Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?
BD Pharmingen™ Biotin Mouse Lineage Panel
(RUO)



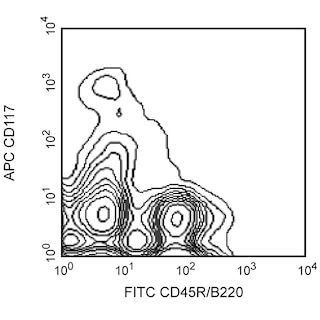
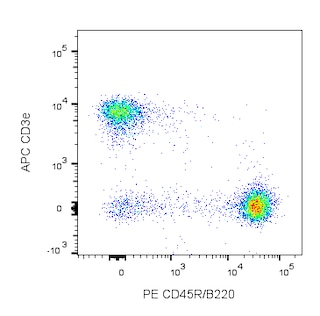
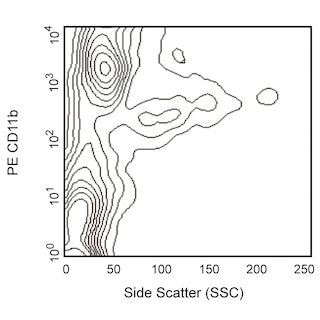
Depletion of lineage-committed cells from mouse bone marrow. BALB/c bone-marrow cells were labeled with BD™ Mouse Biotin Lineage Panel (Cat. No. 559971) and BD™ IMag Streptavidin Particles Plus - MSC (Cat. No. 557812, at 10 µl per 1 x 10^7 total cells). The labeled cells were then separated over a magnetic separation column designed for depletions. To demonstrate the efficiency of the depletion, unmanipulated bone-marrow cells and the lineage-negative fraction were stained with APC Rat Anti-Mouse CD117 (Cat. No. 553356) to detect hematopoietic progenitors, and with PE Rat Anti-Mouse TER-119/Erythroid Cells (Cat. No. 553673), CD45R/B220 (Cat. No. 553089/553090), and CD11b (Cat. No. 557397/553311) to detect lineage-committed cells. The lineage-negative fraction contains a greatly increased proportion of CD117+ cells and less than 5% of lineage-positive contaminants.


