-
Training
- Flow Cytometry Basic Training
-
Product-Based Training
- BD Accuri™ C6 Plus Cell Analyzer
- BD FACSAria™ Cell Sorter Cell Sorter
- BD FACSCanto™ Cell Analyzer
- BD FACSDiscover™ A8 Cell Analyzer
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter
- BD FACSDuet™ Sample Preparation System
- BD FACSLyric™ Cell Analyzer
- BD FACSMelody™ Cell Sorter
- BD FACSymphony™ Cell Analyzer
- BD LSRFortessa™ Cell Analyzer
- Advanced Training
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current location site or be switched to your location?
Overview
The capabilities of flow cytometry instruments in terms of available lasers, detectors and number of measurable parameters have expanded tremendously over the years. Concomitant with that, there is an exponential increase in the number of fluorochromes available for flow cytometry, extending the limits of possibilities for new discoveries. Conventional flow cytometry collects only a discrete portion of the emission spectrum as defined by a single filter per fluorochrome, whereas spectral flow cytometry collects the full spectrum. This increases the flexibility and the capability of spectral flow by enabling autofluorescence profiling and extraction, detection of more fluorochromes per laser line and increased panel size. Find out how spectral flow cytometry differs from conventional flow cytometry and how to design your panels for spectral flow cytometry.
Spectral vs conventional flow cytometry comparison
| Feature | Spectral | Conventional |
| Detector and fluorochrome ratio | More detectors than fluorochromes | 1:1 |
| Individual fluorochrome contribution determination | Unmixing | Compensation |
| Fluorochrome choice | Dependent on laser configuration | Dependent on laser and filter configuration |
| Autofluorescence extraction | Yes | No |
| Resolution of highly similar fluorochromes | Yes | No |
| Multi-color panel capability | 40+ colors | ~28 colors |
Introduction to spectral flow cytometry
Fundamentals of spectral versus conventional flow cytometry
The video addresses the following questions:
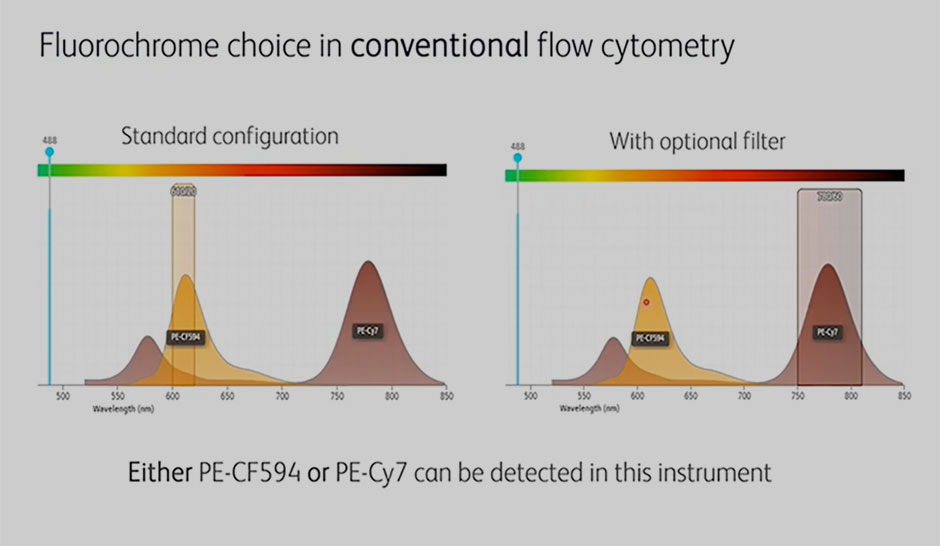
Fluorochrome choice flexibility
The video addresses the following questions:
- How to select fluorochromes in either conventional or spectral flow cytometry?
- How does spectral flow cytometry support the use of more fluorochromes per laser line?
