-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
蛋白质印迹试剂
- 免疫分析 试剂
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD Rhapsody™ 附件试剂盒
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Profiling Assays
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
-
Functional Assays
-
显微成像试剂
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
-
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD Rhapsody™ 附件试剂盒
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Profiling Assays
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- China (Chinese)
-
更改国家/语言
Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




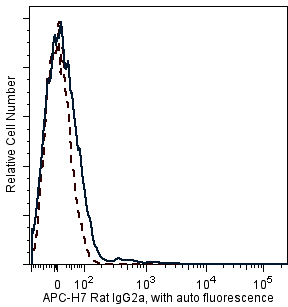
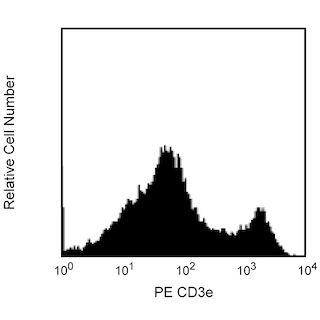
Two-color analysis of the expression of CD8a on mouse T cells. C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with APC-H7 Rat anti-mouse CD8a (Cat. No. 560182/560247, right panel) or APC-H7 Rat IgG2a, k isotype control(Cat. No. 560197, left panel) and PE Hamster anti-mouse CD3e (Cat. No. 553063/553064). Nonviable leukocytes were excluded from the analysis by staining with 7-AAD (Cat. No. 559925). Flow cytometry was performed on a BD™ LSR II flow cytometry system.


