Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?



.png)

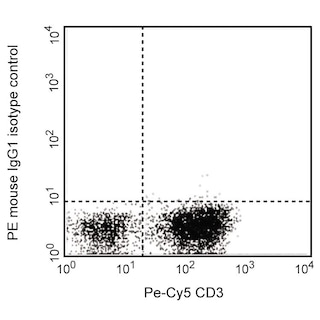
Multiparameter flow cytometric analysis of CD44v6 expression on human peripheral blood leucocyte populations. Human whole blood was stained with either PE Mouse IgG1, κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 554680; Left Plot) or PE Mouse Anti-Human CD44v6 antibody (Cat. No. 566803; Right Plot). After staining, erythrocytes were lysed with BD Pharm Lyse™ Lysing Buffer (Cat. No. 555899). A two-parameter flow cytometric contour plot showing the correlated expression of CD44v6 (or Ig Isotype control staining) versus side light-scatter signals was derived from gated events with the forward and side light scattering properties of viable leucocyte populations. Flow cytometry and data analysis were performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ Cell Analyzer System and FlowJo™ software.

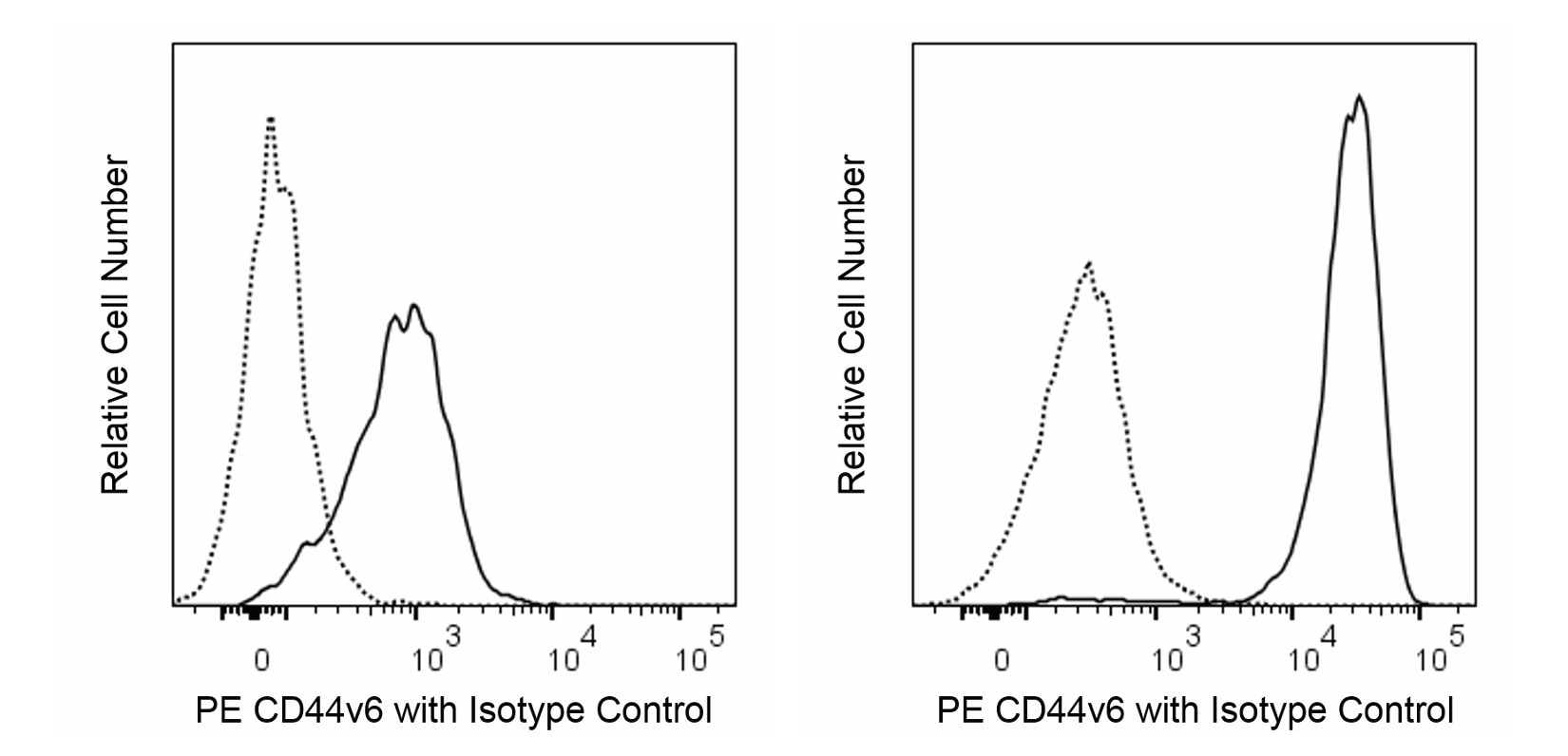
Flow cytometric analysis of CD44v6 expression on fresh or GM-CSF treated human peripheral blood monocytes. Left Panel: Whole blood was stained with PE Mouse IgG1, κ Isotype Control (dotted line histogram) or PE Mouse Anti-Human CD44v6 antibody (solid line histogram). Erythrocytes were lysed with BD Pharm Lyse™ Lysing Buffer. Right Panel: PBMC were cultured with recombinant GM-CSF protein (Cat. No. 550068; 20 ng/ml, 18 h, 37°C). The cells were then stained with either PE Mouse IgG1, κ Isotype Control (dotted line histogram) or PE Mouse anti-Human CD44v6 antibody (solid line histogram). The fluorescent histograms showing CD44v6 expression (or Ig Isotype control staining) were derived from gated events with the light scattering characteristics of viable monocytes. Flow cytometry and data analysis were performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ Cell Analyzer System and FlowJo™ software.
.png)

