-
Training
- Flow Cytometry Basic Training
-
Product-Based Training
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- Advanced Training
-
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- United States (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
BD® CompBeads can be used as surrogates to assess fluorescence spillover (compensation). When fluorochrome conjugated antibodies are bound to BD® CompBeads, they have spectral properties very similar to cells. However, for some fluorochromes there can be small differences in spectral emissions compared to cells, resulting in spillover values that differ when compared to biological controls. It is strongly recommended that when using a reagent for the first time, users compare the spillover on cells and BD® CompBeads to ensure that BD® CompBeads are appropriate for your specific cellular application.
Product Notices
- Researchers should determine the optimal concentration of this reagent for their individual applications.
- The production process underwent stringent testing and validation to assure that it generates a high-quality conjugate with consistent performance and specific binding activity. However, verification testing has not been performed on all conjugate lots.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- CF™ is a trademark of Biotium, Inc.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Human donor specific background has been observed in relation to the presence of anti-polyethylene glycol (PEG) antibodies, developed as a result of certain vaccines containing PEG, including some COVID-19 vaccines. We recommend use of BD Horizon Brilliant™ Stain Buffer in your experiments to help mitigate potential background. For more information visit https://www.bdbiosciences.com/en-us/support/product-notices.
Companion Products




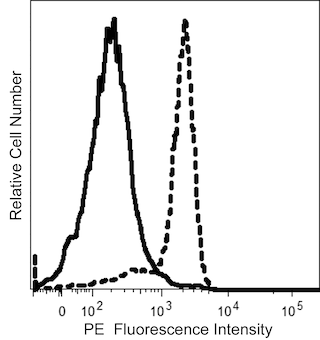

The L243 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to HLA-DR, a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II antigen. HLA-DR antigens are encoded by genes within the Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) Complex located on chromosome 6. HLA-DR is a transmembrane heterodimeric glycoprotein composed of an α chain (36 kDa) and a β subunit (27 kDa) expressed primarily on antigen presenting cells including B cells, dendritic cells, monocytes, macrophages, Langerhans cells, and thymic epithelial cells. HLA-DR is also expressed on activated T cells. This molecule plays a major role in mediating cellular interactions during antigen presentation to CD4-positive T cells.
Development References (16)
-
Brodsky FM. A matrix approach to human class II histocompatibility antigens: reactions of four monoclonal antibodies with the products of nine haplotypes.. Immunogenetics. 1984; 19(3):179-94. (Biology). View Reference
-
Edwards JA, Durant BM, Jones DB, Evans PR, Smith JL. Differential expression of HLA class II antigens in fetal human spleen: relationship of HLA-DP, DQ, and DR to immunoglobulin expression.. J Immunol. 1986; 137(2):490-7. (Biology). View Reference
-
Engleman EG, Warnke R, Fox RI, Dilley J, Benike CJ, Levy R. Studies of a human T lymphocyte antigen recognized by a monoclonal antibody.. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1981; 78(3):1791-5. (Biology). View Reference
-
Grouard G, Durand I, Filgueira L, Banchereau J, Liu YJ. Dendritic cells capable of stimulating T cells in germinal centres.. Nature. 1996; 384(6607):364-7. (Biology). View Reference
-
Lampson LA, Levy R. Two populations of Ia-like molecules on a human B cell line.. J Immunol. 1980; 125(1):293-9. (Biology). View Reference
-
Levacher M, Tallet S, Dazza MC, Dournon E, Rouveix B, Pocidalo JJ. T activation marker evaluation in ARC patients treated with AZT. Comparison with CD4+ lymphocyte count in non-progressors and progressors towards AIDS.. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990; 81(2):177-82. (Biology). View Reference
-
O'Doherty U, Peng M, Gezelter S, et al. Human blood contains two subsets of dendritic cells, one immunologically mature and the other immature.. Immunology. 1994; 82(3):487-93. (Biology). View Reference
-
Robbins PA, Evans EL, Ding AH, Warner NL, Brodsky FM. Monoclonal antibodies that distinguish between class II antigens (HLA-DP, DQ, and DR) in 14 haplotypes.. Hum Immunol. 1987; 18(4):301-13. (Biology). View Reference
-
Stites DP, Casavant CH, McHugh TM, et al. Flow cytometric analysis of lymphocyte phenotypes in AIDS using monoclonal antibodies and simultaneous dual immunofluorescence.. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986; 38(2):161-77. (Biology). View Reference
-
Terstappen LW, Hollander Z, Meiners H, Loken MR. Quantitative comparison of myeloid antigens on five lineages of mature peripheral blood cells. J Leukoc Biol. 1990; 48(2):138-148. (Biology). View Reference
-
Thomas R, Lipsky PE. Human peripheral blood dendritic cell subsets. Isolation and characterization of precursor and mature antigen-presenting cells.. J Immunol. 1994; 153(9):4016-28. (Biology). View Reference
-
Tomkinson BE, Wagner DK, Nelson DL, Sullivan JL. Activated lymphocytes during acute Epstein-Barr virus infection.. J Immunol. 1987; 139(11):3802-7. (Biology). View Reference
-
Warnke R, Miller R, Grogan T, Pederson M, Dilley J, Levy R. Immunologic phenotype in 30 patients with diffuse large-cell lymphoma.. N Engl J Med. 1980; 303(6):293-300. (Biology). View Reference
-
Warnke RA, Levy R. Detection of T and B cell antigens with hybridoma monoclonal antibodies: a biotinavidin-horseradish peroxidase method. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980; 28:771-776. (Biology).
-
Zipf TF, Fox RI, Dilley J, Levy R. Definition of the high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia patient by immunological phenotyping with monoclonal antibodies.. Cancer Res. 1981; 41(11 Pt 2):4786-9. (Biology). View Reference
-
van Es A, Baldwin WM, Oljans PJ, Tanke HJ, Ploem JS, van Es LA. Expression of HLA-DR on T lymphocytes following renal transplantation, and association with graft-rejection episodes and cytomegalovirus infection.. Transplantation. 1984; 37(1):65-9. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.