Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?
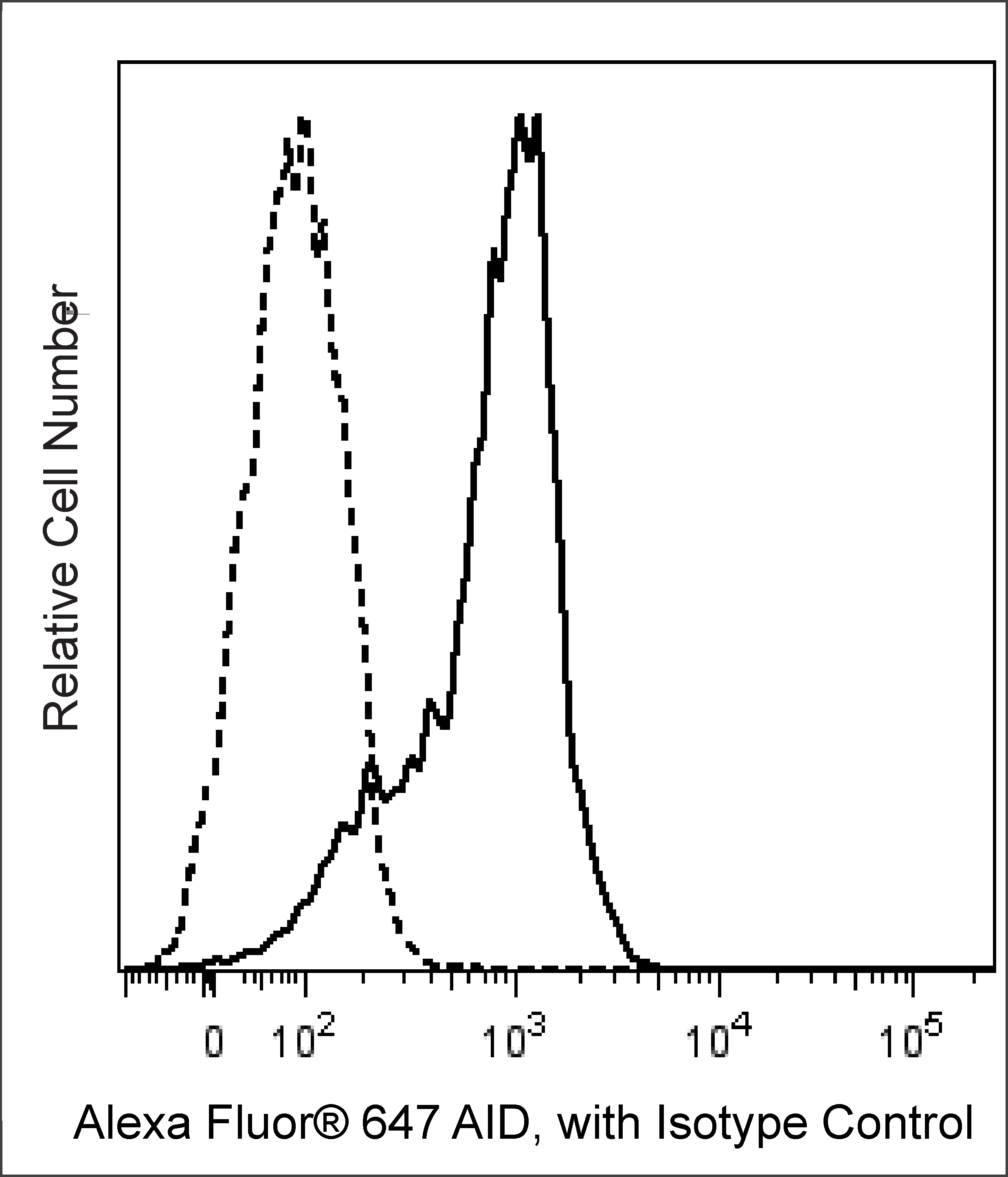




