Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




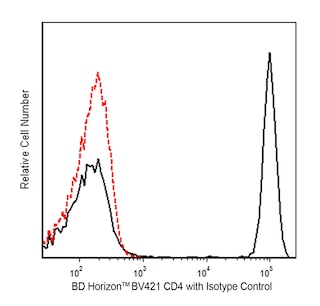
Two-color flow cytometric analysis of Helios expression Left Panel: Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were stained with BD Horizon™ BV421 Mouse Anti-Human CD4 antibody (Cat. No. 562424/562425) and fixed and permeabilized with the BD Pharmingen™ Transcription Factor Buffer Set (Cat. No. 562574/562725). The cells were then stained with either BD Horizon™ RY586 Armenian Hamster IgG2 κ, Isotype Control (Cat. No. 568823; Left Plot) or BD Horizon™ RY586 Armenian Hamster Anti-Helios antibody (Cat. No. 568526/568527; Right Plot). Right Panel: Mouse splenic leucocytes were stained with BD OptiBuild™ BV421 Rat Anti-Mouse CD4 antibody (Cat. No. 740007) and fixed and permeabilized with the BD Pharmingen™ Transcription Factor Buffer Set. The cells were then stained with either Armenian Hamster IgG2 κ, Isotype Control (Left Plot) or BD Horizon™ RY586 Armenian Hamster Anti-Helios antibody (Right Plot). The pseudocolor density plots show the correlated expression of Helios (or Ig Isotype control staining) versus CD4 were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of intact human peripheral blood lymphocytes or splenic leucocytes. Flow cytometry and data analysis were performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ X-20 Cell Analyzer System and FlowJo™ software.


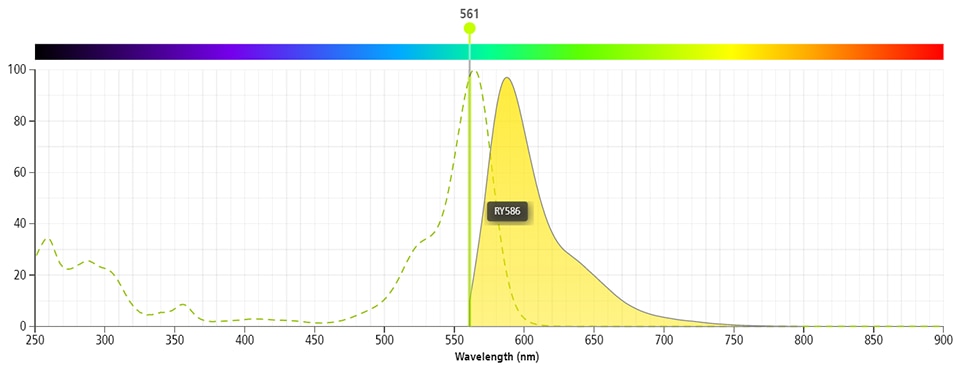
BD Horizon™ RY586 Armenian Hamster Anti-Helios

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
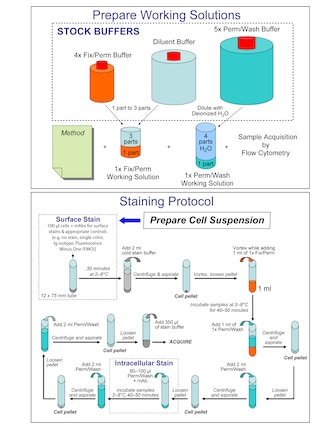
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
BD® CompBeads can be used as surrogates to assess fluorescence spillover (compensation). When fluorochrome conjugated antibodies are bound to BD® CompBeads, they have spectral properties very similar to cells. However, for some fluorochromes there can be small differences in spectral emissions compared to cells, resulting in spillover values that differ when compared to biological controls. It is strongly recommended that when using a reagent for the first time, users compare the spillover on cells and BD® CompBeads to ensure that BD® CompBeads are appropriate for your specific cellular application.
Product Notices
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test).
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Species cross-reactivity detected in product development may not have been confirmed on every format and/or application.
- Human donor specific background has been observed in relation to the presence of anti-polyethylene glycol (PEG) antibodies, developed as a result of certain vaccines containing PEG, including some COVID-19 vaccines. We recommend use of BD Horizon Brilliant™ Stain Buffer in your experiments to help mitigate potential background. For more information visit https://www.bdbiosciences.com/en-us/support/product-notices.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- CF™ is a trademark of Biotium, Inc.
Companion Products