- What are the advantages of using spectral flow cytometry for fluorescent protein detection?
Increased panel size
The video addresses the following questions:
- How does spectral flow cytometry enable resolution of highly similar fluorochromes?
- What are the similarity index and guidelines for the use of highly similar fluorochromes?
- What are the specifics behind a 40-color multicolor spectral flow cytometry panel?
Tools and considerations for the design of multicolor spectral flow cytometry
Spectral flow cytometry is an established technology that has increased the power, flexibility and complexity of flow cytometry. This webinar addresses the fundamental similarities and differences between conventional and spectral flow cytometry and dives deeper into facts and misconceptions around the principles and tools for multicolor spectral flow cytometry panel design.
Watch The Webinar
Topics:
- What is spectral flow cytometry and what makes it unique
- Fundamental rules and tools for panel design common to conventional and spectral flow cytometry
- The do’s and don’ts of panel design specific to spectral flow cytometry
Immunophenotyping and Cell Isolation with High-parameter Spectral Flow Cytometry
Explore how spectral flow cytometry can address the rising demand for high-dimensional cell analysis, from characterizing cell phenotypes to sorting cell groups.
Learn more from this 33c panel sheet.
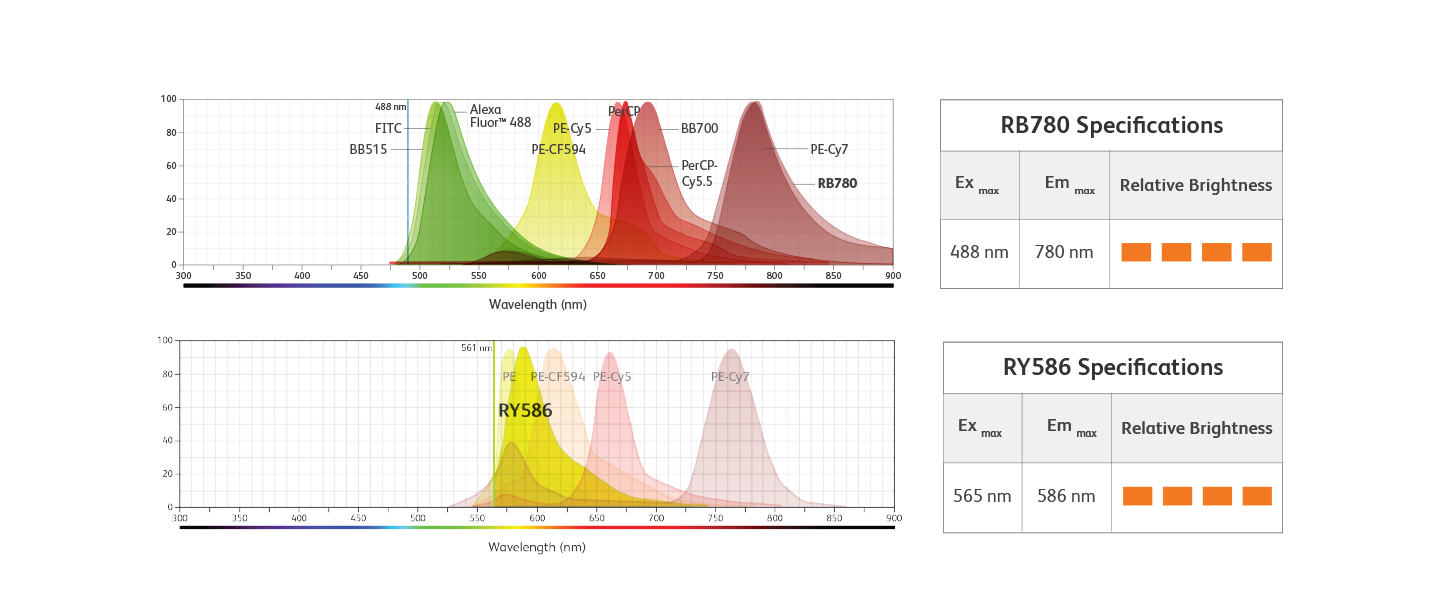
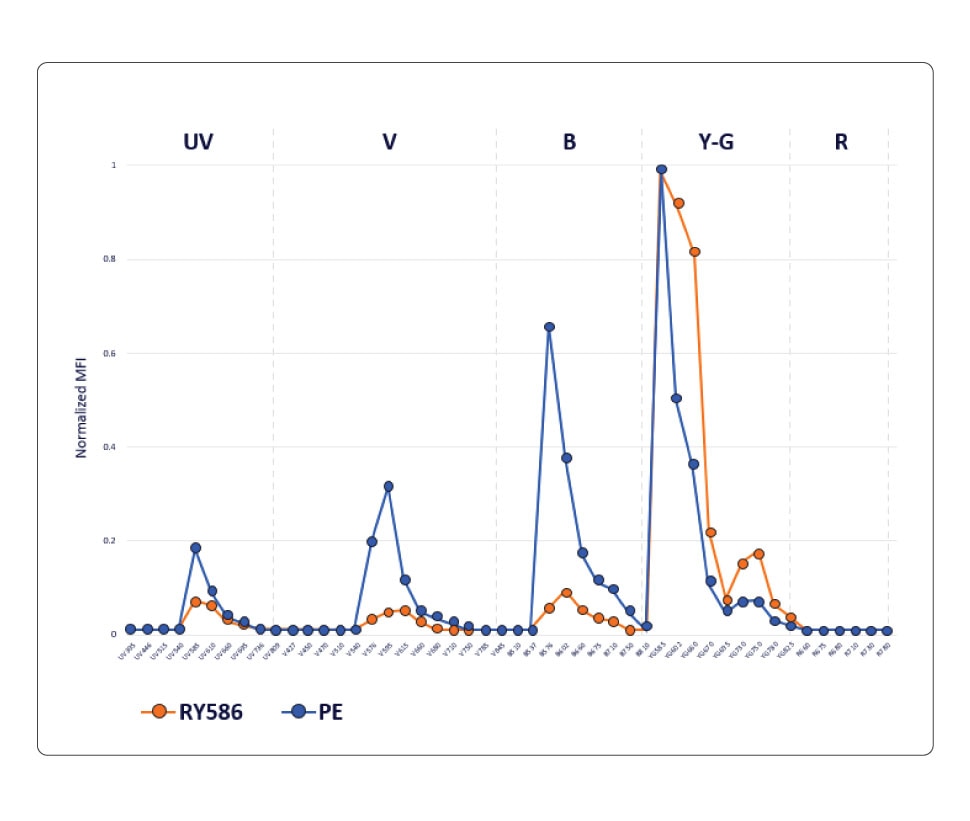
BD Horizon RealYellow™ and BD Horizon RealBlue™ Reagents
Knowing which fluorochrome to use for each marker in your panel and assigning them in a way that can lead to deeper biological insights can sometimes be difficult. BD Biosciences offers new panel design resources to help with these choices as well as a wide array of antibody specificities and fluorochromes for flexible and easy panel design. We’re also developing new reagents such as our family of BD Horizon RealYellow™ and BD Horizon RealBlue™ Reagents with optimized emission spectra and reduced cross-laser excitation. Our goal is to help build your confidence to attain dependable data and streamline the path to accurate results.
BD Biosciences offers cell analyzers and sorters that support both conventional and spectral flow cytometry
What is Spectral Cytometry
Spectral flow cytometry represents an alternative data acquisition and analysis strategy to conventional flow cytometry providing advantages in flexibility of fluorescent label inputs without having to change filters, as well as the ability to multiplex more fluorescent labels in one multicolor sample.