Flow cytometric analysis of Human AID expression in human Ramos cells. Cells from the Ramos (Burkitt's lymphoma, ATCC CRL-1596) cell line were preincubated with BD Pharmingen Human BD Fc Block™ (Cat. No. 564219/564220), fixed with BD Cytofix™ Fixation Buffer (Cat. No. 554655), and permeabilized with BD Phosflow™ Perm Buffer III (Cat. No. 558050). Cells were stained with either Alexa Fluor® 647 Rat IgG2b, κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 557691; dashed line histogram) or Alexa Fluor® 647 Rat Anti-Human AID antibody (Cat. No. 565785; solid line histogram).The fluorescence histogram showing AID expression [or Ig Isotype control staining] was derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of intact cells. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ X-20 Cell Analyzer System.

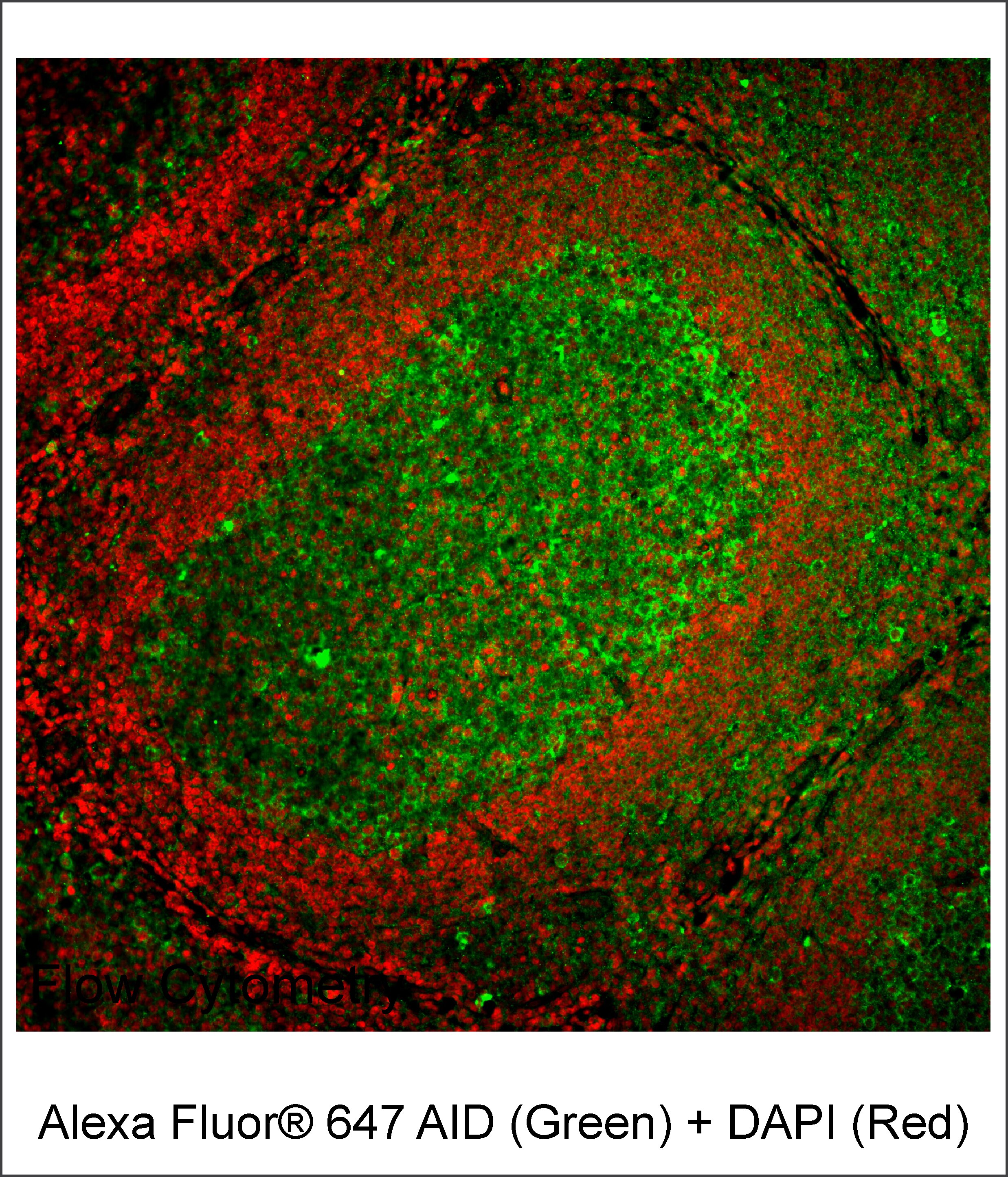
Immunofluorescent staining of human AID expressed in cells from human tonsil. Following antigen retrieval with BD Retrievagen A Buffer (Cat. No. 550524), formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded human tonsil sections were blocked with an Avidin/Biotin Blocking Kit (Vector Laboratories; Cat. No. SP-2001) as recommended by the manufacturer. The sections were stained with Alexa Fluor® 647 Rat Anti-Human AID antibody (pseudo-colored green) and counterstained with BD Pharmingen™ DAPI Solution (Cat. No. 564907; pseudo-colored red). The images were captured on a standard epifluorescence microscope. Original magnification, 20×.


