-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Profiling Assays for Human and Mouse
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
-
Training
- Flow Cytometry Basic Training
-
Product-Based Training
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- Advanced Training
-
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Profiling Assays for Human and Mouse
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
-
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Accuri C6 Plus Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- United States (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?
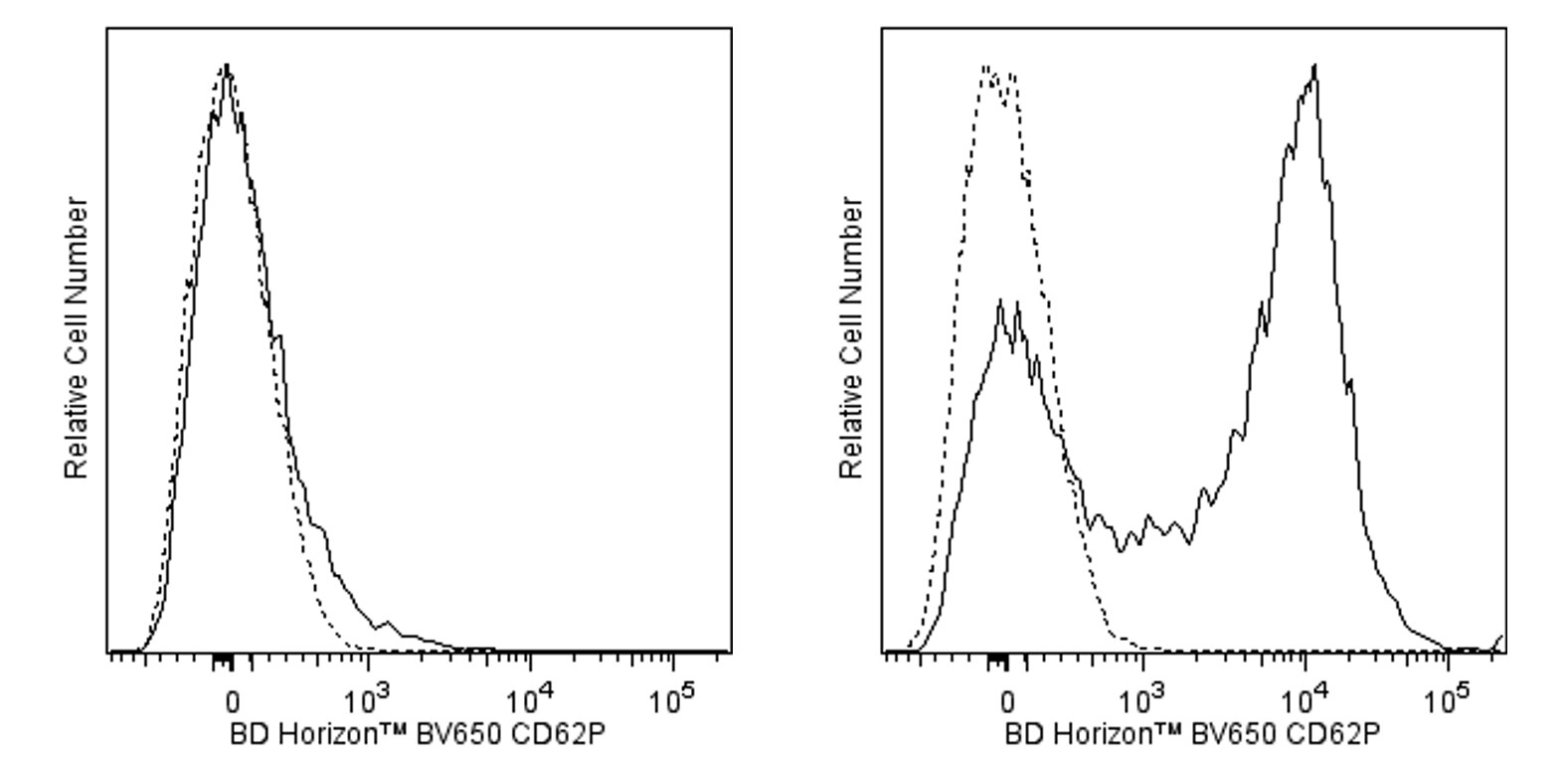



Flow cytometric analysis of CD62P expression on mouse platelets. Mouse platelets were either not activated (Left Panel) or activated with human thrombin (Sigma T-8885; 20 U/ml final concentration; 5 min at 37°C; Right Panel). The platelets were stained with either BD Horizon™ BV650 Rat IgG1, λ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 563906; dashed line histograms) or BD Horizon™ BV650 Rat Anti-Mouse CD62P antibody (Cat. No. 563897; solid line histogram). The fluorescence histograms were derived from events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of platelets. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using a BD™ LSR II Flow Cytometer System.


