-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Profiling Assays for Human and Mouse
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
-
Training
- Flow Cytometry Basic Training
-
Product-Based Training
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- Advanced Training
-
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Profiling Assays for Human and Mouse
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
-
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- United States (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?

.png)

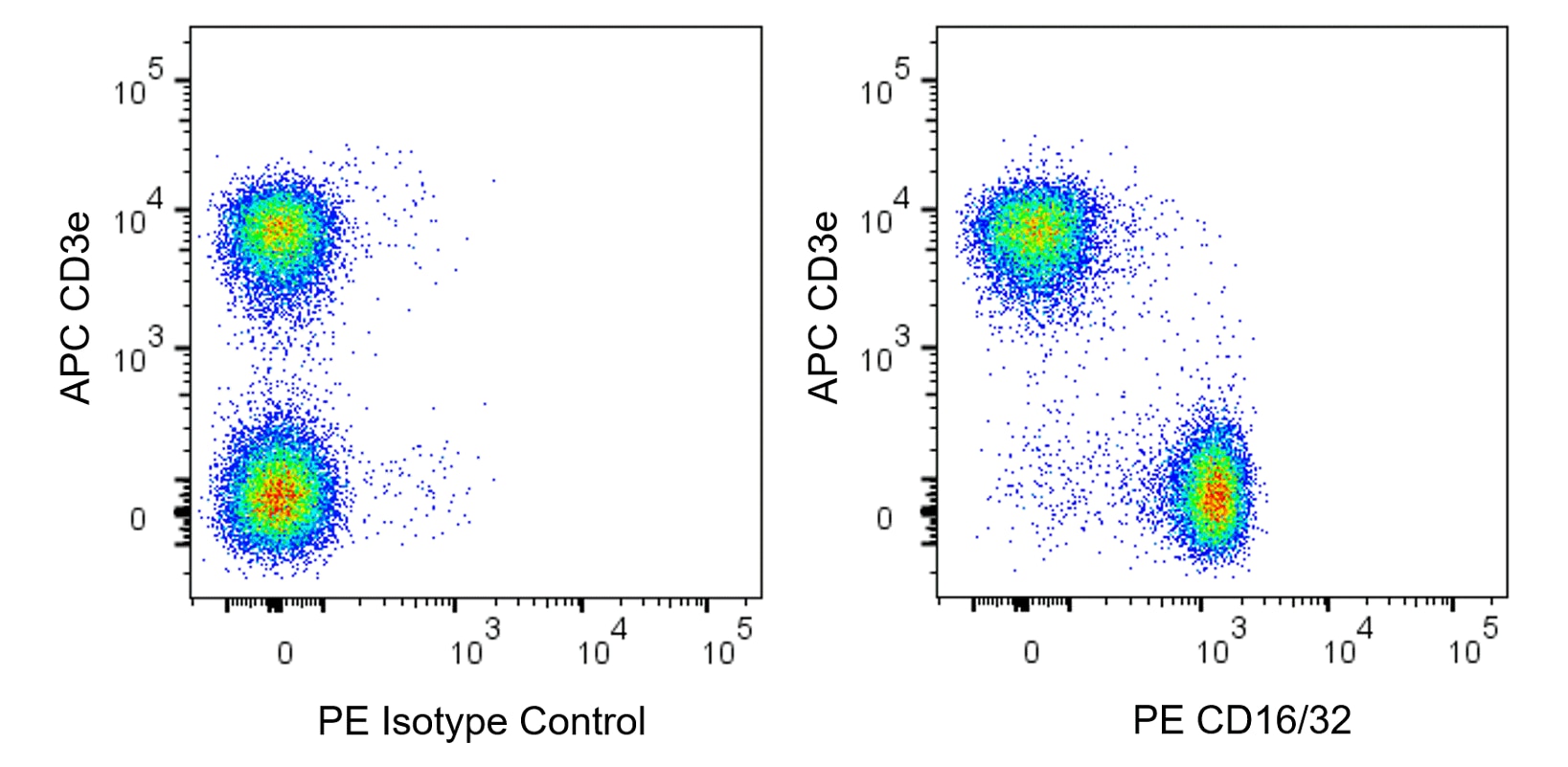
Two-color flow cytometric analysis of CD16/32 expression on mouse splenic lymphocytes. BALB/C mouse splenic leucocytes were stained with APC Armenian Hamster Anti-Mouse CD3e antibody (Cat. No. 553066/561826) and either PE Rat IgG2a, λ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 557076; Left Plot) or PE Rat Anti-Mouse CD16/CD32 antibody (Cat. No. 567020; Right Plot) at 0.5 μg/test. A pseudocolor density plot showing the correlated expression of CD16/CD32 (or Ig Isotype control staining) versus CD3e was derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable lymphocytes. Flow cytometry and data analysis were performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ Cell Analyzer System and FlowJo™ software. Data shown on this Technical Data Sheet are not lot specific.
.png)

