-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
蛋白质印迹试剂
- 免疫分析 试剂
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD Rhapsody™ 附件试剂盒
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
- BD OMICS-One™ WTA Next Assay
-
Functional Assays
-
显微成像试剂
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current location or be switched to your location?

KLRG1
概述
杀伤细胞凝集素样受体G1(KLRG1)是一种免疫检查点受体,由基因KLRG1编码。KLRG1是一种抑制性凝集素样II型跨膜受体,含有细胞质免疫受体酪氨酸抑制基序(ITIM)。1主要是成分为一个由两个30 kDa-38 kDa N-糖基化亚基组成的同源二聚体分子。BD提供多种在人和小鼠细胞中检测KLRG1的克隆。
KLRG1生物学
功能
E、N和R-钙粘蛋白是KLRG1的配体;结合可防止Akt磷酸化并增加细胞周期抑制剂的表达。2结合还可激活信号分子SHP-2和SHIP-1,反过来抑制NK效应功能和T细胞增殖。KLRG1表达与活化T淋巴细胞增殖以及活化NK细胞效应功能的减少相关。3 KLRG1在先天和适应性免疫系统中的白细胞调节中发挥作用,被视为一种细胞衰老或分化标记物。例如,KLRG1可用于定义急性感染4和癌症5中的CD8 T细胞亚群,以区分短寿效应(KLRG1high CD127low)以及记忆前体(KLRG1low CD127high)CD8 T细胞。6
KLRG1-了解急性免疫应答的工具
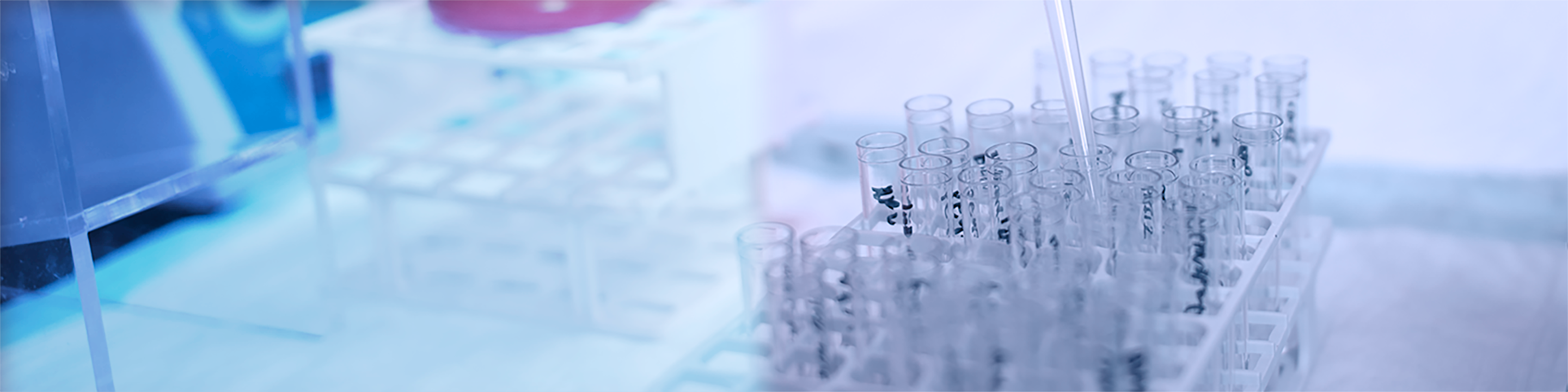
