-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Profiling Assays for Human and Mouse
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
-
Training
- Flow Cytometry Basic Training
-
Product-Based Training
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- Advanced Training
-
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Profiling Assays for Human and Mouse
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
-
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- United States (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




Two-color flow cytometric analysis of CD326 expression on mouse thymocytes and splenic T lymphocytes. BALB/c mouse thymocytes and splenic leucocytes were preincubated with Purified Rat Anti-Mouse CD16/CD32 antibody (Mouse BD Fc Block™) (Cat. No. 553141/553142) and stained with BD Horizon™ RY586 Rat IgG2a, κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 568130; Left Plot) or BD Horizon™ RY586 Rat Anti-Mouse CD326 antibody (Cat. No. 568126/568127) at 0.5 µg/test. Left Plot: Thymocytes were further stained with BD Horizon™ BV421 Rat Anti-Mouse CD4 (Cat. No. 562891) and FITC Rat Anti-Mouse CD8a (Cat. No. 553031/553030/561966) antibodies. The fluorescence histogram showing CD326 expression (or Ig Isotype control staining) was derived from CD4- and CD8-negative gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable thymocytes. Middle and Right Plots: The splenic leucocytes were further stained with FITC Hamster Anti-Mouse CD3e (Cat. No. 553062/553061/561827) and BD Horizon™ BV421 Rat Anti-Mouse CD25 (Cat. No. 564370/566228) antibodies. Two-color flow cytometric contour plots showing the correlated expression of Ig Isotype control staining (Middle Plot) or CD326 (Right Plot) versus CD3e were derived from CD25+ gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable splenic leucocytes. A small population of CD3+CD25+CD326+ cells were detected (Right Plot), whereas the CD25- T cells do not express detectable levels of CD326 (data not shown). Flow cytometry and data analysis were performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ Cell Analyzer System and FlowJo™ software. Data shown on this Technical Data Sheet are not lot specific.


BD Horizon™ RY586 Rat Anti-Mouse CD326

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
BD® CompBeads can be used as surrogates to assess fluorescence spillover (compensation). When fluorochrome conjugated antibodies are bound to BD® CompBeads, they have spectral properties very similar to cells. However, for some fluorochromes there can be small differences in spectral emissions compared to cells, resulting in spillover values that differ when compared to biological controls. It is strongly recommended that when using a reagent for the first time, users compare the spillover on cells and BD® CompBeads to ensure that BD® CompBeads are appropriate for your specific cellular application.
Product Notices
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- CF™ is a trademark of Biotium, Inc.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
Companion Products