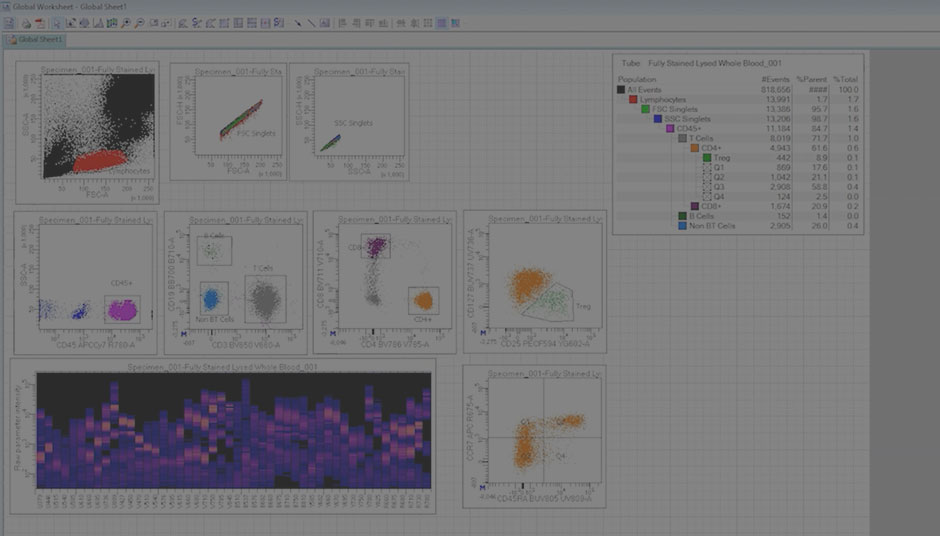
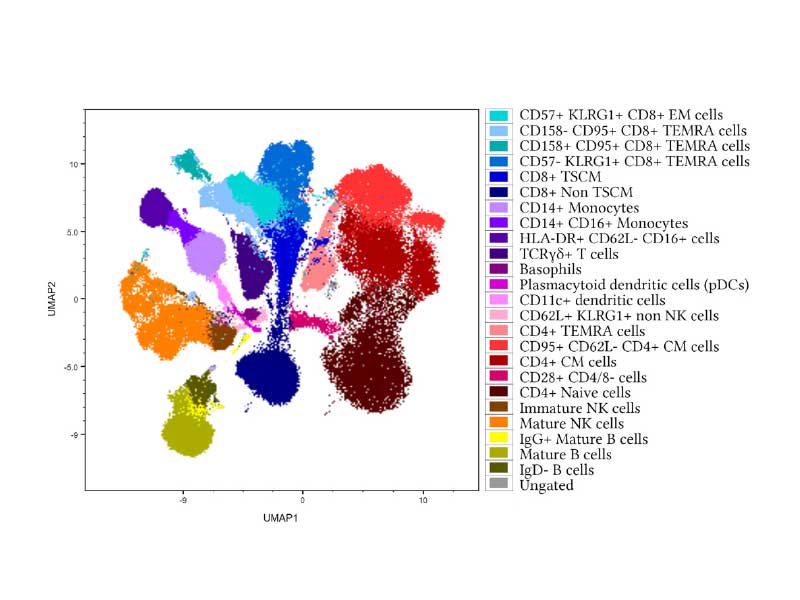
Increase Your Experimental Capabilities
This 40-color panel, created on the BD FACSymphony™ A5 SE Cell Analyzer, uses carefully selected fluorescence reagents to characterize a variety of immune cell populations in human peripheral blood.
Get more information from the BD FACSymphony™ A5 SE Cell Analyzer brochure.