BD Horizon™ BV650 Rat Anti-Mouse CD62P

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- Alexa Fluor® is a registered trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, OR.
- Brilliant Violet™ 650 is a trademark of Sirigen.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products



The RB40.34 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to mouse P-selectin (CD62P), a 140 kDa protein which is expressed on activated platelets, activated endothelial cells, and megakaryocytes. P-selectin mediates the adhesion of neutrophils and monocytes to activated platelets and endothelial cells, mediates leukocyte rolling, and is involved in the migration of leukocytes into inflamed tissues. CD24 and CD162 (PSGL-1) are ligands of CD62P. mAb RB40.34 can block mouse P-selectin binding to its ligands in vitro and in vivo.
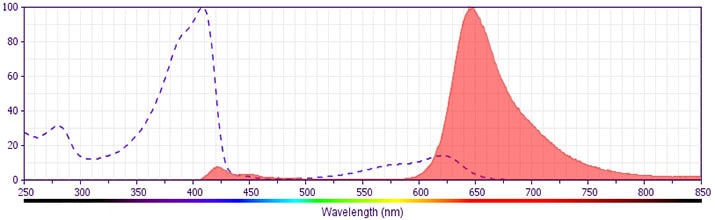
The antibody was conjugated to BD Horizon™ BV650 which is part of the BD Horizon™ Brilliant Violet™ family of dyes. This dye is a tandem fluorochrome of BD Horizon™ BV421 with an Ex Max of 405-nm and an acceptor dye with an Em Max at 650-nm. BD Horizon™ BV650 can be excited by the violet laser and detected in a filter used to detect APC-like dyes (eg, 660/20-nm filter). Due to the excitation and emission characteristics of the acceptor dye, there will be spillover into the APC and Alexa Fluor® 700 detectors. However, the spillover can be corrected through compensation as with any other dye combination.
Development References (9)
-
Aigner S, Ruppert M, Hubbe M, et al. Heat stable antigen (mouse CD24) supports myeloid cell binding to endothelial and platelet P-selectin. Int Immunol. 1995; 7(10):1557-1565. (Biology). View Reference
-
Austrup F, Vestweber D, Borges E, et al. P- and E-selectin mediate recruitment of T-helper-1 but not T-helper-2 cells into inflammed tissues. Nature. 1997; 385(6611):81-83. (Clone-specific: Blocking). View Reference
-
Bosse R, Vestweber D. Only simultaneous blocking of the L- and P-selectin completely inhibits neutrophil migration into mouse peritoneum. Eur J Immunol. 1994; 24(12):3019-3024. (Immunogen: Blocking, ELISA, Flow cytometry, Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Hirata T, Furie BC, Furie B. P-, E-, and L-selectin mediate migration of activated CD8+ T lymphocytes into inflamed skin. J Immunol. 2002; 169(8):4307-4313. (Clone-specific: Blocking). View Reference
-
Katakai T, Mori KJ, Masuda T, Shimizu A. Selective accumulation of type 1 effector cells expressing P-selectin ligand and/or alpha(4)beta(7)-integrin at the lesions of autoimmune gastritis. Int Immunol. 2002; 14(2):167-175. (Clone-specific: Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Ley K, Bullard DC, Arbones ML, et al. Sequential contribution of L- and P-selectin to leukocyte rolling in vivo. J Exp Med. 1995; 181(2):669-675. (Clone-specific: Blocking). View Reference
-
Pendl GG, Robert C, Steinert M, et al. Immature mouse dendritic cells enter inflamed tissue, a process that requires E- and P-selectin, but not P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1. Blood. 2002; 99(3):946-956. (Clone-specific: Blocking). View Reference
-
Tietz W, Allemand Y, Borges E, et al. CD4+ T cells migrate into inflamed skin only if they express ligands for E- and P-selectin. J Immunol. 1998; 161(2):963-970. (Clone-specific: Blocking). View Reference
-
Yang J, Galipeau J, Kozak CA, Furie BC, Furie B. Mouse P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1: molecular cloning, chromosomal localization, and expression of a functional P-selectin receptor. Blood. 1996; 87(10):4176-4186. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.