Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


.png)

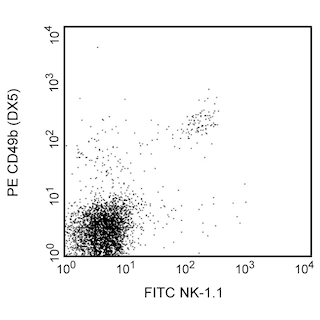
Flow cytometric analysis of CD122 expression on mouse splenic NK cells. C57BL/6 splenocytes were stained with PE Rat Anti-Mouse CD49b (Cat. No. 553858/561066) alone (Left Panel) or simultaneously with FITC Rat Anti-Mouse CD122 (Cat. No. 553361/561693; Right Panel). Two-color contour plots were derived from gated events with the side and forward light-scattering characteristics of viable splenocytes. Flow cytometry was performed on a BD FACScan™ system.
.png)

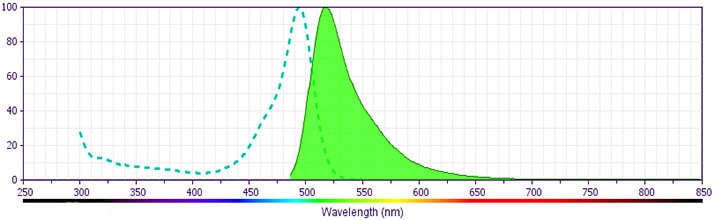
BD Pharmingen™ FITC Rat Anti-Mouse CD122
.png)
규제 상태 범례
Becton, Dickinson and Company의 명시적인 서면 승인 없이는 사용 하실 수 없습니다.
준비 및 보관
제품 고시
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
관련 제품
.png?imwidth=320)
The TM-β1 monoclonal antibody specifically recognizes the 90-100-kDa β chain shared by the IL-2 and IL-15 receptors (IL-2Rβ, CD122). In the periphery, CD122 is expressed on CD8+ T lymphocytes, NK cells, NK-T cells, dendritic epidermal T cells, subsets of intraepithelial lymphocytes, and macrophages. Small subsets of fetal and adult thymocytes constitutively express CD122. CD122+ cells in the bone marrow include committed NK-cell progenitors. IL-2Rβ expression is upregulated by IL-2. CD122 is a transmembrane glycoprotein of the hematopoietin receptor superfamily which can combine with CD132 (γc) alone or CD132 plus CD25 (IL-2Rα) to form intermediate or high-affinity IL-2 receptor complexes, respectively. The β chain of these complexes, CD122, is involved in signal transduction and immunoregulation. The TM-β1 antibody blocks high affinity binding of IL-2 or IL-15 to IL-2Rβ.
개발 참고 자료 (18)
-
Alleva DG, Kaser SB, Monroy MA, Fenton MJ, Beller DI. IL-15 functions as a potent autocrine regulator of macrophage proinflammatory cytokine production: evidence for differential receptor subunit utilization associated with stimulation or inhibition. J Immunol. 1997; 159(6):2941-2951. (Clone-specific). 참조 보기
-
Bendelac A. Mouse NK1+ T cells. Curr Opin Immunol. 1995; 7(3):367-374. (Biology). 참조 보기
-
Cho BK, Wang C, Sugawa S, Eisen HN, Chen J. Functional differences between memory and naive CD8 T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999; 96(6):2976-2981. (Biology). 참조 보기
-
Giri JG, Ahdieh M, Eisenman J, et al. Utilization of the beta and gamma chains of the IL-2 receptor by the novel cytokine IL-15. EMBO J. 1994; 13(12):2822-2830. (Biology). 참조 보기
-
Guy-Grand D, Cuenod-Jabri B, Malassis-Seris M, Selz F, Vassalli P. Complexity of the mouse gut T cell immune system: identification of two distinct natural killer T cell intraepithelial lineages. Eur J Immunol. 1996; 26(9):2248-2256. (Biology). 참조 보기
-
Hanke T, Mitnacht R, Boyd R, Hunig T. Induction of interleukin 2 receptor beta chain expression by self-recognition in the thymus. J Exp Med. 1994; 180(5):1629-1636. (Biology). 참조 보기
-
Kondo M, Ohashi Y, Tada K, Nakamura M, Sugamura K. Expression of the mouse interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain in various cell populations of the thymus and spleen. Eur J Immunol. 1994; 24(9):2026-2030. (Biology). 참조 보기
-
Ku CC, Murakami M, Sakamoto A, Kappler J, Marrack P. Control of homeostasis of CD8+ memory T cells by opposing cytokines. Science. 2000; 288(5466):675-678. (Biology). 참조 보기
-
Malek TR, Furse RK, Fleming ML, Fadell AJ, He YW. Biochemical identity and characterization of the mouse interleukin-2 receptor beta and gamma c subunits. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1995; 15(5):447-454. (Biology). 참조 보기
-
Nakanishi K, Hirose S, Yoshimoto T, et al. Role and regulation of interleukin (IL)-2 receptor alpha and beta chains in IL-2-driven B-cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992; 89(8):3551-3555. (Clone-specific). 참조 보기
-
Ohno H, Ono S, Hirayama N, Shimada S, Saito T. Preferential usage of the Fc receptor gamma chain in the T cell antigen receptor complex by gamma/delta T cells localized in epithelia. J Exp Med. 1994; 179(1):365-369. (Biology). 참조 보기
-
Rosmaraki EE, Douagi I, Roth C, Colucci F, Cumano A, Di Santo JP. Identification of committed NK cell progenitors in adult murine bone marrow. Eur J Immunol. 2001; 31(6):1900-1909. (Biology). 참조 보기
-
Suzuki H, Kundig TM, Furlonger C et al. Deregulated T cell activation and autoimmunity in mice lacking interleukin-2 receptor beta. Science. 1995; 268(5216):1472-1476. (Clone-specific). 참조 보기
-
Takeuchi Y, Tanaka T, Hamamura K et al. Expression and role of interleukin-2 receptor beta chain on CD4-CD8- T cell receptor alpha beta+ cells. Eur J Immunol. 1992; 22(11):2929-2935. (Clone-specific). 참조 보기
-
Tanaka T, Takeuchi Y, Shiohara T et al. In utero treatment with monoclonal antibody to IL-2 receptor beta-chain completely abrogates development of Thy-1+ dendritic epidermal cells. Int Immunol. 1992; 4(4):487-491. (Biology). 참조 보기
-
Tanaka T, Tsudo M, Karasuyama H, et al. A novel monoclonal antibody against murine IL-2 receptor beta-chain. Characterization of receptor expression in normal lymphoid cells and EL-4 cells. J Immunol. 1991; 147(7):2222-2228. (Immunogen). 참조 보기
-
Taniguchi T, Minami Y. The IL-2/IL-2 receptor system: a current overview. Cell. 1993; 73(1):5-8. (Biology). 참조 보기
-
Zhang X, Sun S, Hwang I, Tough DF, Sprent J. Potent and selective stimulation of memory-phenotype CD8+ T cells in vivo by IL-15. Immunity. 1998; 8(5):591-599. (Biology). 참조 보기
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.