Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


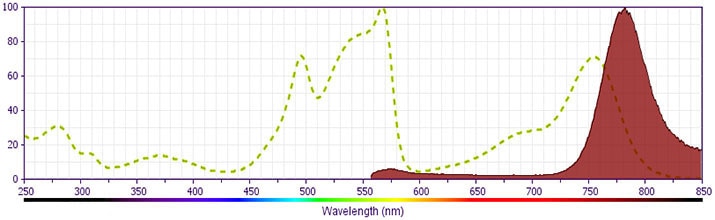
CD13 PE-Cy™7
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Store vials at 2°C–8°C. Conjugated forms should not be frozen. Protect from exposure to light. Each reagent is stable until the expiration date shown on the bottle label when stored as directed.
The CD13 antibody, clone L138 (also known as Leu-M7), is derived from the hybridization of Sp2/0 mouse myeloma cells with spleen cells isolated from BALB/c × C57BL/6 hybrid mice immunized with the KG-1a cell line. The CD13 antibody specifically binds to a glycosylated 150-kilodalton (kDa) type II integral membrane zinc-metalloprotease. The CD13 antigen is also known as aminopeptidase N, APN, ANPEP, and gp150.
Development References (9)
-
Ashmun RA, Holmes KV, Shapiro LH, et al. CD13 (aminopeptidase N) cluster workshop report. In: Schlossman SF. Stuart F. Schlossman .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing V : white cell differentiation antigens : proceedings of the fifth international workshop and conference held in Boston, USA, 3-7 November, 1993. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1995::771-775.
-
Bradstock KF, Favaloro EJ, Kabral A, Kerr A, Hughes WG, Musgrove E. Myeloid progenitor surface antigen identified by monoclonal antibody.. Br J Haematol. 1985; 61(1):11-20. (Biology). View Reference
-
Centers for Disease Control. Update: universal precautions for prevention of transmission of human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis B virus, and other bloodborne pathogens in healthcare settings. MMWR. 1988; 37:377-388. (Biology).
-
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2005. (Biology).
-
Howard MR, Thomas L, Reid MM. Variable detection of myeloid antigens in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia.. J Clin Pathol. 1994; 47(11):1006-9. (Biology). View Reference
-
Kirshenbaum AS, Goff JP, Semere T, Foster B, Scott LM, Metcalfe DD. Demonstration that human mast cells arise from a progenitor cell population that is CD34(+), c-kit(+), and expresses aminopeptidase N (CD13).. Blood. 1999; 94(7):2333-42. (Biology). View Reference
-
Mina-Osorio P, Winnicka B, O'Conor C, et al. CD13 is a novel mediator of monocytic/endothelial cell adhesion.. J Leukoc Biol. 2008; 84(2):448-59. (Biology). View Reference
-
Yeager CL, Ashmun RA, Williams RK, et al. Human aminopeptidase N is a receptor for human coronavirus 229E.. Nature. 1992; 357(6377):420-2. (Biology). View Reference
-
Zola H, Swart B, Nicholson I, Voss E. Leukocyte and Stromal Cell Molecules: The CD Markers. 2007. (Biology).
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.