The 22F6 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to mouse and human Helios. Helios is a member of the Ikaros family of zinc-finger transcription factors, which play important roles in hematopoietic cell development and tumor suppression. Helios expression is restricted to the earliest stages of embryonic hematopoiesis, a variety of epithelial tissues and is notably increased in thymic-derived regulatory CD4+Foxp3+ T (Treg) cells. Its high expression levels in Treg cells are independent from Foxp3 and are believed to contribute, along with other transcription factors, to the phenotypic stability of natural regulatory T cells. Accordingly, it has been demonstrated that Helios directly stimulates Foxp3 transcription while it inhibits ll2 gene expression, contributing for the maintenance of cellular anergy. Helios is also differentially expressed during negative and positive selection in the thymus, marking CD4+ autoreactive cells for deletion. Helios may possibly play roles in T cell activation, since it is upregulated in Th2 and Tfh cells. Despite these roles in T cell development and function, Helios genetic ablation in mice revealed no significant abnormalities in Treg or other T cell subsets. This finding suggests that other Ikaros family members may play redundant roles.
Development References (10)
-
Baine I, Basu S, Ames R, Sellers RS, Macian F. Helios induces epigenetic silencing of IL2 gene expression in regulatory T cells. J Immunol. 2013; 190(3):1008-1016. (Biology). View Reference
-
Cai Q, Dierich A, Oulad-Abdelghani M, Chan S, Kastner P. Helios deficiency has minimal impact on T cell development and function. J Immunol. 183(4)(Biology). View Reference
-
Daley SR, Hu DY, Goodnow CC. Helios marks strongly autoreactive CD4+ T cells in two major waves of thymic deletion distinguished by induction of PD-1 or NF-kappaB. J Exp Med. 2013; 210(2):269-285. (Biology). View Reference
-
Fu W, Ergun A, Lu T, et al. A multiply redundant genetic switch 'locks in' the transcriptional signature of regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol. 2012; 13(10):972-980. (Biology). View Reference
-
Georgopoulos K. Haematopoietic cell-fate decisions, chromatin regulation and ikaros. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002; 2(3):162-174. (Biology). View Reference
-
Kelley CM, Ikeda T, Koipally J, et al. Helios, a novel dimerization partner of Ikaros expressed in the earliest hematopoietic progenitors. Curr Biol. 1998; 8(9):508-515. (Biology). View Reference
-
Serre K, Benezech C, Desanti G, et al. Helios is associated with CD4 T cells differentiating to T helper 2 and follicular helper T cells in vivo independently of Foxp3 expression. PLoS ONE. 2011; 6(6):e20731. (Biology). View Reference
-
Sugimoto N, Oida T, Hirota K, et al. Foxp3-dependent and -independent molecules specific for CD25+CD4+ natural regulatory T cells revealed by DNA microarray analysis. Int Immunol. 18(8)(Biology). View Reference
-
Thornton AM, Korty PE, Tran DQ, et al. Expression of Helios, an Ikaros transcription factor family member, differentiates thymic-derived from peripherally induced Foxp3+ T regulatory cells. J Immunol. 2010; 184(7):3433-3441. (Immunogen: ELISA, Flow cytometry, Western blot). View Reference
-
Yoshimatsu Y, Sujino T, Miyamoto K, et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor signals in epithelial cells govern the recruitment and location of Helios+ Tregs in the gut.. Cell Rep. 2022; 39(6):110773. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical Data Sheets before using this product as described.
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.