Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


.png)

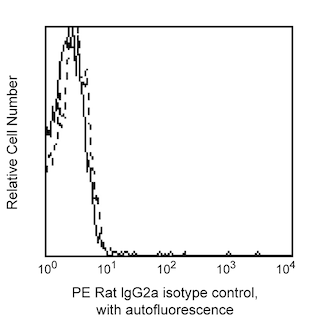
Flow cytometric analysis of H-2 Class I expression on mouse splenocytes or thymocytes. C57BL/6 mouse splenic leucocytes (Left Plot) or thymocytes (Right Plot) were preincubated with Purified Rat Anti-Mouse CD16/CD32 antibody (Mouse BD Fc Block™) (Cat. No. 553141/553142) and stained with either PE Rat IgG2a, κ Isotype Control (Cat. No.557229; dashed line histograms) or PE Mouse Anti-H-2 Class I antibody (Cat. No. 566776; solid line histograms) at 0.25 µg/test. The fluorescence histograms showing H-2 Class I expression (or Ig Isotype control staining) were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable cells. Flow cytometry and data analysis were performed using a BD FACSCelesta™ Flow Cytometer System and FlowJo™ software. Data shown on this Technical Data Sheet are not lot specific.
.png)

BD Pharmingen™ PE Rat Anti-Mouse H-2 Class I
.png)
监管状态图例
未经BD明确书面授权,严禁使用未经许可的任何商品。
准备和存储
商品通知
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
配套商品





The M1/42 monoclonal antibody (mAb) specifically recognizes intact Histocompatibility-2 Region (H-2) class I antigens (Ags), also known as mouse Major Histocompatibility Complex class I (MHC-I) Ags. This mAb reportedly binds to one or more of the H-2 Ags (H-2K, H-2D, and likely H-2L) that are primarily expressed on most nucleated somatic cells of hematopoietic and nonhematopoietic origin. H-2 class I molecules are comprised of a ~45-50 kDa type I transmembrane heavy chain glycoprotein that is noncovalently linked to ~13 kDa β2-microglobulin (β2-m). The extracellular region of the polymorphic heavy chains is comprised of three globular domains (α1, α2, and α3), followed by a transmembrane region and a cytoplasmic tail. Sequence variations are manifest in regions of the α1 and α2 domains that line the peptide-binding cleft involved in Ag presentation. The M1/42 mAb reportedly binds to H-2 class I Ags from multiple mouse haplotypes including a, b, d, j, k, s, and u. It does not bind to separated H-2 class I heavy chains or β2-m. Cell surface CD8 molecules bind to invariant sites of the H-2 heavy chains and can provide coreceptor signaling for Ag-mediated activation through the T cell receptor. H-2 class I molecules that present self-Ags can lead to self-tolerance of maturing CD8+ T cells due to thymic selection. Alternatively, these molecules can present foreign peptide Ags to mature peripheral CD8+ T cells resulting in cell-mediated immune responses against foreign Ags. H-2 class I Ags also serve as ligands for activating and inhibitory receptors expressed by NK cells and some T cells. The M1/42 antibody is useful for analyzing H-2 class I Ag expression on cells or cell lines. Cells from different experimental systems, eg, stressed cells that have undergone infection or transformation, may express little or no H-2 class I Ag. In contrast, cells undergoing activation or responding to certain factors (eg, interferons) may express upregulated levels of these Ags.
研发参考 (5)
-
Bouwer AL, Saunderson SC, Caldwell FJ, et al. NK cells are required for dendritic cell-based immunotherapy at the time of tumor challenge.. J Immunol. 2014; 192(5):2514-21. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). 查看参考
-
P. A. Gorer, S. Lyman, G. D. Snell. Studies on the Genetic and Antigenic Basis of Tumour Transplantation. Linkage between a Histocompatibility Gene and 'Fused' in Mice. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1948; 135(881):499-505. (Biology).
-
Springer TA. Cell-surface differentiation in the mouse. Characterization of "jumping" and "lineage" antigens using xenogeneic rat monoclonal antibodies. In: Kennett RH, McKearn TJ, Bechtol KB, ed. Monoclonal antibodies. Hybridomas: A new dimension in biological analyses. New York and London: Plenum Press; 1980:185-217.
-
Stallcup KC, Springer TA, Mescher MF. Characterization of an anti-H-2 monoclonal antibody and its use in large-scale antigen purification. J Immunol. 1981; 127(30):923-930. (Immunogen: Flow cytometry, Immunoaffinity chromatography, Immunoprecipitation, Radioimmunoassay). 查看参考
-
Watanabe Y, Kuribayashi K, Miyatake S, et al. Exogenous expression of mouse interferon gamma cDNA in mouse neuroblastoma C1300 cells results in reduced tumorigenicity by augmented anti-tumor immunity.. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1989; 86(23):9456-60. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). 查看参考
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.