-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Profiling Assays for Human and Mouse
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
-
Training
- Flow Cytometry Basic Training
-
Product-Based Training
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- Advanced Training
-
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Profiling Assays for Human and Mouse
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
-
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- United States (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
For optimal and reproducible results, BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer should be used anytime two or more BD Horizon Brilliant dyes (including BD OptiBuild Brilliant reagents) are used in the same experiment. Fluorescent dye interactions may cause staining artifacts which may affect data interpretation. The BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer was designed to minimize these interactions. More information can be found in the Technical Data Sheet of the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer (Cat. No. 563794).
Product Notices
- This antibody was developed for use in flow cytometry.
- The production process underwent stringent testing and validation to assure that it generates a high-quality conjugate with consistent performance and specific binding activity. However, verification testing has not been performed on all conjugate lots.
- Researchers should determine the optimal concentration of this reagent for their individual applications.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Violet 650 is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,227,187; 8,455,613; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- Alexa Fluor® is a registered trademark of Life Technologies Corporation.
Companion Products






The 20d5 monoclonal antibody specifically recognizes NKG2A, NKG2C, and NKG2E (also known as CD159a, CD159c, and CD159e which are encoded by Klrc1, Klrc2, and Klrc3, respectively) on a subset of NK and NK-T cells in most strains tested (eg, AKR/J, BALB/c, C3H/He, C57BL/6, CBA/J, DBA/1, FVB/N, 129/Sv, NOD, SWR, and most DBA/2 substrains, but not DBA/2J). The NKG2 molecules are a family of lectin-like receptors that form heterodimers with CD94 on the surface of NK cells. DBA/2J mice do not express CD94, and the lack of CD94 is responsible for the absence of NKG2 expression in this substrain. NKG2 receptors are also expressed on CD8+ T lymphocytes activated in vivo and in vitro. The heterodimers of CD94 with NKG2A, C, or E recognize Qa-1, a nonclassical MHC class I antigen, presenting the Qdm peptide. Studies of CD94/NKG2 heterodimers on human NK cells have demonstrated that the NKG2 components mediate signal transduction for the receptor, with NKG2A being inhibitory and NKG2C being stimulatory. The CD94/NKG2E heterodimer is also thought to be stimulatory. The mouse NKG2A molecule contains two intracytoplasmic sequences that resemble the ITIM (Immunoreceptor Tyrosine- based Inhibitory Motif) consensus sequence. NKG2A transcripts have been shown to be up to 20-fold more abundant than NKG2C and NKG2E mRNA in NK cells of adult mice. The CD94/NKG2 receptors show increased expression on neonatal NK cells compared to the Ly-49 MHC class I receptors, suggesting that CD94/NKG2 receptors and their ligand, Qa-1, may play a role in maintenance of self-tolerance in developing NK cells. The 20d5 antibody is useful for identification of NK cells expressing functional CD94/NKG2 receptors, in contrast to the non-functional CD94 expressed alone, and it blocks the binding of Qdm-complexed Qa-1b tetramers to CD94/NKG2-transfected CHO cells.
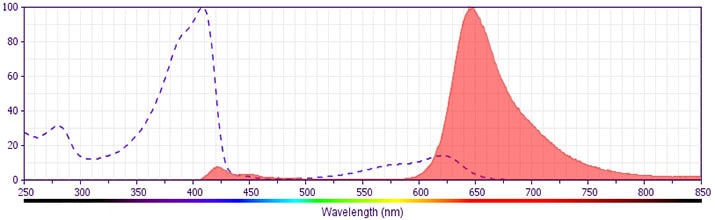
The antibody was conjugated to BD Horizon™ BV650 which is part of the BD Horizon Brilliant™ Violet family of dyes. This dye is a tandem fluorochrome of BD Horizon BV421 with an Ex Max of 405-nm and an acceptor dye with an Em Max at 650-nm. BD Horizon BV650 can be excited by the violet laser and detected in a filter used to detect APC-like dyes (eg, 660/20-nm filter). Due to the excitation and emission characteristics of the acceptor dye, there will be spillover into the APC and Alexa Fluor® 700 detectors. However, the spillover can be corrected through compensation as with any other dye combination.
Development References (7)
-
Kubota A, Kubota S, Lohwasser S, Mager DL, Takei F. Diversity of NK cell receptor repertoire in adult and neonatal mice. Eur J Immunol. 1999; 163(1):212-216. (Biology). View Reference
-
Lohwasser S, Hande P, Mager DL, Takei F. Cloning of murine NKG2A, B and C: second family of C-type lectin receptors on murine NK cells. Eur J Immunol. 1999; 29(3):755-761. (Biology). View Reference
-
McMahon CW, Zajac AJ, Jamieson AM. Viral and bacterial infections induce expression of multiple NK cell receptors in responding CD8(+) T cells. J Immunol. 2002; 169(3):1444-1452. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Vance RE, Jamieson AM, Cado D, Raulet DH. Implications of CD94 deficiency and monoallelic NKG2A expression for natural killer cell development and repertoire formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002; 99(2):868-873. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, Fluorescence activated cell sorting). View Reference
-
Vance RE, Jamieson AM, Raulet DH. Recognition of the class Ib molecule Qa-1(b) by putative activating receptors CD94/NKG2C and CD94/NKG2E on mouse natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 1999; 190(12):1801-1812. (Immunogen: ELISA, Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Vance RE, Kraft JR, Altman JD, Jensen PE, Raulet DH. Mouse CD94/NKG2A is a natural killer cell receptor for the nonclassical major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecule Qa-1(b). J Exp Med. 1998; 188(10):1841-1848. (Biology). View Reference
-
Yokoyama WM. Natural killer cell receptors. Curr Opin Immunol. 1998; 10(3):298-305. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.