-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
-
Training
- Flow Cytometry Basic Training
-
Product-Based Training
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- FACSDuet Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
-
Advanced Training
-
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
-
- FACSAria Product Based Training
- FACSMelody Product-Based Training
- FACSLyric Product-Based Training
- FACSCanto Product-Based Training
- LSRFortessa Product-Based Training
- FACSymphony Product-Based Training
- FACSDuet Product-Based Training
- HTS Product-Based Training
- BD FACSDiscover™ S8 Cell Sorter Product Training
- Singapore (English)
-
Change location/language
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current location site or be switched to your location?
BD Pharmingen™ Purified Mouse Anti-Human Cyclin F
Clone B74-2 (RUO)
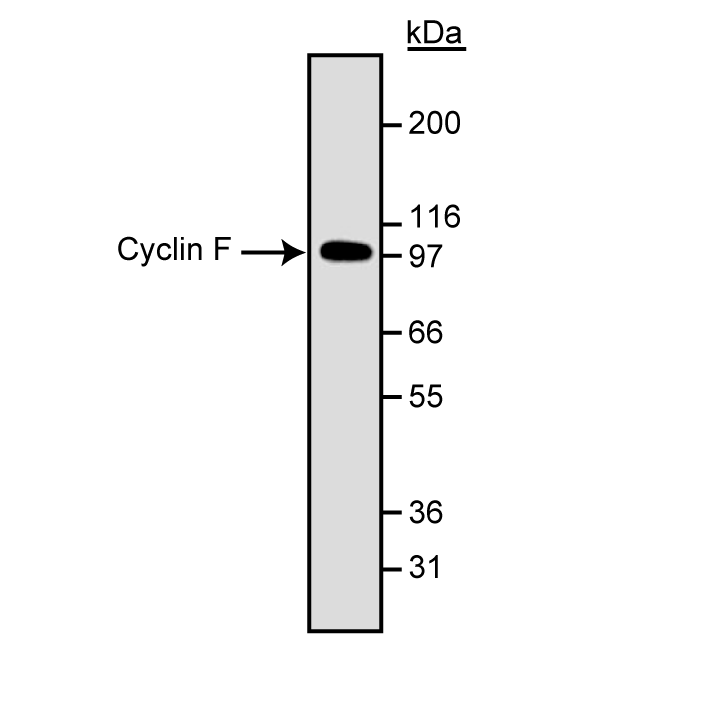



Western blot analysis of cyclin F. Lysate from A-431 epidermoid carcinoma cells were probed with anti-human cyclin F. Cyclin F is identified as a ~ 100 kD band.



Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
Clone B74-2 may be used for western blot analysis (4 µg/ml). A-431 human epidermoid carcinoma cells (ATCC CRL- 1555) are suggested as a positive control for this application.
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (cdks) are evolutionarily conserved proteins that are essential for cell-cycle control in eukaryotes. Cyclins contain a conserved amino acid sequence motif, the cyclin box, which allows their binding to cdks to form active complexes that regulate the progression of the cell cycle. Most cyclins also contain a so-called "destruction box" motif, which targets cyclins for rapid, ubiquitin-mediated degradation, as well as PEST sequences, which are thought to result in protein instability. Certain cyclins may have additional functions not restricted to cell cycle regulation. Thus, cyclins have been placed into functional groups as follows: Group 1 (cyclins A, B, D1, D2, D3, E and F) functions primarily in cell cycle reguation; Group 2 (cyclins C and H) may also play a role in transcriptional regulation; Group 3 (cyclins G1, G2 and I) may play a role distinct from either cell cycle or transcriptional regulation. Cyclin F is a novel cyclin which is structurally most similar to cyclin A, yet cyclin F lacks the destruction box sequence. Cyclin F is the largest of the cyclins, with a predicted M.W. of 87 kD and an observed M.W. of 100-110 kD, which is thought to reflect posttranslational modification of the protein. Like cyclin A, expression of cyclin F is low or undetectable in G0, begins to accumulate in Sphase, peaks in G2 and decreases at M-phase. Overexpression of cyclin F results in an accumulation of cells in G2, suggesting that this cyclin plays a role in G2/M transition during the cell cycle. B74-2 reacts with human cyclin F. A polypeptide fragment containing amino acids 693-776 of immunogen.
Development References (4)
-
Bai C, Richman R, Elledge SJ. Human cyclin F. EMBO J. 1994; 13(24):6087-6098. (Biology). View Reference
-
Bates S, Rowan S, Vousden KH. Characterisation of human cyclin G1 and G2: DNA damage inducible genes. Oncogene. 1996; 13(5):1103-1109. (Biology). View Reference
-
Movsesyan V, Whalin M, Shibutani M, Katagiri Y, Broude E, Guroff G. Down-regulation of cyclin F levels during nerve growth factor-induced differentiation of PC12 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1996; 227(2):203-207. (Biology). View Reference
-
Sherr CJ. Mammalian G1 cyclins. Cell. 1993; 73(6):1059-1065. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.