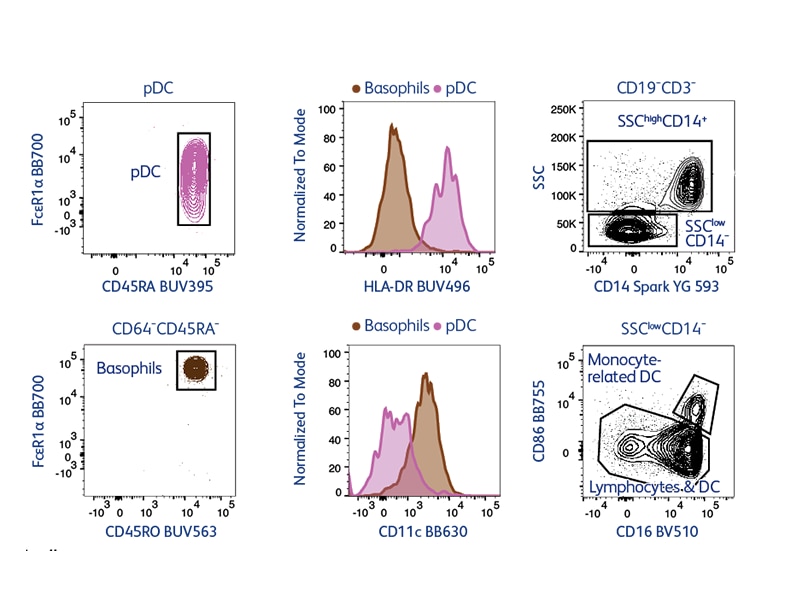
The BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter with BD CellView™ Image Technology and BD SpectralFX™ Technology, the first spectral flow cytometer sorter with sort-capable image analysis, expands the power of cell analysis and sorting to new dimensions by combining spectral flow cytometry with real-time spatial and morphological insights (RTI-SFC)–empowering scientists to address previously impossible-to-answer questions.
The BD FACSymphony™ A5 SE Cell Analyzer features five fixed-alignment lasers and 48 detectors for maximum coverage of the fluorochrome emission spectrum. By enabling both spectral unmixing and compensation-based workflows, the BD FACSymphony™ A5 SE Cell Analyzer increases flexibility in fluorochrome choices and permits simultaneous analysis of fluorochromes with similar spectral signatures. Spectral unmixing can also be used to resolve critical cell populations using autofluorescence unmixing.
The BD FACSymphony™ S6 SE Cell Sorter builds on the foundations of the BD FACSymphony™ A5 Cell Analyzer with easy migration of optimized panels from analyzer to sorter. The BD FACSymphony™ S6 SE Cell Sorter supports both conventional compensation and spectral unmixing methods, with flexibility for up to nine spatially separated lasers and 50 parameters. Together with bioinformatics analysis tools and the broad portfolio of BD high-parameter reagents, the BD FACSymphony™ S6 SE Cell Sorter provides an end-to-end solution for high-parameter experimental success.
Videos
Spectral flow cytometry increases the flexibility and capability of flow cytometry experiments. In contrast to conventional flow cytometry that is limited by the number of detectors and filters for collecting the emission spectrum, spectral flow cytometry has no such limitation and is able to collect the entire spectrum. This enables autofluorescence profiling and extraction, detection of more fluorochromes per laser line and increased panel size, increasing flexibility. Watch our spectral videos presented below that provide an in-depth explanation on these capabilities.
For decades, researchers have relied on flow cytometry to examine and sort cells based on their size, granularity, and fluorescently tagged surface markers. Recent advances in imaging technology offer an exciting opportunity to enrich flow cytometry with spatial and morphological insights, allowing researchers to visually identify cell types that might otherwise be elusive based solely on fluorescently tagged cell surface markers. In this webinar brought to you by BD Biosciences, Raffaello Cimbro will discuss how merging real-time imaging with spectral flow cytometry improves the quality and efficiency of cell analysis and enables his team to tackle previously unanswerable biological questions.