BD Pharmingen™ Biotin Mouse Lineage Panel

Biotin Mouse Lineage Panel
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Description
The Mouse Lineage Panel has been designed to react with cells from the major hematopoietic cell lineages, such as T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes, monocytes/macrophages, granulocytes, and erythrocytes. This Panel of five pre-diluted biotinylated antibodies is designed for the flow cytometric or immunomagnetic enrichment of hematopoietic progenitors from mouse bone marrow by depletion of cells committed to the T- and B-lymphocytic, myeloid (monocytic and granulocytic), and erythroid lineages. The Panel contains sufficient reagents to stain 10^9 bone marrow cells.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
A detailed Labeling Protocol follows. In summary, the biotin-conjugated antibodies simultaneously stain the lineage-committed cells according to their different specificities. Two microliters of each pre-diluted antibody conjugate is sufficient to stain 10^6 cells in 10 µl of staining buffer. Negative selection is then performed to enrich for uncommitted hematopoietic progenitors. The Mouse Lineage Panel can be used with similar efficiency with magnetic particle separation systems or flow cytometric cell sorting. For convenience, all antibodies have been optimized and pre-diluted to provide maximum efficiency for cell separation. The antibodies are provided in separate vials to assure product stability and to allow flexibility of separation protocols.
Hematopoietic progenitor cells separated after staining with the Mouse Lineage Panel have been tested in flow cytometric analysis, colony assays in methylcellulose, differential staining microscopy, immunoprecipitation, and western blot analysis. Use of the Mouse Lineage Panel does not alter the morphology, phenotype, or function of the separated cells in such assays.
LABELING PROTOCOL FOR ENRICHMENT OF HEMATOPOIETIC PROGENITOR CELLS
1. Prepare a single-cell suspension from bone marrow or other hematopoietic organ.
Notes:
-The femurs and tibiae of one adult mouse typically yield 20 -60 × 10^6 hematopoietic cells. Two mice will yield 0.5 -1.0 × 10^6 lineage-negative cells.
-The presence of red blood cells (RBCs) does not affect the staining with the Mouse Lineage Panel. We have observed that initial lysis of RBCs, using buffered ammonium chloride, reduces the effectiveness of the staining. Cell separation by gradient may be more appropriate. If RBC lysis is required for further analysis, it should be performed after the separation procedure.
-If the separated cells are to be used for culture or in vivo assays, aseptic conditions and sterile media/buffers must be used.
2. Count the cells, and resuspend them in cell-staining buffer [eg, BD Pharmingen™ Stain Buffer (FBS), Cat. No. 554656] at a final density of 100 × 10^6 cells per ml.
3. Set aside a sample of unstained cells (~5 × 10^6 cells) to be used in the flow cytometric analysis in Step 7.
4. Add the biotinylated antibodies from the Mouse Lineage Panel, using 2 µl of each prediluted antibody per 10^6 cells, and incubate on ice for 15 minutes.
5. Wash the stained cells twice, using the buffer recommended for the cell-separation system to be used.
6. Resuspend the cells at a final density of 20 - 100 × 10^6 cells per ml. The stained cells can be used in various cell-separation systems.
Notes:
-For each separation method, the recommended protocol described by the manufacturer should be followed.
-For flow cytometric cell sorting, the cells should be labeled with streptavidin (or avidin) bound to an appropriate fluorochrome.
-For immunomagnetic cell separation using a High Gradient Magnetic Separation Column, the cells should be labeled with the
appropriate streptavidin-bound magnetic particles (eg, BD™ IMag Streptavidin Particles Plus - MSC, Cat. No. 557811). For immunomagnetic cell separation using the BD IMag™ Cell Separation Magnet (Cat. No. 552311), we recommend the BD™ IMag Mouse Hematopoietic Progenitor Cell Enrichment Set - DM, Cat. No. 558451).
7. Samples of the total cell suspension, lineage-positive, and lineage-negative fractions should be analyzed by flow cytometry to evaluate the efficiency of the cell-separation procedure.
Note:
-The recommended concentration of the Mouse Lineage Panel antibodies is not saturating and allows the staining of the separated lineage-positive and lineage-negative fractions by the same monoclonal antibodies as used for the depletion.
Product Notices
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products

.png?imwidth=320)

| Description | Quantity/Size | Part Number | EntrezGene ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biotin Hamster anti-Mouse CD3e | 2 mL (1 ea) | 51-01082J | N/A |
| Biotin Rat anti-Mouse CD11b | 2 mL (1 ea) | 51-01712J | N/A |
| Biotin Rat anti-Mouse CD45R | 2 mL (1 ea) | 51-01122J | N/A |
| Biotin Rat anti-Mouse Ly-6G and Ly-6C | 2 mL (1 ea) | 51-01212J | N/A |
| Biotin Rat anti-Mouse TER-119/Erythroid cells | 2 mL (1 ea) | 51-09082J | N/A |
Development References (6)
-
Goodell MA, Rosenzweig M, Kim H, et al. Dye efflux studies suggest that hematopoietic stem cells expressing low or undetectable levels of CD34 antigen exist in multiple species. Nat Med. 1997; 3(12):1337-1345. (Biology). View Reference
-
Morrison SJ, Wandycz AM, Hemmati HD, Wright DE, Weissman IL. Identification of a lineage of multipotent hematopoietic progenitors. Development. 1997; 124(10):1929-1939. (Biology). View Reference
-
Osawa M, Tokumoto Y, Nakauchi H. Hematopoietic stem cells. In: Herzenberg LA, Weir DM, Blackwell C, ed. Weir's Handbook of Experimental Immunology, 5th Edition. Cambridge: Blackwell Science; 1996:66.1-66.5.
-
Sato T, Laver JH, Ogawa M. Reversible expression of CD34 by murine hematopoietic stem cells. Blood. 1999; 94(8):2548-2554. (Biology). View Reference
-
Spangrude GJ, Heimfeld S, Weissman IL. Purification and characterization of mouse hematopoietic stem cells. Science. 1988; 241(4861):58-62. (Biology). View Reference
-
Spangrude GJ, Scollay R. A simplified method for enrichment of mouse hematopoietic stem cells. Exp Hematol. 1990; 18(8):920-926. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.