-
Your selected country is
Middle East / Africa
- Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?
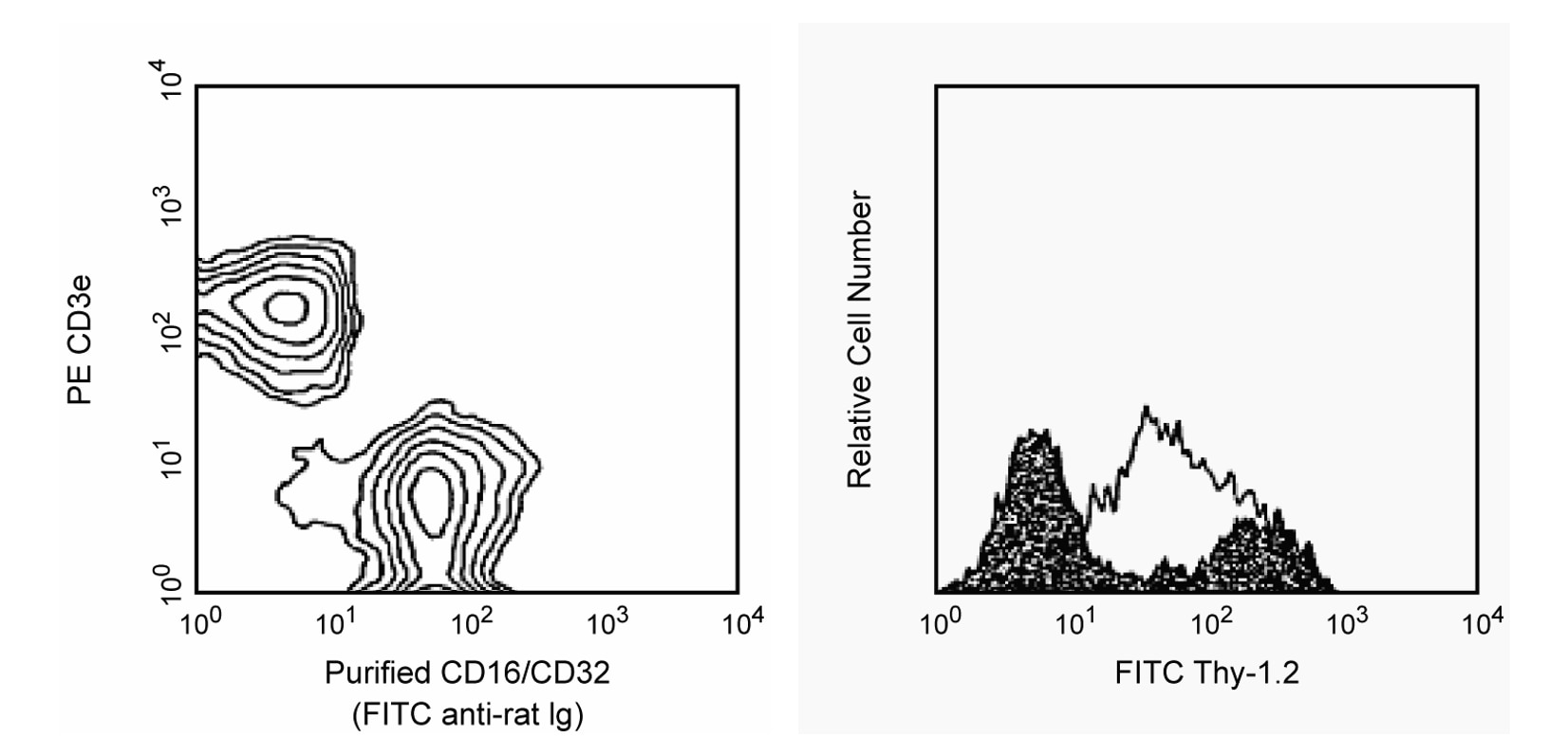



Two color analysis of the expression of CD16/CD32 on mouse spleen cells and demonstration of FCγR-mediated non-specific staining. Left: BALB/c splenocytes were simultaneously stained with PE-conjugated anti-mouse CD3e mAb 145-2C11 (Cat. No. 553063/553064) and purified 2.4G2 mAb. The staining by 2.4G2 antibody was detected with FITC-conjugated mouse anti-rat lg, κ chain mAb MRK-1 (Cat. No. 553872). Right: BALB/c splenocytes were stained with FITC-conjugated rat anti-mouse CD90.2 (Thy-1.2) mAb 53-2.1 (Cat. No. 553003/553004) in the presence of purified 2.4G2 mAb (filled histogram) and without 2.4G2 mAb (open histogram). Flow cytometry was performed on a BD FACScan™ flow cytometry system.


