Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




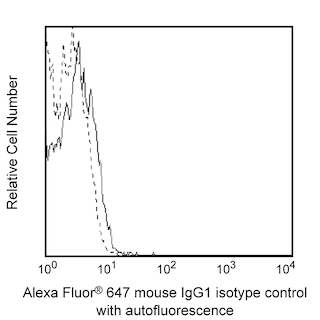
Flow cytometric analysis of Notch1 expression on stimulated human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Phytohemagglutinin-stimulated (3 days) peripheral blood mononuclear cells were stained with either Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse IgG1, κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 557714; dashed line histogram) or Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse Anti-Human Notch1 antibody (Cat. No. 564782; solid line histogram). The fluorescence histogram showing Notch1 expression (or Ig Isotype control staining) was derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable lymphocytes. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using a BD™ LSR II Flow Cytometer System.


BD Pharmingen™ Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse Anti-Human Notch1

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test).
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Alexa Fluor® 647 fluorochrome emission is collected at the same instrument settings as for allophycocyanin (APC).
- Alexa Fluor® is a registered trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, OR.
- The Alexa Fluor®, Pacific Blue™, and Cascade Blue® dye antibody conjugates in this product are sold under license from Molecular Probes, Inc. for research use only, excluding use in combination with microarrays, or as analyte specific reagents. The Alexa Fluor® dyes (except for Alexa Fluor® 430), Pacific Blue™ dye, and Cascade Blue® dye are covered by pending and issued patents.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products


The MHN1-519 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to an extracellular domain of human Notch1. Notch1 is a type 1 transmembrane glycoprotein receptor and member of the Notch family that includes Notch1-Notch4. Notch1 is cleaved in the Golgi and presents as a cell surface heterodimeric receptor. The Notch1 receptor can bind to several membrane-bound ligands including Jagged1, Jagged2, Delta1 and Delta4. Upon ligand binding, Notch1 undergoes proteolytic cleavage that results in the release of the Notch intracellular domain, NICD. NICD translocates to the nucleus where it forms a transcriptional activator complex with various transcriptional factors. These multimeric complexes either positively or negatively regulate the expression of multiple genes including those that orchestrate many facets of embryonic development and the subsequent functioning of multiple organ systems such as the immune, cardiovascular and nervous systems. Within the immune system, Notch signaling significantly affects the development, proliferation, differentiation and survival of numerous cell types including thymocytes and subsets of T and B lymphocytes and dendritic cells. In altered forms, Notch1 has been associated with certain cardiovascular diseases and with some lymphocyte neoplasms.
Development References (6)
-
Auderset F, Coutaz M, Tacchini-Cottier F. The role of Notch in the differentiation of CD4(+) T helper cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2012; 360:115-134. (Biology). View Reference
-
Chiba S. Notch signaling in stem cell systems. Stem Cells. 2006; 24(11):2437-2447. (Biology). View Reference
-
Ellisen LW, Bird J, West DC, et al. TAN-1, the human homolog of the Drosophila notch gene, is broken by chromosomal translocations in T lymphoblastic neoplasms. Cell. 1991; 66(4):649-661. (Biology). View Reference
-
Haraguchi K, Suzuki T, Koyama N et al. Notch activation induces the generation of functional NK cells from human cord blood CD34-positive cells devoid of IL-15. J Immunol. 2009; 182(10):6168-6178. (Immunogen: Blocking, ELISA, Flow cytometry, Inhibition). View Reference
-
Milner LA, Kopan R, Martin DI, Bernstein ID. A human homologue of the Drosophila developmental gene, Notch, is expressed in CD34+ hematopoietic precursors. Blood. 1994; 83(8):2057-2062. (Biology). View Reference
-
Yamanda S, Ebihara S, Asada M, et al. Role of ephrinB2 in nonproductive angiogenesis induced by Delta-like 4 blockade. Blood. 2009; 113(15):3631-3639. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.