BD Pharmingen™ Alexa Fluor® 647 Rat Anti-Human AID

BD Pharmingen™ Alexa Fluor® 647 Rat Anti-Human AID

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- The Alexa Fluor®, Pacific Blue™, and Cascade Blue® dye antibody conjugates in this product are sold under license from Molecular Probes, Inc. for research use only, excluding use in combination with microarrays, or as analyte specific reagents. The Alexa Fluor® dyes (except for Alexa Fluor® 430), Pacific Blue™ dye, and Cascade Blue® dye are covered by pending and issued patents.
- Alexa Fluor® 647 fluorochrome emission is collected at the same instrument settings as for allophycocyanin (APC).
- Alexa Fluor® is a registered trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, OR.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
Companion Products




The EK2-5G9 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to human Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AICDA), also known as AID, or Single-stranded DNA cytosine deaminase. AID is an enzyme that preferentially acts upon certain DNA sequence motifs, such as those located in immunoglobulin variable regions, to induce cytidine-to-uracil mutations. AID-induced mutations initiate both somatic hypermutation (SHM) and class switch recombination (CSR) of the immunoglobulin genes in activated B cells during immune responses. While essential for immunoglobulin gene diversification, dysregulated AID activity can result in genomic instability and oncogenic transformation. Originally thought to be B-cell specific, AID now appears to be abnormally expressed in several epithelial cancers. AID may also play roles in DNA demethylation.
Development References (4)
-
Dahlberg CI, He M, Visnes T, et al. A novel mouse model for the hyper-IgM syndrome: a spontaneous activation-induced cytidine deaminase mutation leading to complete loss of Ig class switching and reduced somatic hypermutation.. J Immunol. 2014; 193(9):4732-8. (Biology). View Reference
-
Greiner A, Tobollik S, Buettner M, et al. Differential expression of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) in nodular lymphocyte-predominant and classical Hodgkin lymphoma.. J Pathol. 2005; 205(5):541-7. (Immunogen: ELISA, Fluorescence microscopy, Immunofluorescence, Immunohistochemistry, Immunoprecipitation, Western blot). View Reference
-
Klemm L, Duy C, Iacobucci I, et al. The B cell mutator AID promotes B lymphoid blast crisis and drug resistance in chronic myeloid leukemia.. Cancer Cell. 2009; 16(3):232-45. (Biology). View Reference
-
Rebhandl S, Huemer M, Greil R, Geisberger R. AID/APOBEC deaminases and cancer.. Oncoscience. 2015; 2(4):320-33. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.