-
Your selected country is
Middle East / Africa
- Change country/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




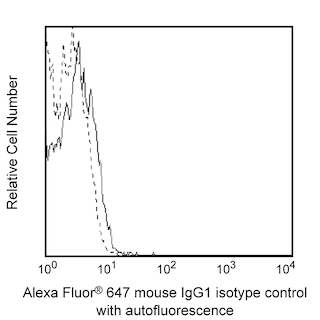
Flow cytometric analysis of CD271 expression on REH cell line. REH cells were stained with either Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse anti-Human CD271 (Cat. No. 560877/560326; solid line histogram) or Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse IgG1 κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 557714; dashed line histogram). Fluorescence histograms depicting CD271 (or Ig isotype control) expression were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable REH cells. Flow cytometry was performed on a BD™ LSR II flow cytometry system.


BD Pharmingen™ Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse anti-Human CD271

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test).
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Alexa Fluor® 647 fluorochrome emission is collected at the same instrument settings as for allophycocyanin (APC).
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- The Alexa Fluor®, Pacific Blue™, and Cascade Blue® dye antibody conjugates in this product are sold under license from Molecular Probes, Inc. for research use only, excluding use in combination with microarrays, or as analyte specific reagents. The Alexa Fluor® dyes (except for Alexa Fluor® 430), Pacific Blue™ dye, and Cascade Blue® dye are covered by pending and issued patents.
- Alexa Fluor® is a registered trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, OR.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products


The C40-1457 monoclonal antibody specifically recognizes CD271 that is also known as the nerve growth factor receptor (NGFR). CD271 is 75 kDa type I transmembrane glycoprotein likewise known as TNFRSF16 that belongs to the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) superfamily. CD271 has been found localized to neuronal axons, Schwann cells, and perineural cells of peripheral nerves. It is also expressed by some epithelial, mesenchymal and lymphoid tissues. NGFR is the receptor for nerve growth factor (NGF), a polypeptide that is essential for normal development of the nervous system. NGF promotes survival and differentiation of sympathetic and sensory neurons during embryological development of the peripheral nervous system. NGF binds to two distinctive surface receptors, the p/140[prototrk] and p75[NGFR]. High affinity binding of NGF requires that both receptor molecules be expressed. NGFR is expressed on human and rat lymphocytes. A subset of lymphoid cells in the spleen, lymph nodes, and follicular dendritic cells in germinal centers of reactive lymph nodes were found to express CD271. It has been reported that NGFR interaction with its ligand, NGF, may play a role in immunoregulation. NGF may also function as a B-cell growth factor.
Development References (7)
-
Brodie C, Gelfand EW. Functional nerve growth factor receptors on human B lymphocytes. Interaction with IL-2. J Immunol. 1992; 148(11):3492-3497. (Biology). View Reference
-
Chesa PG, Rettig WJ, Thomson TM, Old LJ, Melamed MR. Immunohistochemical analysis of nerve growth factor receptor expression in normal and malignant human tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 1988; 36(4):383-389. (Biology). View Reference
-
Guesdon JL, Ternynck T, Avrameas S. The use of avidin-biotin interaction in immunoenzymatic techniques. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979; 27(8):1131-1139. (Biology). View Reference
-
Hempstead BL, Martin-Zanca D, Kaplan DR, Parada LF, Chao MV. High-affinity NGF binding requires coexpression of the trk proto-oncogene and the low-affinity NGF receptor. Nature. 1991; 350(6320):678-683. (Biology). View Reference
-
Holling TM, Bergevoet MW, Wilson L, et al. A Role for EZH2 in Silencing of IFN-γ Inducible MHC2TA Transcription in Uveal Melanoma. J Immunol. 2007; 179(8):5317-5325. (Biology). View Reference
-
Kanellopoulou C, Muljo SA, Dimitrov SD, et al. X chromosome inactivation in the absence of Dicer.. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009; 106(4):1122-1127. (Biology). View Reference
-
Thompson SJ, Schatteman GC, Gown AM, Bothwell M. A monoclonal antibody against nerve growth factor receptor. Immunohistochemical analysis of normal and neoplastic human tissue. Am J Clin Pathol. 1989; 92(4):415-423. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.