-
Training
- Flow Cytometry Basic Training
-
Product-Based Training
- BD Accuri™ C6 Plus Cell Analyzer
- BD FACSAria™ Cell Sorter Cell Sorter
- BD FACSCanto™ Cell Analyzer
- BD FACSDiscover™ A8 Cell Analyzer
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter
- BD FACSDuet™ Sample Preparation System
- BD FACSLyric™ Cell Analyzer
- BD FACSMelody™ Cell Sorter
- BD FACSymphony™ Cell Analyzer
- BD LSRFortessa™ Cell Analyzer
- Advanced Training
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current location site or be switched to your location?
BD Transduction Laboratories™ Purified Mouse Anti-Human AKAP450
Clone 7/AKAP450 (RUO)
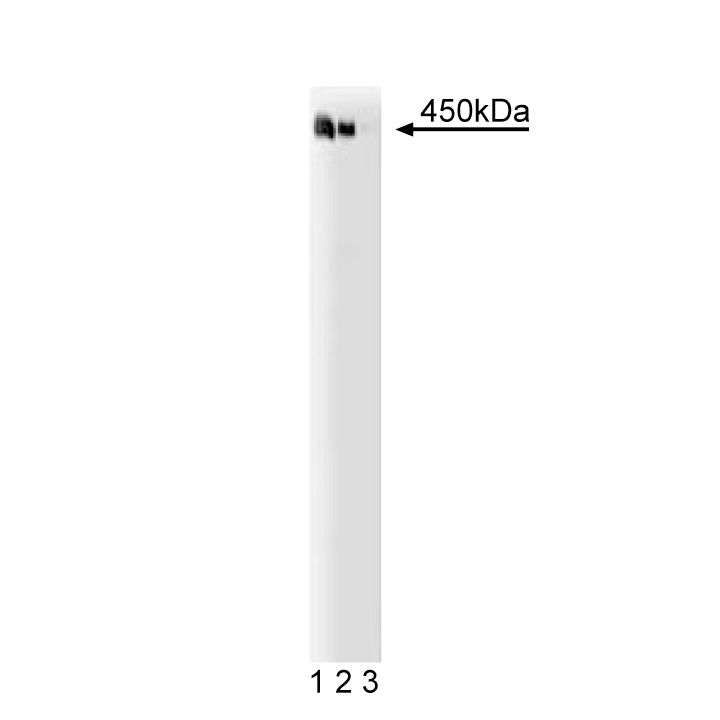




Western blot analysis of AKAP450 on a Jurkat cell lysate (human T-cell leukemia; ATCC TIB-152). Lane 1: 1:250, lane 2: 1:500, lane 3: 1:1000 dilution of the anti- human AKAP450 antibody.

Western blot analysis of AKAP450 on a Jurkat cell lysate (human T-cell leukemia; ATCC TIB-152). Lane 1: 1:250, lane 2: 1:500, lane 3: 1:1000 dilution of the anti- human AKAP450 antibody.

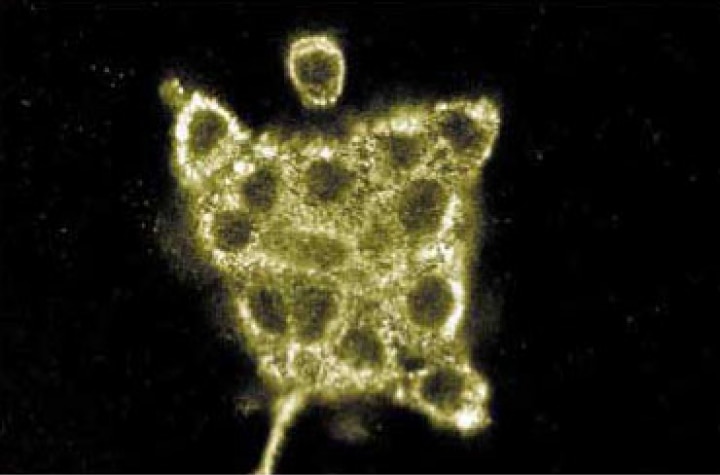
Immunofluorescence staining of A431 cells (human epithelial carcinoma; ATCC CRL-1555).




Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
Companion Products


Compartmentalization of the type II cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) within the cell is essential for its discrete physiological effects. PKA localization is mediated by interactions between the regulatory (RII) subunit and A-kinase anchoring proteins (AKAPs) which position PKA in close proximity to relevant substrates. Some AKAPs exhibit tissue specific expression, while others are detected ubiquitously. AKAP450 localizes PKA type II to centrosomes. The N-terminal portion of AKAP450 (amino acids 1-1626) is almost identical to the Yotiao protein (~210 kDa), an AKAP that localizes PKA to NMDA receptors. In addition, AKAP450 contains three major regions (cc1, cc2, cc3) of coiled coil structures, which are characteristic features of centrosomeal proteins. It is expressed at low levels in multiple tissues, including skeletal muscle and liver, but is highly expressed in kidney. PKA is thought to be involved in the maintenance of the interphase microtubule network and to be necessary for stabilization of minus-end microtubules that originate from the centrosome. Thus AKAP450 may serve as a scaffolding protein to localize PKA and other signaling molecules together in cetrosomes.
This antibody is routinely tested by western blot analysis. Other applications were tested at BD Biosciences Pharmingen during antibody development only or reported in the literature.
Development References (3)
-
Lin JW, Wyszynski M, Madhavan R, Sealock R, Kim JU, Sheng M. Yotiao, a novel protein of neuromuscular junction and brain that interacts with specific splice variants of NMDA receptor subunit NR1. J Neurosci. 1998; 18(6):2017-2027. (Biology). View Reference
-
Westphal RS, Tavalin SJ, Lin JW, et al. Regulation of NMDA receptors by an associated phosphatase-kinase signaling complex. Science. 1999; 285(5424):93-96. (Biology). View Reference
-
Witczak O, Skalhegg BS, Keryer G, et al. Cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding an A-kinase anchoring protein located in the centrosome, AKAP450. EMBO J. 1999; 18(7):1858-1868. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.