BD Pharmingen™ PE Mouse Anti-Human CD44v6

BD Pharmingen™ PE Mouse Anti-Human CD44v6
.png)
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test).
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
Companion Products




The 2F10 monoclonal antibody specifically recognizes exon v6-containing isoforms of the CD44 adhesion receptor (CD44v6). CD44 is a widely-expressed, 85-250 kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein that regulates cellular adhesion, growth, and migration and is involved in cell-cell interactions. CD44 is a member of the hyaladherin family of hyaluronan-binding proteins. It serves as a multifunctional receptor for hyaluronic acid and other ligands including collagens, fibronectin, matrix metalloproteinases, and osteopontin. The standard form of CD44 (CD44s) contains an extracellular region with a hyaluronan-binding link domain and a stem region devoid of variable exon sequences that are followed by a transmembrane domain and a cytoplasmic tail. The cytoplasmic region is linked to the cytoskeleton and may be involved in signaling interactions. Alternative splicing of CD44 gene transcripts results in the differential inclusion of 10 variant exons (v1-10) within the stem region, either individually or in multiple combinations. This results in a large number of variant CD44 (CD44v) isoforms with different cell surface expression levels and functions. CD44 isoforms containing exon v6 (CD44v6) are variably expressed on epithelial cells, monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, and Langerhans cells. It is expressed on certain tumor cells and on cancer stem cells (CSCs) and is implicated in tumor cell metastasis. In addition to playing roles in cellular adhesion and migration, CD44 isoforms with exon v6 sequences may serve as coreceptors for some growth factors and cytokines including hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) which is involved in driving c-Met signaling.
Development References (11)
-
Braumüller H, Gansauge S, Ramadani M, Gansauge F. CD44v6 cell surface expression is a common feature of macrophages and macrophage-like cells - implication for a natural macrophage extravasation mechanism mimicked by tumor cells.. FEBS Lett. 2000; 476(3):240-7. (Biology). View Reference
-
Buckner CM, Calderon TM, Willams DW, Belbin TJ, Berman JW. Characterization of monocyte maturation/differentiation that facilitates their transmigration across the blood-brain barrier and infection by HIV: implications for NeuroAIDS. Cell Immunol. 2011; 267(2):109-123. (Biology). View Reference
-
Casucci M, Nicolis di Robilant B, Falcone L, et al. CD44v6-targeted T cells mediate potent antitumor effects against acute myeloid leukemia and multiple myeloma.. Blood. 2013; 122(20):3461-72. (Biology). View Reference
-
Forster-Horváth C, Bocsi J, Rásó E, et al. Constitutive intracellular expression and activation-induced cell surface up-regulation of CD44v3 in human T lymphocytes.. Eur J Immunol. 2001; 31(2):600-8. (Biology). View Reference
-
Fox SB, Fawcett J, Jackson DG, et al. Normal human tissues, in addition to some tumors, express multiple different CD44 isoforms.. Cancer Res. 1994; 54(16):4539-46. (Immunogen: Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Haegel-Kronenberger H, de la Salle H, Bohbot A, Oberling F, Cazenave JP, Hanau D. Adhesive and/or signaling functions of CD44 isoforms in human dendritic cells.. J Immunol. 1998; 161(8):3902-11. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, Functional assay). View Reference
-
Heider KH, Kuthan H, Stehle G, Munzert G. CD44v6: a target for antibody-based cancer therapy.. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2004; 53(7):567-79. (Clone-specific: Immunocytochemistry). View Reference
-
Horvatinovich JM1, Grogan EW1, Norris M, et al. Soluble CD83 Inhibits T Cell Activation by Binding to the TLR4/MD-2 Complex on CD14+ Monocytes. J Imm. 2017; 198:2286-2301. (Biology). View Reference
-
Marcondes MC, Lanigan CM, Burdo TH, Watry DD, Fox HS. Increased expression of monocyte CD44v6 correlates with the deveopment of encephalitis in rhesus macaques infected with simian immunodeficiency virus.. J Infect Dis. 2008; 197(11):1567-76. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Orian-Rousseau V, Chen L, Sleeman JP, Herrlich P, Ponta H. CD44 is required for two consecutive steps in HGF/c-Met signaling. Genes Dev. 2002; 16(23):3074-3086. (Biology). View Reference
-
Weiss JM, Sleeman J, Renkl AC, et al. An essential role for CD44 variant isoforms in epidermal Langerhans cell and blood dendritic cell function. J Cell Biol. 1997; 137(5):1137-1147. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.