Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?
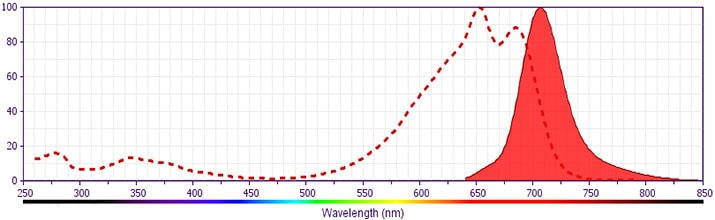
BD Horizon™ APC-R700 Hamster Anti-Mouse CD152
Clone UC10-4F10-11 (also known as UC10-4F10; 4F10)
(RUO)

.png)

Two-color flow cytometric analysis of CD152 expression on activated mouse splenocytes. Mouse splenic leucocytes were stimulated for 72 hours with concanavalin A (ConA). The cells were harvested and preincubated with Purified Rat Anti-Mouse CD16/CD32 antibody (Mouse BD Fc Block™) (Cat. No. 553141/553142). The cells were then stained with PE Rat Anti-Mouse CD8a antibody (Cat. No. 553033/553032/561095) and either BD Horizon™ APC-R700 Hamster IgG1, κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 565129; Left Panel) or BD Horizon APC-R700 Hamster Anti-Mouse CD152 antibody (Cat. No. 565778; Right Panel). Two-color flow cytometric dot plots showing the correlated expression of CD152 (or Ig Isotype control staining) versus CD8a were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable activated leucocytes. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ Cell Analyzer System.
.png)

BD Horizon™ APC-R700 Hamster Anti-Mouse CD152
.png)
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
BD® CompBeads can be used as surrogates to assess fluorescence spillover (compensation). When fluorochrome conjugated antibodies are bound to BD® CompBeads, they have spectral properties very similar to cells. However, for some fluorochromes there can be small differences in spectral emissions compared to cells, resulting in spillover values that differ when compared to biological controls. It is strongly recommended that when using a reagent for the first time, users compare the spillover on cells and BD® CompBeads to ensure that BD® CompBeads are appropriate for your specific cellular application.
Product Notices
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Alexa Fluor® is a registered trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, OR.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- Alexa Fluor™ is a trademark of Life Technologies Corporation.
- For U.S. patents that may apply, see bd.com/patents.
Companion Products





.png?imwidth=320)
The UC10-4F10-11 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to CD152, which is also known as Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4). CD152 is expressed on activated T lymphocytes 2-3 days after stimulation through T cell receptor. CTLA-4 has significant similarity to CD28 in amino acid sequence, structure, and genomic organization. Furthermore, CD152 and CD28 share common B7 family counter-receptors. Unlike CD28, CD152 expression appears to be restricted to activated T cells and CD25+CD4+ regulatory T (Treg) cells. Whereas CD28 delivers a costimulatory signal required for T-cell activation, CTLA-4 is a negative regulator of cell-mediated immune responses. CD152 may play roles in induction and/or maintenance of immunological tolerance, regulation of protective immunity, and autoimmune responses, and regulation of some aspects of thymocyte maturation. This hamster mAb to a mouse leukocyte antigen does not cross-react with rat leucocytes.
Development References (11)
-
Alegre ML, Noel PJ, Eisfelder BJ, et al. Regulation of surface and intracellular expression of CTLA4 on mouse T cells. J Immunol. 1996; 157(11):4762-4770. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, Fluorescence microscopy, Immunofluorescence, Intracellular Staining/Flow Cytometry). View Reference
-
Cilio CM, Daws MR, Malashicheva A, Sentman CL, Holmberg D. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 is induced in the thymus upon in vivo activation and its blockade prevents anti-CD3-mediated depletion of thymocytes. J Exp Med. 1998; 188(7):1239-1246. (Clone-specific: Blocking, Intracellular Staining/Flow Cytometry). View Reference
-
Issazadeh S, Zhang M, Sayegh MH, Khoury SJ.. Acquired thymic tolerance: role of CTLA4 in the initiation and maintenance of tolerance in a clinically relevant autoimmune disease model. J Immunol. 1999; 162(2):761-765. (Clone-specific: In vivo exacerbation). View Reference
-
Kearney ER, Walunas TL, Karr RW, et al. Antigen-dependent clonal expansion of a trace population of antigen-specific CD4+ T cells in vivo is dependent on CD28 costimulation and inhibited by CTLA-4. J Immunol. 1995; 155(3):1032-1036. (Clone-specific: In vivo exacerbation). View Reference
-
Lee KM, Chuang E, Griffin M, et al. Molecular basis of T cell inactivation by CTLA-4. Science. 1998; 282(5397):2263-2266. (Clone-specific: Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
McCoy K, Camberis M, Gros GL. Protective immunity to nematode infection is induced by CTLA-4 blockade. J Exp Med. 1997; 186(2):183-187. (Clone-specific: In vivo exacerbation). View Reference
-
Perkins D, Wang Z, Donovan C, et al. Regulation of CTLA-4 expression during T cell activation. J Immunol. 1996; 156(11):4154-4159. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Perrin PJ, Maldonado JH, Davis TA, June CH, Racke MK. CTLA-4 blockade enhances clinical disease and cytokine production during experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 1996; 157(4):1333-1336. (Clone-specific: In vivo exacerbation). View Reference
-
Read S, Malmstrom V, Powrie F. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 plays an essential role in the function of CD25(+)CD4(+) regulatory cells that control intestinal inflammation. J Exp Med. 2000; 192(2):295-302. (Clone-specific: Intracellular Staining/Flow Cytometry). View Reference
-
Takahashi T, Tagami T, Yamazaki S, et al. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by CD25(+)CD4(+) regulatory T cells constitutively expressing cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4. J Exp Med. 2000; 192(2):303-309. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, In vivo exacerbation). View Reference
-
Walunas TL, Lenschow DJ, Bakker CY, et al. CTLA-4 can function as a negative regulator of T cell activation.. Immunity. 1994; 1(5):405-13. (Immunogen: Flow cytometry, Immunoprecipitation, Stimulation). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.