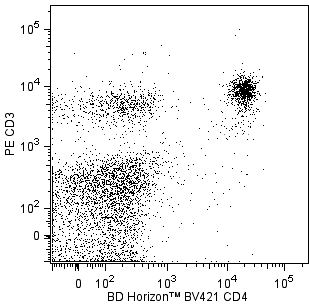
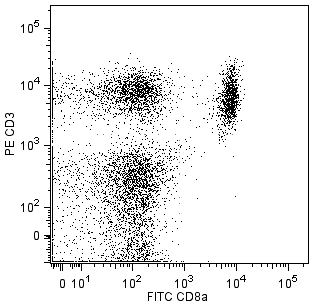
The G8.8 monoclonal antibody recognizes CD326/Ep-CAM (Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule), also known as gp40 in the mouse and by a variety of names (including GA733-2, CO17-1A, and EGP) in the human. In the mouse, Ep-CAM is a 40-42 kDa cell-surface type 1 transmembrane glycoprotein expressed on thymic epithelial cells, thymic dendritic cells, immature thymocytes, a small subset of peripheral T lymphocytes, intestinal epithelium, kidney-collecting tubule epithelium, keratinocytes, Langerhans cells and lymph node and splenic dendritic cells. Profiles of Ep-CAM expression on fetal thymocytes and on the CD4[-] CD8[-], CD4[+] CD8[+], CD4[-] CD8[+], and CD4[+] CD8[-] subsets of adult thymocytes have been published. In unrelated studies, mouse Ep-CAM mRNA was detected in tissues containing epithelial cells (kidney, stomach, intestine, lung, and thymus) and in plasma cells and plasmacytomas, but not in heart, muscle, liver, brain, spleen, B lymphomas, or pre-B lymphomas. Ep-CAM is a Ca[2+] independent homophilic adhesion molecule that is proposed to play roles in the development and normal function of epithelial tissues and in the progression of carcinomas.
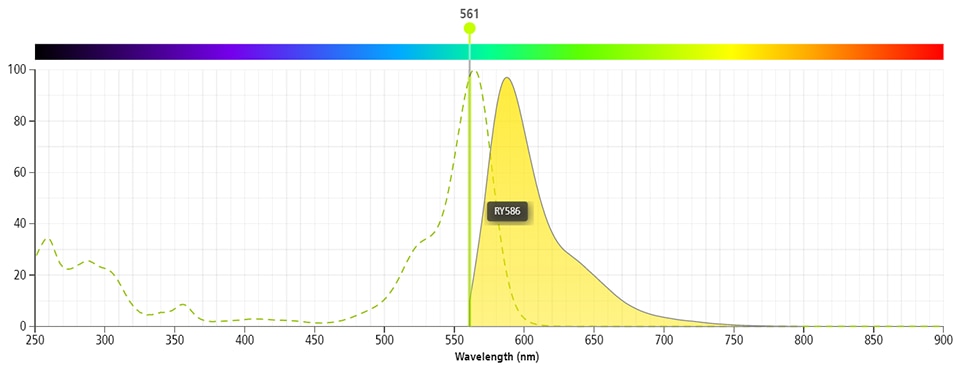
The BD Horizon RealYellow™ 586 (RY586) Dye is part of the BD family of yellow-green dyes. It is a small organic fluorochrome with an excitation maximum (Ex Max) at 565-nm and an emission maximum (Em Max) at 586-nm. Driven by BD innovation, RY586 can be used on both spectral and conventional cytometers and is designed to be excited by the Yellow-Green laser (561-nm) with minimal excitation by the 488-nm Blue laser. For conventional instruments equipped with a Yellow-Green laser (561-nm), RY586 can be used as an alternative to PE and we recommend using an optical filter centered near 586-nm (eg, a 586/15-nm bandpass filter). For spectral instruments equipped with a Yellow-Green laser (561-nm), it can be used in conjunction with PE. Compared to PE, RY586 is similar in brightness, minimal spillover into Blue detectors, and increased spillover into the 610/20-nm (PE-CF594) detector. Please ensure that your instrument configuration (lasers and optical filters) is appropriate for this dye.
Development References (9)
-
Basak S, Speicher D, Eck S, Wunner W. Colorectal carcinoma invasion inhibition by CO17-1A/GA733 antigen and its murine homologue. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998; 90(9):691-697. (Biology). View Reference
-
Bergsagel PL, Victor-Kobrin C, Timblin CR, Trepel J, Kuehl WM. A murine cDNA encodes a pan-epithelial glycoprotein that is also expressed on plasma cells. J Immunol. 1992; 148(2):590-596. (Biology). View Reference
-
Birebent B, Somasundaram R, Purev E. Anti-idiotypic antibody and recombinant antigen vaccines in colorectal cancer patients. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2001; 39((1-2)):107-113. (Biology). View Reference
-
Borkowski TA, Nelson AJ, Farr AG, Udey MC. Expression of gp40, the murine homologue of human epithelial cell adhesion molecule (Ep-CAM), by murine dendritic cells. Eur J Immunol. 1996; 26(1):110-114. (Clone-specific: Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Farr A, Nelson A, Truex J, Hosier S. Epithelial heterogeneity in the murine thymus: a cell surface glycoprotein expressed by subcapsular and medullary epithelium. J Histochem Cytochem. 1991; 39(5):345-353. (Immunogen: Electron microscopy, Immunohistochemistry, Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Litvinov SV, Balzar M, Winter MJ. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (Ep-CAM) modulates cell-cell interactions mediated by classic cadherins. J Biol Chem. 1997; 139(5):1337-1348. (Biology). View Reference
-
Nelson AJ, Dunn RJ, Peach R, Aruffo A, Farr AG. The murine homolog of human Ep-CAM, a homotypic adhesion molecule, is expressed by thymocytes and thymic epithelial cells. Eur J Immunol. 1996; 26(2):401-408. (Clone-specific: Electron microscopy, Immunohistochemistry, Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Taguchi N, Hashimoto Y, Naiki M. Abnormal thymic expression of epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EP-CAM) in New Zealand Black (NZB) mice. J Autoimmun. 1999; 13(4):393-400. (Clone-specific: Electron microscopy). View Reference
-
Zutter MM. Gastrointestinal carcinoma antigen GA733: target for immunodestruction and potential modifier of invasiveness and chemoresponsiveness. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998; 90(9):642-644. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.