogen: Blocking). View Reference
-
Yokoyama WM. Natural killer cell receptors. Curr Opin Immunol. 1998; 10(3):298-305. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.