-
抗体試薬
- フローサイトメトリー用試薬
-
ウェスタンブロッティング抗体試薬
- イムノアッセイ試薬
-
シングルセル試薬
- BD® AbSeq Assay | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits | シングルセル試薬
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Profiling Assays (VDJ Assays) | シングルセル試薬
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
-
細胞機能評価のための試薬
-
顕微鏡・イメージング用試薬
-
細胞調製・分離試薬
-
- BD® AbSeq Assay | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits | シングルセル試薬
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit | シングルセル試薬
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Profiling Assays (VDJ Assays) | シングルセル試薬
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- Japan (Japanese)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


.png)

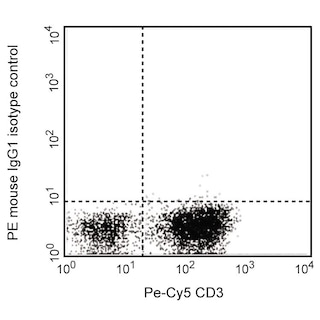
LEFT: Analysis of doublecortin (DCX) in human embryonic stem (ES) cell-derived neurons. A sorted population of neural stem cells (NSC), that had been derived from H9 cells (WiCell, Madison, WI), were differentiated in NSC differentiation medium [containing N2 and B-27 supplements (Life Technologies), recombinant human BDNF and GDNF (Peprotech), dibutryl cyclic AMP (Sigma)] for 4 weeks. The neurons were harvested, fixed in BD Cytofix™ buffer (Cat. No. 554655), permeabilized with BD™ Phosflow Perm/Wash buffer I (Cat. No. 557885) and stained with matching concentrations of a PE Mouse IgG1, κ isotype control (shaded histogram, Cat. No. 554680) or the PE Mouse anti-Doublecortin antibody (open histogram). Histograms were derived from gated events based on light scattering characteristics for the H9-derived neurons. The dimmer peak consists of NSC and glial progenitors, and the brighter peak consists of the immature neuron population that is staining positive for doublecortin. RIGHT: Analysis of doublecortin (DCX) on human ES cell-derived neurons and glia. NSC derived from H9 cells (WiCell, Madison, WI) were differentiated in NSC differentiation medium for 11 days followed by AGM™ Astrocyte Growth Medium (Lonza) for 16 days. The neurons and glia were harvested, fixed and permeabilized, and stained with PE Mouse Anti-Doublecortin and Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse anti-GFAP (Cat. No. 561470) monoclonal antibodies. The dot plot was derived from gated events based on light scattering characteristics for the H9-derived constituents. All flow cytometry was performed on a BD LSR™ II flow cytometry system.
.png)

BD Pharmingen™ PE Mouse anti-Doublecortin
.png)
Regulatory Statusの凡例
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation and Storage
Product Notices
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test).
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
関連製品



The cerebral cortex is composed of multiple layers of neurons of distinct types and functions, which perform in unison to orchestrate cognitive function. The formation of the cortex relies on complex signaling mechanisms, which mediate the migration of newly formed neurons from deep within the brain to the superficial regions. Defects in neuronal migration and disruption of the multi-layered cortex are apparent in conditions such as X-linked lissencephaly (XLIS) and subcortical laminar heterotopia (SCLH) or "double cortex" (DC) syndrome. Mutations in the doublecortin gene have been linked to these brain disorders. Doublecortin is highly expressed in developing brain, primarily in migrating neurons. It is significantly homologous with the N-terminal region of the product of the KIAA0369 gene, a protein that is also similar to the CaM kinase family in its C-terminal region. Doublecortin has four potential MAP kinase family phosphorylation sites and a putative site for Abl tyrosine phosphorylation. Thus, doublecortin is thought to be an integral component of tyrosine kinase signal transduction pathways that regulate neuronal migration and development of the cerebral cortex.
The 30/Doublecortin monoclonal antibody reacts with mouse and human doublecortin.
Development References (3)
-
Gleeson JG, Allen KM, Fox JW, et al. Doublecortin, a brain-specific gene mutated in human X-linked lissencephaly and double cortex syndrome, encodes a putative signaling protein. Cell. 1998; 92(1):63-72. (Biology). View Reference
-
Magavi SS, Leavitt BR, Macklis JD. Induction of neurogenesis in the neocortex of adult mice. Nature. 2000; 405(6789):951-955. (Biology). View Reference
-
des Portes V, Pinard JM, Billuart P, et al. A novel CNS gene required for neuronal migration and involved in X-linked subcortical laminar heterotopia and lissencephaly syndrome. Cell. 1998; 92(1):51-61. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.