Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
For optimal and reproducible results, BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer should be used anytime two or more BD Horizon Brilliant dyes (including BD OptiBuild Brilliant reagents) are used in the same experiment. Fluorescent dye interactions may cause staining artifacts which may affect data interpretation. The BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer was designed to minimize these interactions. More information can be found in the Technical Data Sheet of the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer (Cat. No. 563794).
Product Notices
- This antibody was developed for use in flow cytometry.
- The production process underwent stringent testing and validation to assure that it generates a high-quality conjugate with consistent performance and specific binding activity. However, verification testing has not been performed on all conjugate lots.
- Researchers should determine the optimal concentration of this reagent for their individual applications.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Ultraviolet 737 is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,227,187; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
Companion Products
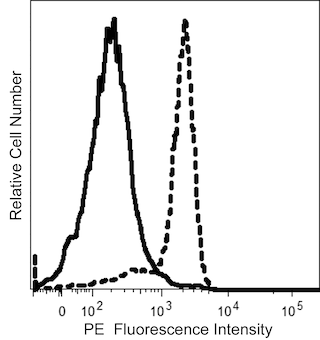





The L138 monoclonal antibody (also known as Leu-M7) specifically binds to a glycosylated 150 kDa type II integral membrane zinc-metalloprotease. The CD13 antigen is also known as aminopeptidase N, APN, ANPEP, and gp150. The CD13 antigen is expressed on granulocytes, monocytes, mast cells, and granulocyte/macrophage progenitor cells (CFU-GM), but not on lymphocytes, platelets, or erythrocytes. It is expressed on most acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells and some chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) cells. The CD13 antigen is also expressed on epithelial cells of the kidney, small intestine, and respiratory tract, as well as in synaptic membranes in the central nervous system (CNS). The CD13 antigen is involved in the metabolism of many regulatory peptides. Clustering of the CD13 antigen by various forms of ligation promotes the adhesion between monocytes and endothelial cells. The CD13 antigen is the receptor for human coronavirus 229E, the causative agent for some cases of upper respiratory infection.
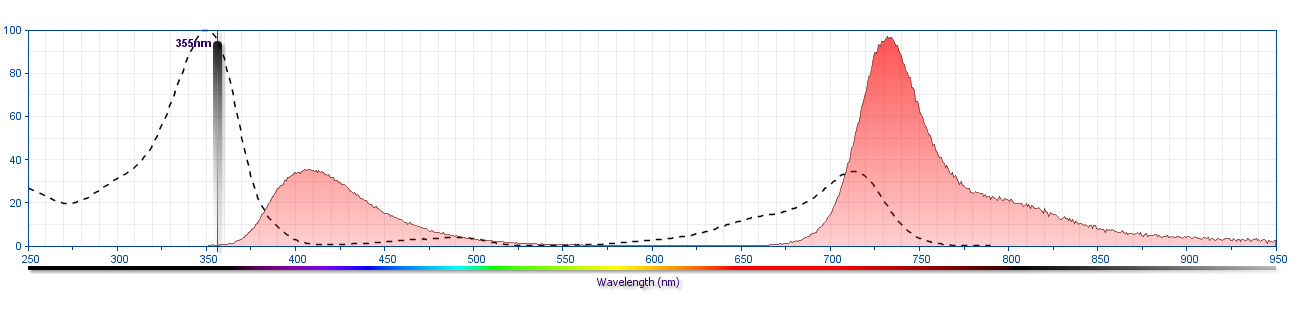
The antibody was conjugated to BD Horizon™ BUV737 which is part of the BD Horizon Brilliant™ Ultraviolet family of dyes. This dye is a tandem fluorochrome of BD Horizon BUV395 with an Ex Max of 348-nm and an acceptor dye with an Em Max at 737-nm. BD Horizon Brilliant BUV737 can be excited by the ultraviolet laser (355 nm) and detected with a 740/35 filter. Due to the excitation of the acceptor dye by other laser lines, there may be significant spillover into channels detecting Alexa Fluor® 700-like dyes (eg, 712/20-nm filter).
Due to spectral differences between labeled cells and beads, using BD™ CompBeads can result in incorrect spillover values when used with BD Horizon BUV737 reagents. Therefore, the use of BD CompBeads or BD CompBeads Plus to determine spillover values for these reagents is not recommended. Different BUV737 reagents (eg, CD4 vs. CD45) can have slightly different fluorescence spillover therefore, it may also be necessary to use clone specific compensation controls when using these reagents.
Development References (20)
-
Gadd S. Cluster report: CD13. In: Knapp W. W. Knapp .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing IV : white cell differentiation antigens. Oxford New York: Oxford University Press; 1989::782-784.