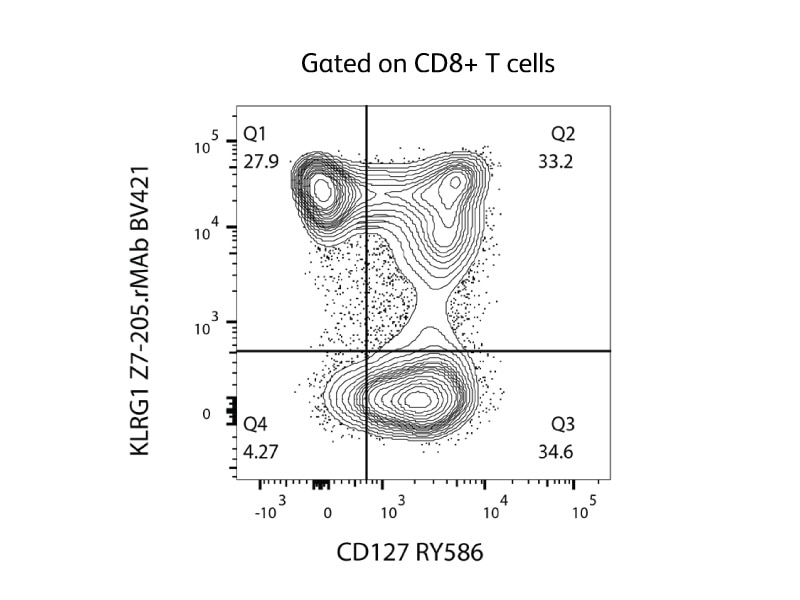
在急性感染期间,抗原特异性CD8 T细胞扩增并分化表达为KLRG1high CD127low的CD8记忆前体效应细胞(MPEC)以及表达为KLRG1low CD127high的短寿效应细胞(SLEC)。7 CD127是白细胞介素7的受体,可通过增加抗凋亡因子表达来决定细胞的寿命;因此,MPEC的CD127表达水平高于SLEC。8 相应图例显示了使用针对KLRG1和CD127的荧光偶联抗体在CD8 T细胞上检测MPEC(Q1)和SLEC(Q3)的情况。
CD8 T细胞分化为MPEC还是SLEC由几种转录因子决定,其表达受局部细胞因子条件的影响。高水平炎性细胞因子(如IL-12和IFN)会增加T-bet和Blimp-1等转录因子的表达,从而促进SLEC分化;相反,低水平炎性细胞因子会增加Id3和Eomes等转录因子的表达,从而促进MDEC分化。9-10 BD支持使用多种试剂来检测转录因子,包括荧光偶联抗体和破膜系统。
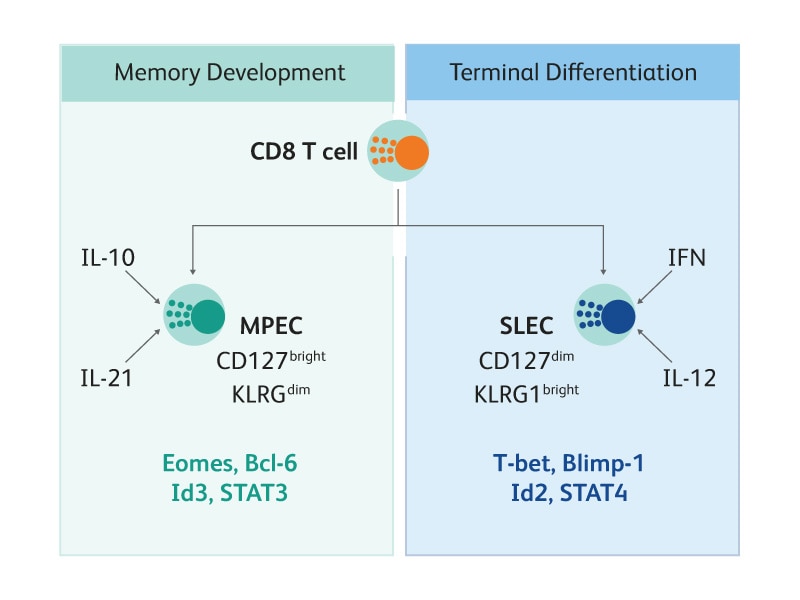
抗原特异性CD8 T细胞分化为MPEC还是SLEC取决于环境中存在的炎性因子,炎性因子会影响驱动发育的几种转录因子的表达。11
KLRG1与疾病
研究报告称,在肿瘤微环境中T细胞高度表达KLRG1,使其成为免疫肿瘤学的潜在治疗靶点。12,13随后,小鼠癌症模型中的抗KLRG1抗体治疗(单独治疗或联合抗PD-1治疗)可有效用于肿瘤消退和减少转移。
人KLRG1
人KLRG1在大量NK细胞、淋巴因子激活杀伤(LAK)细胞和贴壁LAK(A-LAK)细胞亚群,以及在CD8+和CD4+ T淋巴细胞亚群上表达,但不在肥大细胞上表达。1 BD开发了一种靶向人KLRG1的新型重组单克隆抗体(rMab),它可改善分离并有可能帮助区分表达KLRG1的新型免疫细胞亚群。
小鼠KLRG1
