Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




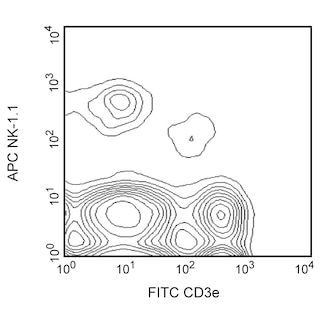
Expression of CD94 on mouse splenic NK cells. C57BL/6 splenocytes were preincubated with Mouse BD Fc Block™ purified anti-mouse CD16/CD32 mAb 2.4G2 (Cat. no. 553141/553142), then simultaneously stained with biotinconjugated rat IgG2a isotype control mAb R35-95 (Cat. no. 553928, Left panel) or biotinylated mAb 18d3 (Right panel) and APC-conjugated anti- mouse NK-1.1 mAb PK136 (Cat. no. 550627), followed by Streptavidin-PE (Cat. no. 554061). The CD94[dim] and CD94[bright] subpopulations of NK cells are observed in all strains tested, although the relative proportions of the two subsets may vary. Flow cytometry was performed on a BD FACSCalibur™ flow cytometry system.


BD Pharmingen™ Biotin Rat Anti-Mouse CD94

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
We have found that the use of Mouse BD Fc Block, purified anti-mouse CD16/CD32 mAb 2.4G2 (Cat. no. 553141/553142) reduces the non-specific staining of non-NK cells by this biotin conjugate. This antibody is not useful for immunohistochemical staining of frozen sections.
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
Companion Products


.png?imwidth=320)
The 18d3 monoclonal antibody specifically recognizes CD94 on all NK cells, NK1.1- or DX5-positive T lymphocytes (NK-T cells), and a subset of CD8-positive T lymphocytes in most strains tested (eg, A/J, AKR/J, BALB/c, C3H/He, C57BL/6, CBA/J, DBA/1, FVB/N, 129/Sv, NOD, SWR, and most DBA/2 substrains, but not DBA/2J). DBA/2J mice do not express CD94.3 CD94 is also expressed on CD8+ T lymphocytes activated in vivo. CD94 is a type-II transmembrane protein with an extracellular lectin-like domain and a short cytoplasmic tail which is not believed to have any signalling function. Heterodimers of CD94 with NKG2A, NKG2C, or NKG2E recognize Qa-1 (a non-classical MHC class I antigen) presenting the Qdm peptide. Studies on CD94/NKG2 heterodimers on human NK cells have demonstrated that the NKG2 components mediate signal transduction for the receptor, NKG2A being inhibitory and NKG2C being stimulatory. Similarly, the mouse NKG2A molecule contains two intracytoplasmic sequences which resemble the ITIM (Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-based Inhibitory Motif) consensus sequence. CD94/NKG2 receptors appear on fetal NK cells before the Ly- 49 MHC class I receptors, suggesting that CD94/NKG2 receptors and their ligand, Qa-1, may play a role in maintenance of self-tolerance in developing NK cells.
Development References (8)
-
Ho EL, Heusel JW, Brown MG. Murine Nkg2d and Cd94 are clustered within the natural killer complex and are expressed independently in natural killer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998; 95(11):6320-6325. (Biology). View Reference
-
McMahon CW, Zajac AJ, Jamieson AM. Viral and bacterial infections induce expression of multiple NK cell receptors in responding CD8(+) T cells. J Immunol. 2002; 169(3):1444-1452. (Biology). View Reference
-
Sivakumar PV, Gunturi A, Salcedo M, et al. Cutting edge: expression of functional CD94/NKG2A inhibitory receptors on fetal NK1.1+Ly-49- cells: a possible mechanism of tolerance during NK cell development. J Immunol. 1999; 162(12):6976-6980. (Biology). View Reference
-
Toomey JA, Salcedo M, Cotterill LA. Stochastic acquisition of Qa1 receptors during the development of fetal NK cells in vitro accounts in part but not in whole for the ability of these cells to distinguish between class I-sufficient and class I-deficient targets. J Immunol. 1999; 163(6):3176-3184. (Biology). View Reference
-
Vance RE, Jamieson AM, Cado D, Raulet DH. Implications of CD94 deficiency and monoallelic NKG2A expression for natural killer cell development and repertoire formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002; 99(2):868-873. (Biology). View Reference
-
Vance RE, Jamieson AM, Raulet DH. Recognition of the class Ib molecule Qa-1(b) by putative activating receptors CD94/NKG2C and CD94/NKG2E on mouse natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 1999; 190(12):1801-1812. (Immunogen). View Reference
-
Vance RE, Kraft JR, Altman JD, Jensen PE, Raulet DH. Mouse CD94/NKG2A is a natural killer cell receptor for the nonclassical major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecule Qa-1(b). J Exp Med. 1998; 188(10):1841-1848. (Biology). View Reference
-
Yokoyama WM. Natural killer cell receptors . Curr Opin Immunol. 1998; 10:298-305. (Biology).
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.