-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Profiling Assays for Human and Mouse
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
-
Dehydrated Culture Media
-
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Profiling Assays for Human and Mouse
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- Canada (English)
-
Change country/language
Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


.png)

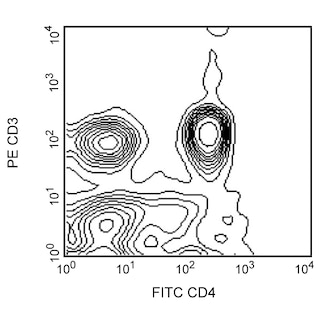
Two-color flow cytometric analysis of the expression of CD4 on rat splenocytes. Lewis splenocytes were incubated simultaneously with FITC Mouse Anti-Rat CD4 (Cat. No. 554843/561834) and PE Mouse Anti-Rat CD3 (Cat. No. 554833) monoclonal antibodies. The CD3-negative CD4-dim cells are the monocyte/macrophage population. The fluorescence contour plots were derived from gated events based on the light-scattering characteristics of viable splenocytes. Flow cytometry was performed on a BD FACScan™.
.png)

BD Pharmingen™ FITC Mouse Anti-Rat CD4
.png)
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products


.png?imwidth=320)
The OX-38 antibody specifically recognizes the CD4 antigen on most thymocytes, a subpopulation of mature T lymphocytes (ie, MHC class II-restricted T cells, including most T helper cells), monocytes, macrophages, and some dendritic cells. CD4 is an antigen coreceptor on the T-cell surface which interacts with MHC class II molecules on antigen-presenting cells. It participates in T-cell activation through its association with the T-cell receptor complex and protein tyrosine kinase lck. The OX-38 antibody has been reported to bind to the same epitope of CD4 as that recognized by W3/25 mAb, which is a different epitope than that recognized by OX-35 mAb. In vivo blocking of some cell-mediated immune responses by mAb OX-38 has been reported. Injection of OX-38 mAb induces allograft unresponsiveness in rats, with varying results depending on the rat strain used (high or low responder). Furthermore, in vivo depletion of CD4+ lymphocytes has been reported with this antibody.
Development References (9)
-
Arima T, Goss JA, Walp LA, Flye MW. Administration of anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody with intrathymic injection of alloantigen results in rat cardiac allograft tolerance. Surgery. 1995; 118(2):265-273. (Clone-specific: Depletion). View Reference
-
Bañuls MP, Alvarez A, Ferrero I, Zapata A, Ardavin C. Cell-surface marker analysis of rat thymic dendritic cells. Immunology. 1993; 79(2):298-304. (Biology). View Reference
-
Bierer BE, Sleckman BP, Ratnofsky SE, Burakoff SJ. The biologic roles of CD2, CD4, and CD8 in T-cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989; 7:579-599. (Biology). View Reference
-
Janeway CA Jr. The T cell receptor as a multicomponent signalling machine: CD4/CD8 coreceptors and CD45 in T cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992; 10:645-674. (Biology). View Reference
-
Jefferies WA, Green JR, Williams AF. Authentic T helper CD4 (W3/25) antigen on rat peritoneal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1985; 162(1):117-127. (Immunogen: Flow cytometry, Functional assay, Immunoaffinity chromatography, Immunoprecipitation, Inhibition). View Reference
-
Liu L, Zhang M, Jenkins C, MacPherson GG. Dendritic cell heterogeneity in vivo: two functionally different dendritic cell populations in rat intestinal lymph can be distinguished by CD4 expression. J Immunol. 1998; 161(3):1146-1155. (Biology). View Reference
-
Stitz L, Sobbe M, Bilzer T. Preventive effects of early anti-CD4 or anti-CD8 treatment on Borna disease in rats. J Virol. 1992; 66(6):3316-3323. (Clone-specific: Blocking). View Reference
-
Suzuki H, Hara MH, Miyahara T, et al. Microchimerism and graft acceptance: IV. Cardiac allograft acceptance following anti-adhesion molecule antibody therapy. Transplant Proc. 1996; 28(4):2058-2060. (Clone-specific: Blocking). View Reference
-
Yin D, Fathman CG. Tissue-specific effects of anti-CD4 therapy in induction of allograft unresponsiveness in high and low responder . Transpl Immunol. 1995; 3(3):258-264. (Clone-specific: Blocking). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.