在所有受试小鼠品系中,小鼠KLRG1是大鼠肥大细胞功能相关抗原的同源物(例如,AKR/J、BALB/c、C3H/HeN、C3H.SW、C57BL/6、DBA/1、SJL和129/J)。与在肥大细胞上表达的大鼠MAFA不同,小鼠KLRG1在大量NK细胞、淋巴因子激活杀伤(LAK)细胞和贴壁LAK(A-LAK)细胞,以及在活化CD8+ T淋巴细胞亚群和小部分CD4+、CD8+ T细胞上表达,而不在肥大细胞上表达。2,14 在MHC I类缺陷小鼠中,KLRG1表达降低,尽管无法检测到KLRG1与MHC I类抗原的直接结合。15
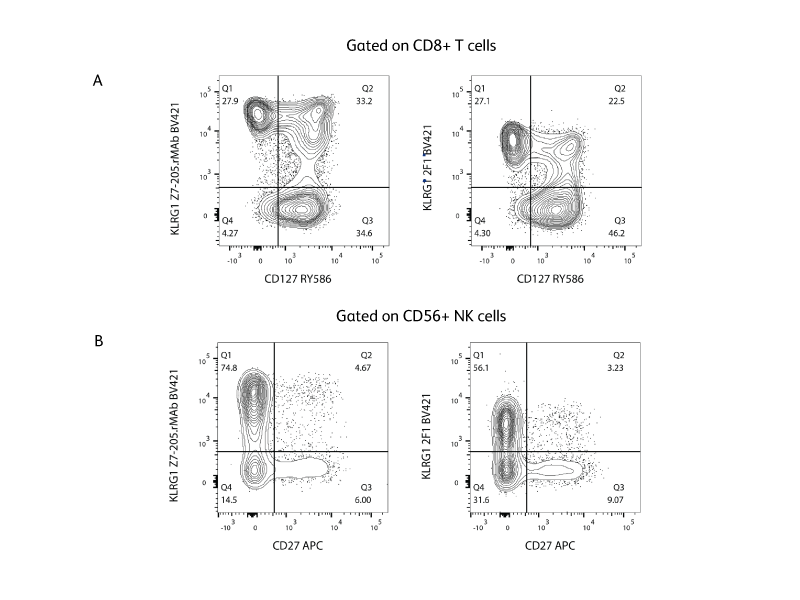
克隆2F1是针对小鼠KLRG1的特异性克隆,可用于多种形式和试剂盒,包括BD® AbSeq和BD Lyoplate™筛选多色实验方案。虽然2F1可与人KLRG1发生交叉反应,我们仍建议使用克隆Z7-205.rMAb来检测人KLRG1,因为后者染色更为明亮。
克隆2F1用于多组学分析,以表征B细胞淋巴瘤小鼠模型中 的免疫细胞群肿瘤应答。分析来自B细胞淋巴瘤小鼠模型中的脾细胞免疫细胞群,并根据21色细胞分选实验方案将其分选成几个细胞簇。使用34-plex BD® AbSeq Panel分析这类细胞簇的蛋白质和mRNA表达。以下热图显示了内源性CD8 T细胞簇中的蛋白质和mRNA差异分析(包括KLRG1)。
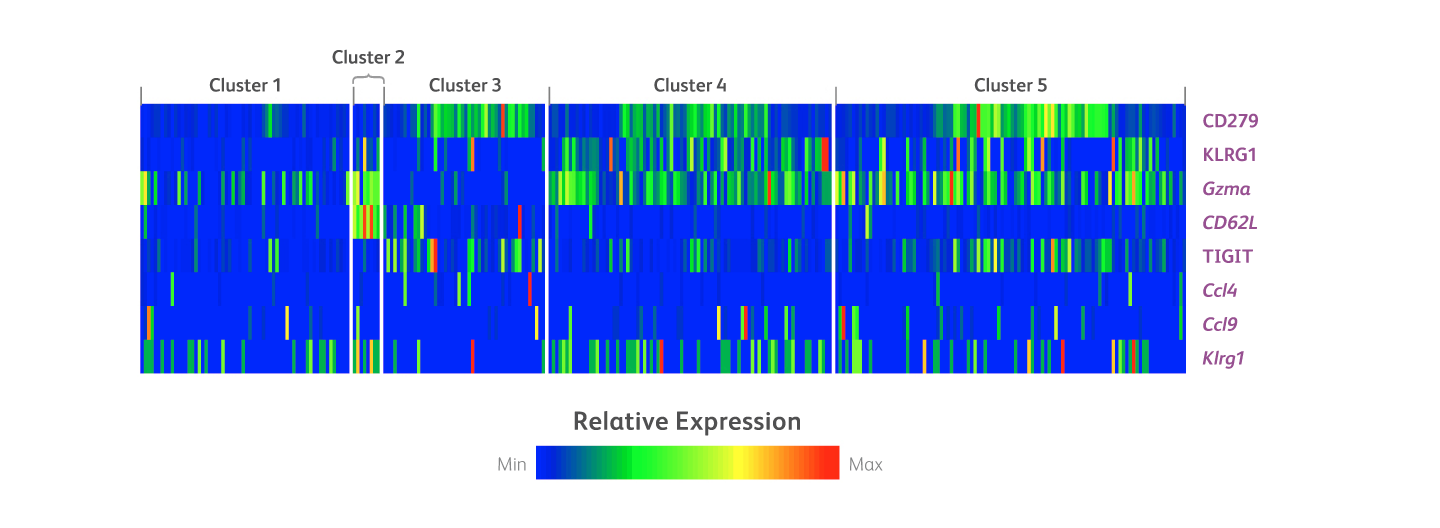
有关B细胞淋巴瘤小鼠模型中成簇免疫细胞群的蛋白质和mRNA差异分析(包括KLRG1)热图。
]参考文献
- Beyersdorf NB, Ding X, Karp K, Hanke T. Expression of inhibitory "killer cell lectin-like receptor G1" identifies unique subpopulations of effector and memory CD8T cells. Eur J Immunol. 2001; 31(12):3443-3452.
