-
Your selected country is
Middle East / Africa
- Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
BD® CompBeads can be used as surrogates to assess fluorescence spillover (compensation). When fluorochrome conjugated antibodies are bound to BD® CompBeads, they have spectral properties very similar to cells. However, for some fluorochromes there can be small differences in spectral emissions compared to cells, resulting in spillover values that differ when compared to biological controls. It is strongly recommended that when using a reagent for the first time, users compare the spillover on cells and BD® CompBeads to ensure that BD® CompBeads are appropriate for your specific cellular application.
Product Notices
- Researchers should determine the optimal concentration of this reagent for their individual applications.
- The production process underwent stringent testing and validation to assure that it generates a high-quality conjugate with consistent performance and specific binding activity. However, verification testing has not been performed on all conjugate lots.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- CF™ is a trademark of Biotium, Inc.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
Companion Products




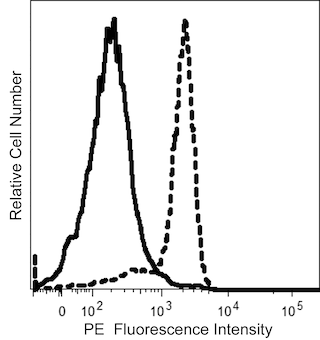

The ITEM-4 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to the TWEAK Receptor (TWEAK-R/TWEAKR), which is also known as CD266, or Fibroblast growth factor inducible 14 (FGF-inducible 14, FN14). The TWEAK Receptor is a ~14 kDa type I transmembrane protein that is the 12A family member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily (TNFRSF12A). It is expressed at low levels in a variety of tissues including, heart, placenta, lung, muscle, and pancreas. TWEAK Receptors are relatively highly expressed on HUVEC cells and certain tumor cell lines. TWEAK-induced TWEAK Receptor-mediated signaling can play roles in inflammation, the induction of apoptosis in certain cell types, the proliferation and migration of endothelial cells, and can promote angiogenesis within healthy and diseased tissues, eg, tumors. The ITEM-4 antibody can induce the death of certain TWEAK-sensitive tumor target cell lines. The TWEAK Receptor binds TWEAK (CD255) and can signal intracellularly by interactions with TRAF1, 2, and 3 cytoplasmic proteins leading to NF-κB activation. The ITEM-4 antibody reportedly crossreacts strongly with mouse CD266 as demonstrated by flow cytometric analysis and functional assays.
Development References (8)
-
Brown SA, Richards CM, Hanscom HN, Feng SL, Winkles JA. The Fn14 cytoplasmic tail binds tumour-necrosis-factor-receptor-associated factors 1, 2, 3 and 5 and mediates nuclear factor-kappaB activation. Biochem J. 2003; 371(Pt 2):395-403. (Biology). View Reference
-
Harada N, Nakayama M, Nakano H, Fukuchi Y, Yagita H, Okumura K. Pro-inflammatory effect of TWEAK/Fn14 interaction on human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002; 299(3):488-493. (Biology). View Reference
-
Moreno JA1, Muñoz-García B, Martín-Ventura JL, et al. The CD163-expressing macrophages recognize and internalize TWEAK: potential consequences in atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 2009; 207(1):103-110. (Clone-specific: Western blot). View Reference
-
Nakayama M, Harada N, Okumura K, Yagita H. Characterization of murine TWEAK and its receptor (Fn14) by monoclonal antibodies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003; 306(4):819-825. (Clone-specific: Cytotoxicity, Flow cytometry, Functional assay). View Reference
-
Nakayama M, Ishidoh K, Kojima Y, et al. Fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 mediates multiple pathways of TWEAK-induced cell death. J Immunol. 2003; 170(1):341-348. (Immunogen: Activation, Apoptosis, Cytotoxicity, Flow cytometry, Functional assay, Stimulation). View Reference
-
Nakayama M, K. Ishidoh, N. Kayagaki, et al. Multiple pathways of TWEAK-induced cell death. J Immunol. 2002; 168(2):734-743. (Biology). View Reference
-
Roos C, Wicovsky A, Müller N, et al. Soluble and transmembrane TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis differentially activate the classical and noncanonical NF-kappa B pathway. J Immunol. 2010; 185(3):1593-1605. (Clone-specific: Blocking, Functional assay). View Reference
-
Wiley SR, Cassiano L, Lofton T, et al. A novel TNF receptor family member binds TWEAK and is implicated in angiogenesis. Immunity. 2001; 15(5):837-846. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.