-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
-
Dehydrated Culture Media
-
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
- Canada (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?
BD Pharmingen™ Purified Mouse Anti-Neurofilament Protein (NF-M) w/Control
Clone RNF406 (RUO)
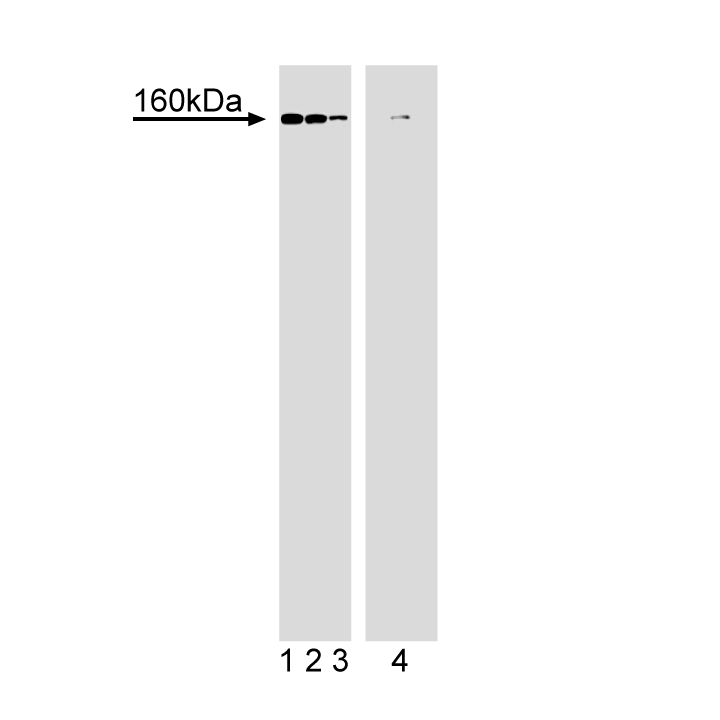
Western blot analysis of NF-M. Lysate from rat whole brain was either untreated (lanes 1-3) or treated with alkaline phosphatase (50 µg/ml at 37°C for 30 minutes, lane 4). The lysate was then probed with anti-neurofilament (clone RNF406, Cat. No. 8124KC) at concentrations of 1.0 (lane 1), 0.5 (lanes 2, 4), and 0.25 µg/ml (lane 3). RNF406 is identified as a band of 160 kDa. Alkaline phosphatase treatment caused a significant reduction of the NF-M band.


Western blot analysis of NF-M. Lysate from rat whole brain was either untreated (lanes 1-3) or treated with alkaline phosphatase (50 µg/ml at 37°C for 30 minutes, lane 4). The lysate was then probed with anti-neurofilament (clone RNF406, Cat. No. 8124KC) at concentrations of 1.0 (lane 1), 0.5 (lanes 2, 4), and 0.25 µg/ml (lane 3). RNF406 is identified as a band of 160 kDa. Alkaline phosphatase treatment caused a significant reduction of the NF-M band.

Western blot analysis of NF-M. Lysate from rat whole brain was either untreated (lanes 1-3) or treated with alkaline phosphatase (50 µg/ml at 37°C for 30 minutes, lane 4). The lysate was then probed with anti-neurofilament (clone RNF406, Cat. No. 8124KC) at concentrations of 1.0 (lane 1), 0.5 (lanes 2, 4), and 0.25 µg/ml (lane 3). RNF406 is identified as a band of 160 kDa. Alkaline phosphatase treatment caused a significant reduction of the NF-M band.



Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Description
Intermediate filaments (IF) are a subset of cytoskeletal proteins which function to give overall structural integrity to the plasma membrane as well as organize cells 160kDa into specific tissues. IF proteins can be divided into six major types based upon the similarity in sequence. Neurofilaments (NF) are classified as Type IV intermediate filaments and are composed of three polypeptides, designated NF-L (~68 kDa), NF-M (~160 kDa), and NF-H (~200 kDa) which differ in molecular weight. The distribution of these neurofilaments is mostly limited to the central and peripheral nervous systems and restricted to neurons. NF proteins function to provide radial growth of the neuron. Most neurons are composed of all three NF proteins, although the role of each individual NF polypeptide has not been fully elucidated. Both phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated forms of NF's are found in the brain; phosphorylation status is dependent upon the stage of development and region of the brain. The exact role for the phosphorylation of neutrofilaments remains to be elucidated, but aberrant neurofilament phosphorylation occurs in a number of neurodegenerative diseases. For example, in a rat model for spontaneous type I diabetes, the NF-M neurofilament in the sural nerve of BB rats showed a 2.5-fold increase in phosphorylation. Phosphorylation may play a role in regulating the incorporation of slow transported neurofilament proteins into the stable cytoskeletal network of the axon, thereby helping to regulate the diameter of the axon. The antibody only recognizes the phosphorylated form of neurofilament NF-M; it does not recognize the nonphosphorylated form of the molecule. A neurofilament cytoskeletal preparation from calf brain was used as the immunogen. The antibody has only been evaluated in rat, but may also recognize NF-M from other species due to the highly conserved nature of this molecule.
Preparation And Storage
Store the antibody at 4°C. Store the positive control lysate (Cat. No. 51-16646N) at -20°C.
Recommended Assay Procedures
Applications include western blot analysis (0.25-1.0 µg/ml). Rat whole brain lysate [50 µg (1 µg/µl)] is provided as a ready-to-use western blot positive control (Cat. No. 51-16646N).
It has been reported, but not tested at BD Pharmingen, that clone RNF406 cross-reacts with human, rabbit, dog, chicken, mouse, hamster, cow, monkey, guinea pig, sheep and xenopus.
BD Biosciences Pharmingen offers several neurofilament antibodies. Lysate from rat whole brain was used to evaluate these antibodies; these results are summarized in the following table. However, actual bands observed could vary according to the cell model system used.
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
| Description | Quantity/Size | Part Number | EntrezGene ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| N/A | 50.0 | N/A | N/A |
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.