- Henson SM, Akbar AN. KLRG1--more than a marker for T cell senescence. Age (Dordr). 2009;31(4):285-291. doi:10.1007/s11357-009-9100-9
- Henson SM, Franzese O, Macaulay R, et al. KLRG1 signaling induces defective Akt (ser473) phosphorylation and proliferative dysfunction of highly differentiated CD8+ T cells. Blood. 2009;113(26):6619-6628. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-01-199588
- Wang D, Diao H, Getzler AJ, et al. The Transcription Factor Runx3 Establishes Chromatin Accessibility of cis-Regulatory Landscapes that Drive Memory Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Formation. Immunity. 2018; 48(4):659-674.e6.
- Tata A, Dodard G, Fugère C, et al. Combination blockade of KLRG1 and PD-1 promotes immune control of local and disseminated cancers. Oncoimmunology. 2021;10(1):1933808. Published 2021 Jun 15. doi:10.1080/2162402X.2021.1933808
- Joshi NS, Cui W, Chandele A, et al. Inflammation directs memory precursor and short-lived effector CD8(+) T cell fates via the graded expression of T-bet transcription factor. Immunity. 2007;27(2):281-295. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2007.07.010
- Joshi NS, Kaech SM. Effector CD8 T cell development: a balancing act between memory cell potential and terminal differentiation. J Immunol. 2008;180(3):1309-1315. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.180.3.1309
- Amsen D, Backer RA, Helbig C. Decisions on the road to memory. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;785:107-120. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-6217-0_12
- Obar JJ, Jellison ER, Sheridan BS, et al. Pathogen-induced inflammatory environment controls effector and memory CD8+ T cell differentiation. J Immunol. 2011;187(10):4967-4978. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1102335
- Plumlee CR, Obar JJ, Colpitts SL, et al. Early effector CD8 T cells display plasticity in populating the short-lived effector and memory-precursor pools following bacterial or viral infection. Scientific Reports. 2015;5(1). doi:10.1038/srep12264
- Joshi N, Cui W, Chandele A, et al. Inflammation Directs Memory Precursor and Short-Lived Effector CD8+ T Cell Fates via the Graded Expression of T-bet Transcription Factor. Immunity. 2007;27(2):281-295. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2007.07.010
- Greenberg SA, Kong SW, Thompson E, Gulla SV. Co-inhibitory T cell receptor KLRG1: Human cancer expression and efficacy of neutralization in murine cancer models. Oncotarget. 2019;10(14):1399-1406. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.26659
- Akhmetzyanova I, Zelinskyy G, Littwitz-Salomon E, et al. CD137 Agonist Therapy Can Reprogram Regulatory T Cells into Cytotoxic CD 4+ T Cells with Antitumor Activity. J Immunol. 2016; 196(1):484-92.
- Hanke T, Corral L, Vance RE, Raulet DH. 2F1 antigen, the mouse homolog of the rat "mast cell function-associated antigen", is a lectin-like type II transmembrane receptor expressed by natural killer cells. Eur J Immunol. 1998; 28(12):4409-4417.
- Corral L, Hanke T, Vance RE, Cado D, Raulet DH. NK cell expression of the killer cell lectin-like receptor G1 (KLRG1), the mouse homolog of MAFA, is modulated by MHC class I molecules. Eur J Immunol. 2000; 30(3):920-930.
仅供研究使用,不用于诊断或治疗