-
Ashmun RA, Holmes KV, Shapiro LH, et al. CD13 (aminopeptidase N) cluster workshop report. In: Schlossman SF. Stuart F. Schlossman .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing V : white cell differentiation antigens : proceedings of the fifth international workshop and conference held in Boston, USA, 3-7 November, 1993. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1995::771-775.
-
Bradstock KF, Favaloro EJ, Kabral A, Kerr A, Hughes WG, Musgrove E. Myeloid progenitor surface antigen identified by monoclonal antibody.. Br J Haematol. 1985; 61(1):11-20. (Biology). View Reference
-
Büchi G, Girotto M, Baldini G, et al. Differentiation phenotypes on cells of acute myeloid leukemia studied by My7, My9, My4, Mo1 and Ja monoclonal antibodies.. Pathologica. 79(1064):699-704. (Biology). View Reference
-
Cheson BD, Cassileth PA, Head DR, et al. Report of the National Cancer Institute-sponsored workshop on definitions of diagnosis and response in acute myeloid leukemia.. J Clin Oncol. 1990; 8(5):813-9. (Biology). View Reference
-
Drexler HG. Classification of acute myeloid leukemias--a comparison of FAB and immunophenotyping.. Leukemia. 1987; 1(10):697-705. (Biology). View Reference
-
Foon KA, Gale RP, Todd RF. Recent advances in the immunologic classification of leukemia.. Semin Hematol. 1986; 23(4):257-83. (Biology). View Reference
-
Griffin JD, Ritz J, Beveridge RP, Lipton JM, Daley JF, Schlossman SF. Expression of MY7 antigen on myeloid precursor cells.. Int J Cell Cloning. 1983; 1(1):33-48. (Biology). View Reference
-
Howard MR, Thomas L, Reid MM. Variable detection of myeloid antigens in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia.. J Clin Pathol. 1994; 47(11):1006-9. (Clone-specific). View Reference
-
Kirshenbaum AS, Goff JP, Semere T, Foster B, Scott LM, Metcalfe DD. Demonstration that human mast cells arise from a progenitor cell population that is CD34(+), c-kit(+), and expresses aminopeptidase N (CD13).. Blood. 1999; 94(7):2333-42. (Biology). View Reference
-
Lee SH, Crocker PR, Westaby S, et al. Isolation and immunocytochemical characterization of human bone marrow stromal macrophages in hemopoietic clusters.. J Exp Med. 1988; 168(3):1193-8. (Biology). View Reference
-
Look AT, Ashmun RA, Shapiro LH, et al. Report on the CD13 (aminopeptidase N) cluster Workshop. In: Knapp W. W. Knapp .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing IV : white cell differentiation antigens. Oxford New York: Oxford University Press; 1989:784-787.
-
Mina-Osorio P, Winnicka B, O'Conor C, et al. CD13 is a novel mediator of monocytic/endothelial cell adhesion.. J Leukoc Biol. 2008; 84(2):448-59. (Biology). View Reference
-
Pombo de Oliveira MS, Matutes E, Rani S, Morilla R, Catovsky D. Early expression of MCS2 (CD13) in the cytoplasm of blast cells from acute myeloid leukaemia.. Acta Haematol. 1988; 80(2):61-4. (Biology). View Reference
-
Sakai K, Hattori T, Sagawa K, Yokoyama M, Takatsuki K. Biochemical and functional characterization of MCS-2 antigen (CD13) on myeloid leukemic cells and polymorphonuclear leukocytes.. Cancer Res. 1987; 47(21):5572-6. (Biology). View Reference
-
Terstappen LW, Hollander Z, Meiners H, Loken MR. Quantitative comparison of myeloid antigens on five lineages of mature peripheral blood cells. J Leukoc Biol. 1990; 48(2):138-148. (Clone-specific). View Reference
-
Yang P, Wang X. COVID-19: a new challenge for human beings. Cell Mol Immunol. 2020; 17(5):555-557. (Biology). View Reference
-
Yeager CL, Ashmun RA, Williams RK, et al. Human aminopeptidase N is a receptor for human coronavirus 229E.. Nature. 1992; 357(6377):420-2. (Biology). View Reference
-
Zola H. Leukocyte and stromal cell molecules : the CD markers. Hoboken, N.J.: Wiley-Liss; 2007.
-
van Dongen JJ, Lhermitte L, Böttcher S, et al. EuroFlow antibody panels for standardized n-dimensional flow cytometric immunophenotyping of normal, reactive and malignant leukocytes. Leukemia. 2012; 26(9):1908-1975. (Clone-specific). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical Data Sheets before using this product as described.
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.