BD Pharmingen™ Purified Rat Anti-Mouse CD16/CD32 (Mouse BD Fc Block™)

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
To specifically stain cells bearing FcγII and FcγIII receptors for flow cytometric analysis: Incubate cell suspension with this antibody (≤ 1 μg/million cells) followed by an appropriate fluorochrome-conjugated second-step reagent.
To reduce Fc receptor-mediated binding by antibodies of interest or Fc receptor-mediated binding by PE-CY5 tandem dye conjugates to FcγII and FcγIII receptor-bearing mouse cells for flow cytometric analysis:
1. Preincubate cell suspension with Mouse BD Fc Block™ purified anti-mouse CD16/CD32 mAb 2.4G2 (eg, ≤ 1 μg/million cells in 100 μl) at 4˚C for 5 minutes.
2. Add antibody of interest directly to preincubated cells in the presence of Mouse BD Fc Block™ (ie, Mouse BD Fc Block™ need not be washed off before staining cells).
3. If anti-Ig second-step is necessary, a reagent must be chosen which will not bind to Mouse BD Fc Block™ (eg, rat IgG2b, κ).
For additional information on using Mouse BD Fc Block™, refer to the "Reducing non-specific staining with Fc Block" section of our Flow Cytometry protocols at our website: https://www.bdbiosciences.com/en-us/resources/protocols/flow-cytometry
Product Notices
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Sodium azide is a reversible inhibitor of oxidative metabolism; therefore, antibody preparations containing this preservative agent must not be used in cell cultures nor injected into animals. Sodium azide may be removed by washing stained cells or plate-bound antibody or dialyzing soluble antibody in sodium azide-free buffer. Since endotoxin may also affect the results of functional studies, we recommend the NA/LE (No Azide/Low Endotoxin) antibody format, if available, for in vitro and in vivo use.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
The 2.4G2 antibody specifically recognizes a common nonpolymorphic epitope on the extracellular domains of the mouse FcγIII (CD16) and FcγII (CD32) Receptors. It has also been reported to bind the FcγI receptor (CD64) via its Fc domain. 2.4G2 mAb blocks non-antigen-specific binding of immunoglobulins to the FcγIII and FcγII, and possibly FcγI, Receptors in vitro and in vivo. CD16 and/or CD32 are expressed on natural killer cells, monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells (at low levels), Kupffer cells, granulocytes, mast cells, B lymphocytes, immature thymocytes, and some activated mature T lymphocytes.
