-
Training
- Flow Cytometry Basic Training
-
Product-Based Training
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- Advanced Training
-
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- United States (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




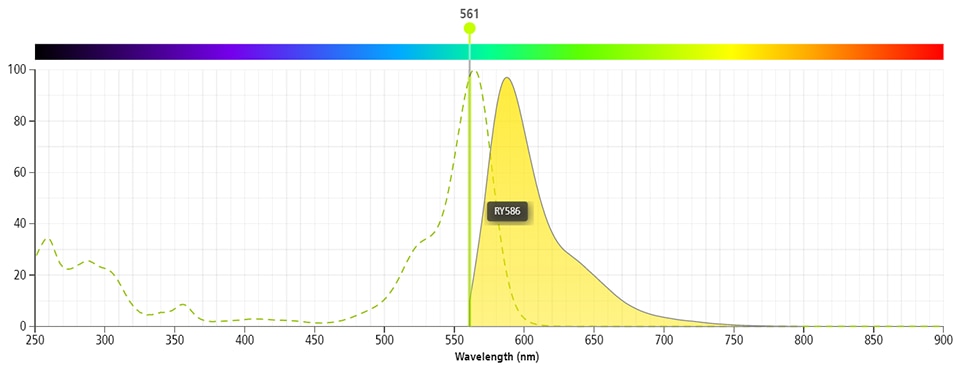
Two-color flow cytometric analysis of IFN-γ expression in stimulated human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells were stimulated for 5 hours with Phorbol 12-Myristate 13-Acetate (PMA; Sigma P-8139; 50 ng/ml final concentration) and Ionomycin (Sigma I-0634; 1 μg/ml final concentration) in the presence of BD GolgiStop™ Protein Transport Inhibitor (containing Monensin) (Cat. No. 554724). The cells were harvested, washed with BD Pharmingen™ Stain Buffer (FBS) (Cat. No. 554656) and stained with BD Horizon™ BV421 Mouse Anti-Human CD3 antibody (Cat. No. 562426). The cells were subsequently washed and fixed with BD Cytofix™ Fixation Buffer (Cat. No. 554655). They were then washed and stained in BD Perm/Wash™ Buffer (Cat. No. 554723) with either BD Horizon™ RY586 Mouse IgG1, κ Isotype Control (Cat No. 568097; Left Plot) or BD Horizon™ RY586 Mouse Anti-Human IFN-γ antibody (Cat No. 568503/568506; Right Plot). The bivariate pseudocolor density plot showing the correlated expression of IFN-γ (or Ig Isotype control staining) versus CD3 was derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of intact lymphocytes. Flow cytometry and data analysis were performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ X-20 Cell Analyzer System and FlowJo™ software.


BD Horizon™ RY586 Mouse Anti-Human IFN-γ

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
BD® CompBeads can be used as surrogates to assess fluorescence spillover (compensation). When fluorochrome conjugated antibodies are bound to BD® CompBeads, they have spectral properties very similar to cells. However, for some fluorochromes there can be small differences in spectral emissions compared to cells, resulting in spillover values that differ when compared to biological controls. It is strongly recommended that when using a reagent for the first time, users compare the spillover on cells and BD® CompBeads to ensure that BD® CompBeads are appropriate for your specific cellular application.
Product Notices
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test).
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- CF™ is a trademark of Biotium, Inc.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- Human donor specific background has been observed in relation to the presence of anti-polyethylene glycol (PEG) antibodies, developed as a result of certain vaccines containing PEG, including some COVID-19 vaccines. We recommend use of BD Horizon Brilliant™ Stain Buffer in your experiments to help mitigate potential background. For more information visit https://www.bdbiosciences.com/en-us/support/product-notices.
- Species cross-reactivity detected in product development may not have been confirmed on every format and/or application.
Companion Products






The 4S.B3 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to interferon-γ (IFN-γ). The immunogen used to generate this hybridoma was partially purified human IFN-γ obtained from supernatants of human PBMC stimulated with Staphylococcus aureus. Interferon-γ (IFN-γ) is a potent multifunctional cytokine that is produced by several activated cell types including NK, NKT, CD4+TCRαβ+, CD8+TCRαβ+, and TCRγδ+ T cells. IFN-γ exerts its biological effects through specific binding to the high-affinity IFN-γ Receptor Complex comprised of IFN-γRα (CD119) and IFN-γRβ subunits. In addition to its antiviral effects, IFN-γ upregulates a number of lymphoid cell functions including the antimicrobial and antitumor responses of macrophages, NK cells, and neutrophils. In addition, IFN-γ can exert strong regulatory influences on the proliferation, differentiation, and effector responses of B cell and T cell subsets. These influences can involve IFN-γ's capacity to boost MHC class I and II expression by antigen-presenting cells as well as to direct effects on B cells and T cells themselves. Human IFN-γ is a 14-18 kDa glycoprotein containing 143 amino acid residues.
Development References (8)
-
Fonteneau JF, Le Drean E, Le Guiner S, Gervois N, Diez E, Jotereau F. Heterogeneity of biologic responses of melanoma-specific CTL. J Immunol. 1997; 159(6):2831-2839. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Jeong SH, Qiao M, Nascimbeni M, et al. Immunization with hepatitis C virus-like particles induces humoral and cellular immune responses in nonhuman primates. J Virol. 2004; 78(13):6995-7003. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Meager A, Parti S, Barwick S, Spragg J, O'Hagan K. Detection of hybridomas secreting monoclonal antibodies to human gamma interferon using a rapid screening technique and specificity of certain monoclonal antibodies to gamma interferon. J Interferon Res. 1984; 4(4):619-625. (Immunogen: Immunoprecipitation, Radioimmunoassay). View Reference
-
Meager A. Characterization of interferons and immunoassays. In: Clemens MJ, Morris AG, Gearing AJH, ed. Lymphokines and Interferons. A Practical Approach. Oxford: IRL Press Ltd; 1987:105-127.
-
Prussin C, Metcalfe DD. Detection of intracytoplasmic cytokine using flow cytometry and directly conjugated anti-cytokine antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1995; 188(1):117-128. (Methodology: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Rotteveel FT, Kokkelink I, van Lier RA, et al. Clonal analysis of functionally distinct human CD4+ T cell subsets. J Exp Med. 1988; 168(5):1659-1673. (Clone-specific: ELISA). View Reference
-
Weisgrau KL, Ries M, Pomplun N, Evans DT, Rakasz EG. OMIP-035: Functional analysis of natural killer cell subsets in macaques. Cytometry A. 2016; 89(9):799-802. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Yoshino N, Ami Y, Terao K, Tashiro F, Honda M. Upgrading of flow cytometric analysis for absolute counts, cytokines and other antigenic molecules of cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) by using anti-human cross-reactive antibodies. Exp Anim. 2000; 49(2):97-110. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.