Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




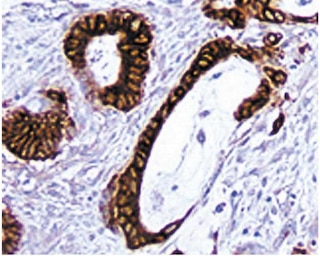
Immunohistochemical staining of CD40. Frozen sections of normal mouse thymus was reacted with the 3/23 antibody. B lymphocytes and dendritic cells can be identified by the brown labeling of their cell surface membranes. Amplification 20x.


BD Pharmingen™ Purified Rat Anti-Mouse CD40

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
Immunohistochemistry: Clone 3/23 is recommended to test for immunohistochemical staining on acetone-fixed frozen sections or zinc-fixed paraffin sections of mouse spleen or thymus. IHC of formalin-fixed paraffin embedded sections is not recommended. The isotype control recommended for use with this antibody is purified rat IgG2a (Cat. No. 559073). For optimal indirect immunohistochemical staining, the 3/23 antibody should be titrated (1:10 to 1:50 dilution) and visualized via a three-step staining procedure in combination with biotinylated polyclonal anti-rat Ig (multiple adsorbed) (Cat. No. 559286) as the secondary antibody and streptavidin-HRP (Cat. No. 550946) together with the DAB detection system (Cat. No. 550880). More conveniently, the anti-rat Ig HRP detection kit (Cat. No. 551013) can be used which contains the biotinylated secondary antibody, the antibody diluent, streptavidin-HRP and a DAB substrate for use in the staining procedure.
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- This antibody has been developed for the immunohistochemistry application. However, a routine immunohistochemistry test is not performed on every lot. Researchers are encouraged to titrate the reagent for optimal performance.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products




The 3/23 clone monoclonal antibody specifically binds to CD40, a 40-50 kDa glycoprotein expressed on B lymphocytes and other antigen-presenting cells. CD40 has been reported to be transiently expressed on activated CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and in some mouse strains, the 3/23 mAb has been reported to react with 5-10% of T lymphocytes in adult mouse, but not neonatal, spleen. CD40 plays a key role in B-cell growth and differentiation where interactions of CD40 with its ligand, CD154, are involved in the initiation, effector, and memory stages of cell-mediated immune responses. In addition, CD40 has been reported to be involved with the triggering of NK cells and NK-T cells. Ligation of CD40 with the 3/23 antibody has been reported to induce splenic B cells to express the costimulatory molecule CD86 (B7-2). In addition, although the 3/23 antibody by itself is a weak B-cell mitogen, it has been reported to synergize markedly with mitogenic anti-IgM, anti-IgD mAb or IL-4 to promote B-cell proliferation.
Development References (5)
-
Hasbold J, Johnson-Leger C, Atkins CJ, Clark EA, Klaus GG. Properties of mouse CD40: cellular distribution of CD40 and B cell activation by monoclonal anti-mouse CD40 antibodies. Eur J Immunol. 1994; 24(8):1835-1842. (Immunogen: Activation, (Co)-stimulation). View Reference
-
Hasbold J, Klaus GG. B cells from CBA/N mice do not proliferate following ligation of CD40. Eur J Immunol. 1994; 24(1):152-157. (Biology: Activation, (Co)-stimulation). View Reference
-
Klaus GG, Holman M, Hasbold J. Properties of mouse CD40: the role of homotypic adhesion in the activation of B cells via CD40. Eur J Immunol. 1994; 24(11):2714-2719. (Biology). View Reference
-
Noelle RJ, Ledbetter JA, Aruffo A. CD40 and its ligand, an essential ligand-receptor pair for thymus-dependent B-cell activation. Immunol Today. 1992; 13(11):431-433. (Biology). View Reference
-
Parry SL, Hasbold J, Holman M, Klaus GG. Hypercross-linking surface IgM or IgD receptors on mature B cells induces apoptosis that is reversed by costimulation with IL-4 and anti-CD40. J Immunol. 1994; 152(6):2821-2829. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.