-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
-
Dehydrated Culture Media
-
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
- Canada (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?
BD Pharmingen™ Purified Mouse anti-FADD (pS194)
Clone J119-857.36 (RUO)
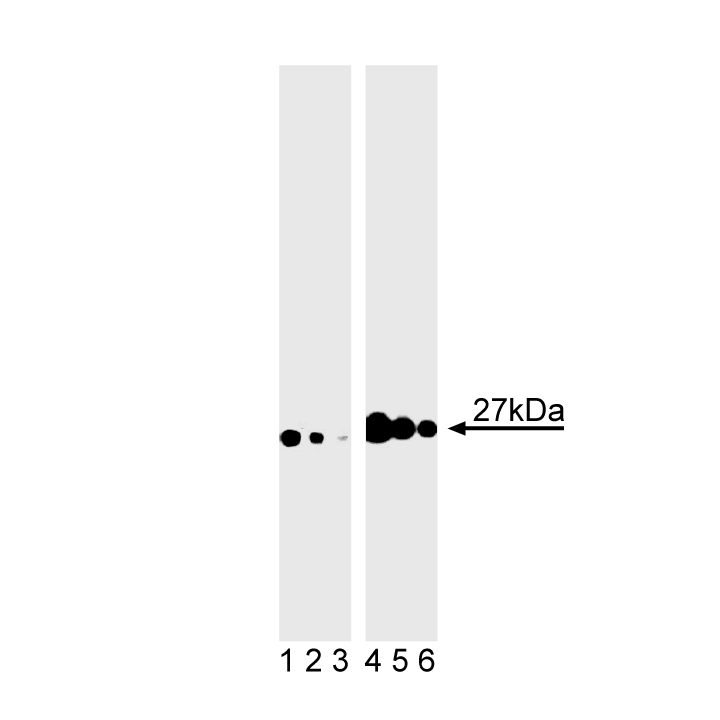
Western blot analysis of FADD (pS194) in human epidermis. Lysates from control (lanes 1-3l) and calyculin A-plus-okadaic acid-treated (lanes 4-6) human A-431 epidermoid carcinoma were probed with purified mouse anti-FADD (pS194) monoclonal antibody at concentrations of 2.0 (lanes 1 and 4), 1.0 (lanes 2 and 5), and 0.5 µg/ml (lanes 3 and 6). FADD (pS194) is identified as a band of 27 kDa in the treated cells.


Western blot analysis of FADD (pS194) in human epidermis. Lysates from control (lanes 1-3l) and calyculin A-plus-okadaic acid-treated (lanes 4-6) human A-431 epidermoid carcinoma were probed with purified mouse anti-FADD (pS194) monoclonal antibody at concentrations of 2.0 (lanes 1 and 4), 1.0 (lanes 2 and 5), and 0.5 µg/ml (lanes 3 and 6). FADD (pS194) is identified as a band of 27 kDa in the treated cells.

Western blot analysis of FADD (pS194) in human epidermis. Lysates from control (lanes 1-3l) and calyculin A-plus-okadaic acid-treated (lanes 4-6) human A-431 epidermoid carcinoma were probed with purified mouse anti-FADD (pS194) monoclonal antibody at concentrations of 2.0 (lanes 1 and 4), 1.0 (lanes 2 and 5), and 0.5 µg/ml (lanes 3 and 6). FADD (pS194) is identified as a band of 27 kDa in the treated cells.



Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
During apoptosis, cells exhibit morphological signs of the death process: cell shrinkage, membrane blebbing, and chromatin condensation. The role of the cell surface cytokine receptor, Fas (Apo-1, CD95), in apoptosis has been well characterized. The tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor type I (TNFRI, CD120a) and TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor 2 (TRAILR2, DR5) can trigger cell death, as well as various other responses. Fas, TNFRI, and TRAILR2 affect a common target in the cell death pathway, FADD (Fas-Associated via Death Domain or FAS-Associating protein with Death Domain, also known as MORT1). FADD is an adaptor protein that specifically binds to Fas and other death domain-containing proteins via their homologous death domains. FADD also contains an N-terminal Death Effector Domain (DED) that interacts with the DED-containing procaspases-8 and -10 to initiate apoptosis. The role of FADD serine 194 (S194) phosphorylation in the regulation of apoptosis and cell cycle progression is under investigation.
The J119-857.36 monoclonal antibody recognizes the phosphorylated S194 of human FADD.
Development References (4)
-
Alappat EC, Volkland J, Peter ME. Cell cycle effects by C-FADD depend on its C-terminal phosphorylation site. J Biol Chem. 2003; 278(43):41585-41588. (Biology).
-
Hua ZC, Sohn SJ, Kang C, Cado D, Winoto A. A function of Fas-associated death domain protein in cell cycle progression localized to a single amino acid at its C-terminal region. Immunity. 2003; 18(4):513-521. (Biology).
-
Tibbetts MD, Zheng L, Lenardo MJ. The death effector domain protein family: regulators of cellular homeostasis. Nat Immunol. 2003; 4(5):404-409. (Biology).
-
Tourneur L, Buzyn A, Chiocchia G. FADD adaptor in cancer. Med Immunol. 2005; 4(1):1. (Biology).
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.