Development References (19)
-
Araujo-Jorge T, Rivera MT, el Bouhdidi A, Daeron M, Carlier Y. An Fc gamma RII-, Fc gamma RIII-specific monoclonal antibody (2.4G2) decreases acute Trypanosoma cruzi infection in mice. Infect Immun. 1993; 61(11):4925-4928. (Clone-specific: Blocking). View Reference
-
Benhamou M, Bonnerot C, Fridman WH, Daeron M. Molecular heterogeneity of murine mast cell Fc gamma receptors. J Immunol. 1990; 144(8):3071-3077. (Clone-specific: Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Jensen WA, Marschner S, Ott VL, Cambier JC. FcgammaRIIB-mediated inhibition of T-cell receptor signal transduction involves the phosphorylation of SH2-containing inositol 5-phosphatase (SHIP), dephosphorylation of the linker of activated T-cells (LAT) and inhibition of calcium mobilization. Biochem Soc Trans. 2001; 29(6):840-846. (Clone-specific: Blocking). View Reference
-
Kaji K, Takeshita S, Miyake K, Takai T, Kudo A. Functional association of CD9 with the Fc gamma receptors in macrophages. J Immunol. 2001; 166(5):3256-3265. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation). View Reference
-
Katz HR, Arm JP, Benson AC, Austen KF. Maturation-related changes in the expression of Fc gamma RII and Fc gamma RIII on mouse mast cells derived in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol. 1990; 145(10):3412-3417. (Clone-specific: Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Kurlander RJ, Ellison DM, Hall J. The blockade of Fc receptor-mediated clearance of immune complexes in vivo by a monoclonal antibody (2.4G2) directed against Fc receptors on murine leukocytes. J Immunol. 1984; 133(2):855-862. (Clone-specific: Blocking). View Reference
-
Latour S, Bonnerot C, Fridman WH, Daeron M. Induction of tumor necrosis factor-alpha production by mast cells via Fc gamma R. Role of the Fc gamma RIII gamma subunit. J Immunol. 1992; 149(6):2155-2162. (Clone-specific: (Co)-stimulation). View Reference
-
Lewis VA, Koch T, Plutner H, Mellman I. A complementary DNA clone for a macrophage-lymphocyte Fc receptor. Nature. 1986; 324(6095):372-375. (Clone-specific). View Reference
-
Maeda K, Burton GF, Padgett DA, et al. Murine follicular dendritic cells and low affinity Fc receptors for IgE (Fc epsilon RII). J Immunol. 1992; 148(8):2340-2347. (Clone-specific: Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Mellman IS, Unkeless JC. Purificaton of a functional mouse Fc receptor through the use of a monoclonal antibody. J Exp Med. 1980; 152(4):1048-1069. (Clone-specific: Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Perussia B, Tutt MM, Qiu WQ, et al. Murine natural killer cells express functional Fc gamma receptor II encoded by the Fc gamma R alpha gene. J Exp Med. 1989; 170(1):73-86. (Clone-specific). View Reference
-
Ravetch JV, Luster AD, Weinshank R, et al. Structural heterogeneity and functional domains of murine immunoglobulin G Fc receptors. Science. 1986; 234(4777):718-725. (Clone-specific). View Reference
-
Rodewald HR, Awad K, Moingeon P, et al. Fc gamma RII/III and CD2 expression mark distinct subpopulations of immature CD4-CD8- murine thymocytes: in vivo developmental kinetics and T cell receptor beta chain rearrangement status. J Exp Med. 1993; 177(4):1079-1092. (Biology). View Reference
-
Rodewald HR, Moingeon P, Lucich JL, Dosiou C, Lopez P, Reinherz EL. A population of early fetal thymocytes expressing Fc gamma RII/III contains precursors of T lymphocytes and natural killer cells. Cell. 1992; 69(1):139-150. (Clone-specific: Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Takezawa R, Watanabe Y, Akaike T. Direct evidence of macrophage differentiation from bone marrow cells in the liver: a possible origin of Kupffer cells. J Biochem (Tokyo). 1995; 118(6):1175-1183. (Clone-specific). View Reference
-
Titus JA, Finkelman FD, Stephany DA, Jones JF, Segal DM. Quantitative analysis of Fc gamma receptors on murine spleen cell populations by using dual parameter flow cytometry. J Immunol. 1984; 133(2):556-561. (Biology). View Reference
-
Unkeless JC. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody directed against mouse macrophage and lymphocyte Fc receptors. J Exp Med. 1979; 150(3):580-596. (Immunogen). View Reference
-
Vremec D, Zorbas M, Scollay R, et al. The surface phenotype of dendritic cells purified from mouse thymus and spleen: investigation of the CD8 expression by a subpopulation of dendritic cells. J Exp Med. 1992; 176(1):47-58. (Clone-specific). View Reference
-
Witmer MD, Steinman RM. The anatomy of peripheral lymphoid organs with emphasis on accessory cells: light-microscopic immunocytochemical studies of mouse spleen, lymph node, and Peyer's patch. Am J Anat. 1984; 170(3):465-481. (Clone-specific: Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.