Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?
.png)
.png)
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
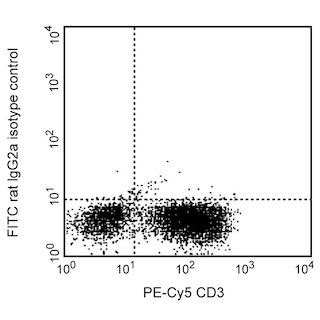
The RM4-5 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to the CD4 (L3T4) differentiation antigen expressed on most thymocytes, subpopulations of mature T lymphocytes (i.e., MHC class II-restricted T cells, including most T helper cells and immunosuppressive regulatory T cells), and a subset of NK-T cells. CD4 has also been reported to be detected on pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells, bone marrow myeloid and B-lymphocyte precursors, intrathymic lymphoid precursors, and a subset of splenic dendritic cells. CD4 has been reported to be expressed on the plasma membrane of mouse egg cells and is involved in adhesion of the egg to MHC class II-bearing sperm. CD4 is an antigen coreceptor on the T-cell surface which interacts with MHC class II molecules on antigen-presenting cells. It participates in T-cell activation through its association with the T-cell receptor complex and protein tyrosine kinase lck. Purified RM4-5 mAb has been reported to block the binding of FITC-conjugated anti-mouse CD4 clones GK1.5 and H129.19, but not the RM4-4 clone.
This antibody is routinely tested by flow cytometric analysis. Other applications were tested at BD Biosciences Pharmingen during antibody development only or reported in the literature.
Development References (14)
-
Allman D, Li J, Hardy RR. Commitment to the B lymphoid lineage occurs before DH-JH recombination. J Exp Med. 1999; 189(4):735-740. (Biology). View Reference
-
Bendelac A. Mouse NK1+ T cells. Curr Opin Immunol. 1995; 7(3):367-374. (Biology). View Reference
-
Bierer BE, Sleckman BP, Ratnofsky SE, Burakoff SJ. The biologic roles of CD2, CD4, and CD8 in T-cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989; 7:579-599. (Biology). View Reference
-
Bosselut R, Zhang W, Ashe JM, Kopacz JL, Samelson LE, Singer A. Association of the adaptor molecule LAT with CD4 and CD8 coreceptors identifies a new coreceptor function in T cell receptor signal transduction. J Exp Med. 1999; 190(10):1517-1526. (Biology: Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Frederickson GG, Basch RS. L3T4 antigen expression by hemopoietic precursor cells. J Exp Med. 1989; 169(4):1473-1478. (Biology). View Reference
-
Godfrey DI, Kennedy J, Mombaerts P, Tonegawa S, Zlotnik A. Onset of TCR-β gene rearrangement and role of TCR-β expression during CD3-CD4-CD8- thymocyte differentiation. J Immunol. 1994; 152(10):4783-4792. (Biology). View Reference
-
Guo MW, Watanabe T, Mori E, Mori T. Molecular structure and function of CD4 on murine egg plasma membrane. Zygote. 1995; 3(1):65-73. (Biology). View Reference
-
Janeway CA Jr. The T cell receptor as a multicomponent signalling machine: CD4/CD8 coreceptors and CD45 in T cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992; 10:645-674. (Biology). View Reference
-
Martin P, del Hoyo GM, Anjuere F, et al. Concept of lymphoid versus myeloid dendritic cell lineages revisited: both CD8alpha(-) and CD8alpha(+) dendritic cells are generated from CD4(low) lymphoid-committed precursors. Blood. 2000; 96(7):2511-2519. (Biology). View Reference
-
Nakamura T. Personal Communication. .
-
Shevach EM. Regulatory T cells in autoimmmunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000; 18:423-449. (Biology). View Reference
-
Wineman JP, Gilmore GL, Gritzmacher C, Torbett BE, Muller-Sieburg CE. CD4 is expressed on murine pluripotent hematopoietic stem cells. Blood. 1992; 180(7):1717-1724. (Biology). View Reference
-
Wu L, Antica M, Johnson GR, Scollay R, Shortman K. Developmental potential of the earliest precursor cells from the adult mouse thymus. J Exp Med. 1991; 174(6):1617-1627. (Biology). View Reference
-
Wu L, Scollay R, Egerton M, Pearse M, Spangrude GJ, Shortman K. CD4 expressed on earliest T-lineage precursor cells in the adult murine thymus. Nature. 1991; 349(6304):71-74. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.