Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
For optimal and reproducible results, BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer should be used anytime two or more BD Horizon Brilliant dyes (including BD OptiBuild Brilliant reagents) are used in the same experiment. Fluorescent dye interactions may cause staining artifacts which may affect data interpretation. The BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer was designed to minimize these interactions. More information can be found in the Technical Data Sheet of the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer (Cat. No. 563794).
Product Notices
- This antibody was developed for use in flow cytometry.
- The production process underwent stringent testing and validation to assure that it generates a high-quality conjugate with consistent performance and specific binding activity. However, verification testing has not been performed on all conjugate lots.
- Researchers should determine the optimal concentration of this reagent for their individual applications.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
Companion Products
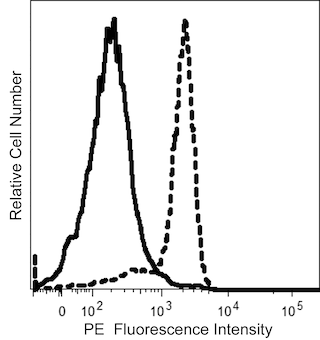





The GHI/61 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to human CD163. CD163 is also known as Scavenger receptor cysteine-rich type 1 protein M130 (M130), Hemoglobin scavenger receptor and Macrophage-associated antigen. CD163 is a 110-130 kDa transmembrane glycoprotein. CD163 is a monocyte/macrophage-restricted antigen expressed on the majority of tissue macrophages and peripheral blood monocytes. CD163 belongs to the scavenger receptor superfamily. Its expression on monocytes is upregulated upon cellular activation. CD163 expression reportedly changes on monocytes and macrophages as these cells differentiate. This finding suggests a role for this molecule in the differentiation and/or regulation of monocyte and macrophage function. CD163 may play a role in the clearance and endocytosis of hemoglobin and haptoglobin complexes by macrophages.
It has been reported (Maniecki et al., 2011) that the presence of calcium impacts the binding affinity of clone GHI/61 to CD163. There is a variation in detecting CD163 positive monocytes when the cells are prepared with different anticoagulants, where heparin was observed to have the highest inhibitory effect on clone GHI/61.
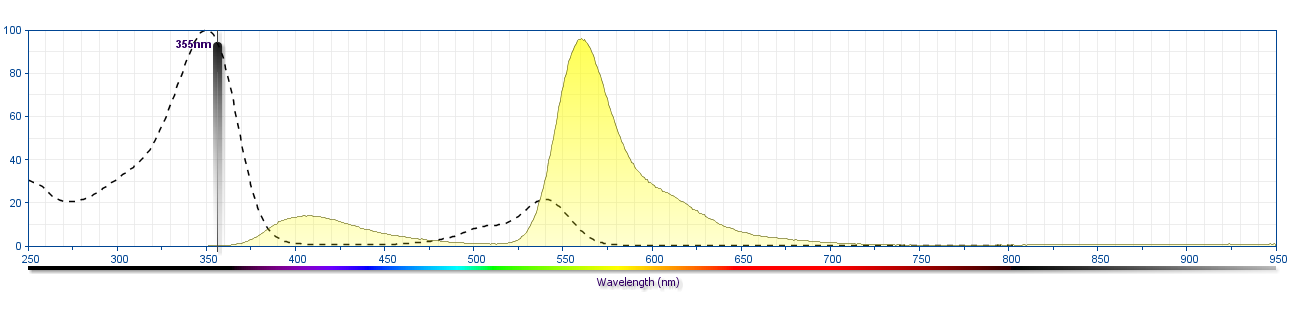
The antibody was conjugated to BD Horizon™ BUV563 which is part of the BD Horizon Brilliant™ Ultraviolet family of dyes. This dye is a tandem fluorochrome of BD Horizon BUV395 which has an Ex Max of 348 nm and an acceptor dye. The tandem has an Em Max at 563 nm. BD Horizon BUV563 can be excited by the 355 nm ultraviolet laser. On instruments with a 561 nm Yellow-Green laser, the recommended bandpass filter is 585/15 nm with a 535 nm long pass to minimize laser light leakage. When BD Horizon BUV563 is used with an instrument that does not have a 561 nm laser, a 560/40 nm filter with a 535 nm long pass may be more optimal. Due to the excitation and emission characteristics of the acceptor dye, there may be spillover into the PE and PE-CF594 detectors. However, the spillover can be corrected through compensation as with any other dye combination.
Development References (5)
-
Kishimoto T. Tadamitsu Kishimoto .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing VI : white cell differentiation antigens : proceedings of the sixth international workshop and conference held in Kobe, Japan, 10-14 November 1996. New York: Garland Pub.; 1997.
-
Law SK, Micklem KJ, Shaw JM. A new macrophage differentiation antigen which is a member of the scavenger receptor superfamily. Eur J Immunol. 1993; 23(9):2320-2325. (Biology). View Reference
-
Maniecki MB, Etzerodt A, Moestrup S, Møller J, Graversen J. Comparative assessment of the recognition of domain-specific CD163 monoclonal antibodies in human monocytes explains wide discrepancy in reported levels of cellular surface CD163 expression. Immunobiology. 2011; 216(8):882-890. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, Western blot). View Reference
-
Pulford K, Micklem K, McCarthy S, Cordell J, Jones M, Mason DY. A monocyte/macrophage antigen recognized by the four antibodies GHI/61, Ber-MAC3, Ki-M8 and SM4. Immunology. 1992; 75(4):588-595. (Immunogen: Blocking, Flow cytometry, Immunoaffinity chromatography, Immunohistochemistry, Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Pulford K, Micklem K, Thomas J, Jones M, Mason DY. A 72-kD B cell-associated surface glycoprotein expressed at high levels in hairy cell leukaemia and plasma cell neoplasms. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991; 85(3):429-435. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical Data Sheets before using this product as described.
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.