BD Pharmingen™ APC-H7 Rat anti-Mouse CD8a

监管状态图例
未经BD明确书面授权,严禁使用未经许可的任何商品。
准备和存储
商品通知
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Please observe the following precautions: Absorption of visible light can significantly alter the energy transfer occurring in any tandem fluorochrome conjugate; therefore, we recommend that special precautions be taken (such as wrapping vials, tubes, or racks in aluminum foil) to prevent exposure of conjugated reagents, including cells stained with those reagents, to room illumination.
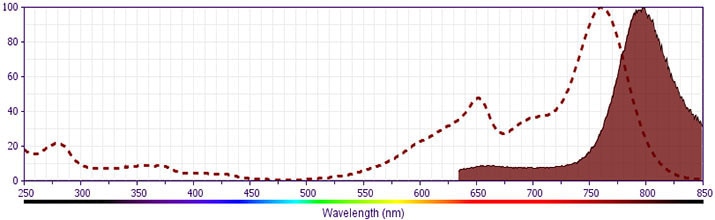
- BD APC-H7 is a tandem conjugate and an analog of APC-Cy7 with the same spectral properties. It has decreased intensity but it is engineered for greater stability and less spillover in the APC channel and consequently offers better performance than APC-Cy7. It has an absorption maximum of approximately 650 nm. When excited by light from a red laser, the APC fluorochrome can transfer energy to the cyanine dye, which then emits at a longer wavelength. The resulting fluorescent emission maximum is approximately 767 nm. BD recommends that a 750-nm longpass filter be used along with a red-sensitive detector such as the Hamamatsu R3896 PMT. As with APC-Cy7 special filters are required when using APC-H7 in conjunction with APC. Note: Although our APC-H7 products demonstrate higher lot-to lot consistency than other APC tandem conjugate products, and every effort is made to minimize the lot-to-lot variation in residual emission from APC, it is strongly recommended that every lot be tested for differences in the amount of compensation required and that individual compensation controls are run for each APC-H7 conjugate.
- Although BD APC-H7 is engineered to minimize spillover to the APC channel and is more stable and less affected by light, temperature, and formaldehyde-based fixatives, compared to other APC-cyanine tandem dyes, it is still good practice to minimize as much as possible, any light, temperature and fixative exposure when working with all fluorescent conjugates.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Cy is a trademark of GE Healthcare.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
配套商品
The 53-6.7 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to the 38 kDa α and 34 kDa α' chains of the CD8 differentiation antigen (Ly-2 or Lyt-2) of all mouse strains tested. The CD8 α and α' chains (CD8a) form heterodimers with the CD8 β chain (CD8b, Ly-3, or Lyt-3) on the surface of most thymocytes. A subpopulation of mature T lymphocytes (i.e., MHC class I-restricted T cells, including most T suppressor/cytotoxic cells) expresses almost exclusively the CD8 αβ heterodimer. Subsets of γδ TCR-bearing T cells, intestinal intrapithelial lymphocytes, and dendritic cells express CD8a without CD8b. It has been suggested that the expression of the CD8a/CD8b heterodimer is restricted to T lymphocytes which matured in the thymus or in an extrathymic environment that had been influenced by thymus-initiated neuroendocrine signals. CD8 is an antigen coreceptor on the T-cell surface which interacts with MHC class I molecules on antigen-presenting cells or epithelial cells. It participates in T-cell activation through its association with the T-cell receptor complex and protein tyrosine kinase lck (p56 [lck]). The CD8 α and α' chains arise from alternatively spliced messengers of a single CD8a gene. The longer α form associates with p56 [lck] via a CXCP motif in its cytoplasmic domain, which it shares with CD4, but not with CD8b. The truncated α' chain is unable to associate with p56 [lck], and it may function to attenuate the CD8-mediated costimulatory signal during intrathymic T-cell maturation. In vivo and in vitro treatment with 53-6.7 mAb has reportedly been effective at depleting CD8+ peripheral T lymphocytes. The 53-6.7 antibody has also been reported to cross-react with CD8 α- and α'-like polypeptides on subsets of thymic and peripheral lymphocytes in the Egyptian toad, Bufo regularis.
研发参考 (25)
-
Bierer BE, Sleckman BP, Ratnofsky SE, Burakoff SJ. The biologic roles of CD2, CD4, and CD8 in T-cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989; 7:579-599. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Fujiura Y, Kawaguchi M, Kondo Y, et al. Development of CD8 alpha alpha+ intestinal intraepithelial T cells in beta 2-microglobulin- and/or TAP1-deficient mice. J Immunol. 1996; 156(8):2710-2715. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Hathcock KS. T cell depletion by cytotoxic elimination. Curr Protoc Immunol. 1991; 1:3.4.1-3.4.3. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Janeway CA Jr. The T cell receptor as a multicomponent signalling machine: CD4/CD8 coreceptors and CD45 in T cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992; 10:645-674. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Kruisbeek AM, Shevach EM. Proliferative assays for T cell function. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2004; 3:3.12.1-3.12.14. (Biology). 查看参考
-
LeFrancois L. Extrathymic differentiation of intraepithelial lymphocytes: generation of a separate and unequal T-cell repertoire. Immunol Today. 1991; 12(12):436-438. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Ledbetter JA, Herzenberg LA. Xenogeneic monoclonal antibodies to mouse lymphoid differentiation antigens. Immunol Rev. 1979; 47:63-90. (Immunogen). 查看参考
-
Ledbetter JA, Rouse RV, Micklem HS, Herzenberg LA. T cell subsets defined by expression of Lyt-1,2,3 and Thy-1 antigens. Two-parameter immunofluorescence and cytotoxicity analysis with monoclonal antibodies modifies current views. J Exp Med. 1980; 152(2):280-295. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Ledbetter JA, Seaman WE, Tsu TT, Herzenberg LA. Lyt-2 and lyt-3 antigens are on two different polypeptide subunits linked by disulfide bonds. Relationship of subunits to T cell cytolytic activity. J Exp Med. 1981; 153(6):1503-1516. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Leishman AJ, Naidenko OV, Attinger A, et al. T cell responses modulated through interaction between CD8alphaalpha and the nonclassical MHC class I molecule, TL. Science. 2001; 294(5548):1848-1849. (Biology). 查看参考
-
MacDonald HR, Schreyer M, Howe RC, Bron C. Selective expression of CD8 alpha (Ly-2) subunit on activated thymic gamma/delta cells. Eur J Immunol. 1990; 20(4):927-930. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Mitnacht R, Bischof A, Torres-Nagel N, Hunig T. Opposite CD4/CD8 lineage decisions of CD4+8+ mouse and rat thymocytes to equivalent triggering signals: correlation with thymic expression of a truncated CD8 alpha chain in mice but not rats. J Immunol. 1998; 160(2):700-707. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Murosaki S, Yoshikai Y, Ishida A, et al. Failure of T cell receptor V beta negative selection in murine intestinal intra-epithelial lymphocytes. Int Immunol. 1991; 3(10):1005-1013. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Nakayama K, Nakayama K, Negishi I, et al. Requirement for CD8 beta chain in positive selection of CD8-lineage T cells. Science. 1994; 263(5150):1131-1133. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Negm HI, Mansour MH, Saad AH, Abdel Halim RS. Structural characterization of an Lyt-2/3 homolog expressed on Bufo regularis lymphocytes. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 1996; 113(1):79-87. (Biology). 查看参考
-
O'Rourke AM, Mescher MF. The roles of CD8 in cytotoxic T lymphocyte function. Immunol Today. 1993; 14(4):183-188. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Rocha B, Vassalli P, Guy-Grand D. The extrathymic T-cell development pathway. Immunol Today. 1992; 14(3):140-141. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Sydora BC, Brossay L, Hagenbaugh A, Kronenberg M, Cheroutre H. TAP-independent selection of CD8+ intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1996; 156(11):4209-4216. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Traver D, Akashi K, Manz M, et al. Development of CD8alpha-positive dendritic cells from a common myeloid progenitor. Science. 2000; 290(5499):2152-2154. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Walker ID, Murray BJ, Hogarth PM, Kelso A, McKenzie IF. Comparison of thymic and peripheral T cell Ly-2/3 antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1984; 14(10):906-910. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Wang J, Klein JR. Thymus-neuroendocrine interactions in extrathymic T cell development. Science. 1994; 265(5180):1860-1862. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Zamoyska R, Derham P, Gorman SD, et al. Inability of CD8 alpha' polypeptides to associate with p56lck correlates with impaired function in vitro and lack of expression in vivo. Nature. 1989; 342(6247):278-281. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Zamoyska R, Vollmer AC, Sizer KC, Liaw CW, Parnes JR. Two Lyt-2 polypeptides arise from a single gene by alternative splicing patterns of mRNA. Cell. 1985; 43(1):153-163. (Biology). 查看参考
-
Zamoyska R. The CD8 coreceptor revisited: one chain good, two chains better. Immunity. 1994; 1(4):243-246. (Biology). 查看参考
-
van Ewijk W, van Soest PL, van den Engh GJ. Fluorescence analysis and anatomic distribution of mouse T lymphocyte subsets defined by monoclonal antibodies to the antigens Thy-1, Lyt-1, Lyt-2, and T-200. J Immunol. 1981; 127(6):2594-2604. (Biology). 查看参考
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.