Topics to be Covered:
- A novel integration of spectral flow cytometry with real-time imaging
- Advancing drug discovery by sorting cells based on their morphology and protein localization
Do you want to transition from conventional to spectral flow cytometry? Or maybe you’re already doing spectral flow cytometry and want to improve the quality of your data? Gain a deeper understanding of spectral flow cytometry by going back to the fundamentals. Join Peter Mage for an engineer’s perspective on the science of spectral flow cytometry as he explains how the concepts at the heart of spectral technology can inform your experiment design.
Topics to be Covered:
- The relationship between conventional and spectral flow cytometry technology
- The difference between conventional compensation and spectral unmixing
- How to build an intuitive mental model for spectral flow cytometry that can help you understand your experiments and data in a new light
High-dimensional immunoprofiling is essential for studying host response to immunotherapy, infection and disease in murine model systems. However, the difficulty of multiparameter panel design combined with a lack of existing murine tools has prevented the comprehensive study of all major leukocyte phenotypes in a single assay.
To fill this niche, we present a 40-color flow cytometry panel for deep immunophenotyping in primary and secondary lymphoid tissues. Importantly, the panel solely relies on extracellular staining to preserve cells for downstream experiments and can identify functional lymphocyte and myeloid subsets. In this webinar, we will discuss how the panel was engineered, as well as special considerations in reagent optimization, spectral unmixing, autofluorescence extraction and multi-dimensional analysis.
Real-time image feature extraction enables novel avenues of research and sort possibilities as we can classify and characterize cell populations based on spatial distribution of fluorescence. The possibilities broaden further when these imaging capabilities are coupled with next-generation spectral immunophenotyping. Although spectral cytometry can seem intimidating or complex, our advanced spectral cytometry system, BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter with BD CellView™ Image Technology and BD SpectralFX™ Technology, combines full-spectrum optics and optimized hardware design with a system-aware algorithm, next-generation quality control (QC) and guided software workflow so users can get started quickly.
In this webinar, Aaron Middlebrook, Sr. Staff Scientist, R&D, BD, and Peter Mage, Associate Principal Engineer, Advanced Technology Group, BD, will demonstrate the power of real-time imaging, spectral flow cytometry (RTI-SFC) and share best practices in experimental setup and examples of applications using this novel technology.
Topics to be Covered:
- Panel considerations for RTI-SFC
- Benefits and limitations of combining spectral immunophenotyping with imaging
- Maximizing data yield through computational analyses
Spectral flow cytometry is an established technology that has increased the power, flexibility and complexity of flow cytometry. This webinar addresses the fundamental similarities and differences between conventional and spectral flow cytometry and dives deeper into facts and misconceptions around the principles and tools for multicolor spectral flow cytometry panel design.
Topics to be Covered:
- What is spectral flow cytometry and what makes it unique
- Fundamental rules and tools for panel design common to conventional and spectral flow cytometry
- The do’s and don’ts of panel design specific to spectral flow cytometry
Flow cytometry is a powerful technique for the analysis and isolation of cells based on their physical and biochemical properties. As the complexity and diversity of biological systems are increasingly revealed, there is a growing need for high-parameter cell analysis to characterize the heterogeneity and assess functionality of specific cell populations.
In recent years, spectral flow cytometry has emerged as a powerful technology that enables higher-dimensional cell analysis and sorting by capturing the full emission spectra of each fluorophore. This newer approach has pushed the boundaries for improved fluorescent dyes that can be used together without compromising biology as panels get larger and thus contributes to advancing research in various fields, such as immunology, cell biology, cancer, stem cells, and microbiology.
This webcast will review the principles and concepts of spectral flow cytometry, describe current technology innovations, and showcase some of the exciting discoveries made possible by spectral flow cytometry, while also discussing practical tips and best practices for researchers who want to adopt this technology.
Contact Us
*Required fields
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Alexa Fluor (AF) is a trademark of Thermo Fisher Scientific. Cy is a trademark of Global Life Sciences Germany GmbH or an affiliate doing business as Cytiva.