BD Pharmingen™ PE Rat Anti-Mouse CD16/CD32
.png)
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
BD™ CompBeads can be used as surrogates to assess fluorescence spillover (Compensation). When fluorochrome conjugated antibodies are bound to BD CompBeads, they have spectral properties very similar to cells. However, for some fluorochromes there can be small differences in spectral emissions compared to cells, resulting in spillover values that differ when compared to biological controls. It is strongly recommended that when using a reagent for the first time, users compare the spillover on cells and BD CompBead to ensure that BD CompBeads are appropriate for your specific cellular application.
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products



.png?imwidth=320)

The Ab93 monoclonal antibody (aka, Antibody93) specifically recognizes a common epitope on the extracellular domains of mouse CD16 (Fc gamma RIII/FcγRIII encoded by Fcgr3) and CD32 (Fc gamma RIIB/FcγRIIB encoded by Fcgr2b). Therefore, Ab93 is referred to as an Anti-CD16/32 or Anti-FcgRII/III antibody. CD16 is variably expressed on neutrophils, macrophages, and natural killer (NK) cells whereas CD32 is expressed on B cells, monocytes, granulocytes, platelets and endothelial cells. CD16 and CD32 serve as low affinity receptors for IgG Fc constant regions and are involved in regulating various cellular functions including antibody-dependent cellular toxicity (ADCC), phagocytosis, effector cell degranulation, and B cell proliferation. In addition to identifying CD16- or CD32-positive cells, the Ab93 antibody is useful in phenotyping studies for blocking nonspecific staining due to Fc receptor-mediated binding of other antibodies. Ab93 is also useful in functional studies due to its Fc receptor blocking capability or by its capacity to crosslink Fc receptors leading to signal transduction that triggers cellular responses. Ab93 (Rat IgG2a, λ) and clone 2.4G2 (Rat IgG2b, κ), another mouse CD16/32-specific antibody, reportedly have similar specificities. The differences in the Ig heavy chain or Ig light chain isotypes of these CD16/32-specific antibodies afford flexibility in the design of experimental model systems involving other antibodies.
Development References (5)
-
Hirohashi T, Uehara S, Chase CM, et al. Complement independent antibody-mediated endarteritis and transplant arteriopathy in mice.. Am J Transplant. 2010; 10(3):510-7. (Clone-specific: Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Honjo K, Kubagawa Y, Kubagawa H. Is Toso/IgM Fc receptor (FcμR) expressed by innate immune cells?. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013; 110(28):E2540-1. (Clone-specific: Blocking, Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Nimmerjahn F, Ravetch JV. FcγRs in health and disease. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2011; 350:105-125. (Biology). View Reference
-
Oliver AM, Grimaldi JC, Howard MC, Kearney JF. Independently ligating CD38 and Fc gammaRIIB relays a dominant negative signal to B cells.. Hybridoma. 1999; 18(2):113-9. (Immunogen: Blocking, Flow cytometry, Fluorescence microscopy, Functional assay, Immunofluorescence, Inhibition). View Reference
-
Torii I, Oka S, Hotomi M, et al. PIR-B-deficient mice are susceptible to Salmonella infection.. J Immunol. 2008; 181(6):4229-39. (Clone-specific: Blocking, Flow cytometry). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.