-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® OMICS-One Immune Profiler Protein Panel
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
-
Thought Leadership
- Product News
- Blogs
-
Scientific Publications
-
Events
- Expanding PARADIGM to Infectious Disease Modeling: HIV & Tuberculosis
- CYTO 2023: Advancing the World of Cytometry
- Advances in Immune Monitoring Series
- Validating Flow Cytometry Assays for Cell Therapy
- Enhancing Cell Analysis with a New Set of Eyes
- BD Biosciences at International Clinical Cytometry Society 2025
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?
BD Transduction Laboratories™ Purified Mouse Anti-Moesin
Clone 38/Moesin (RUO)
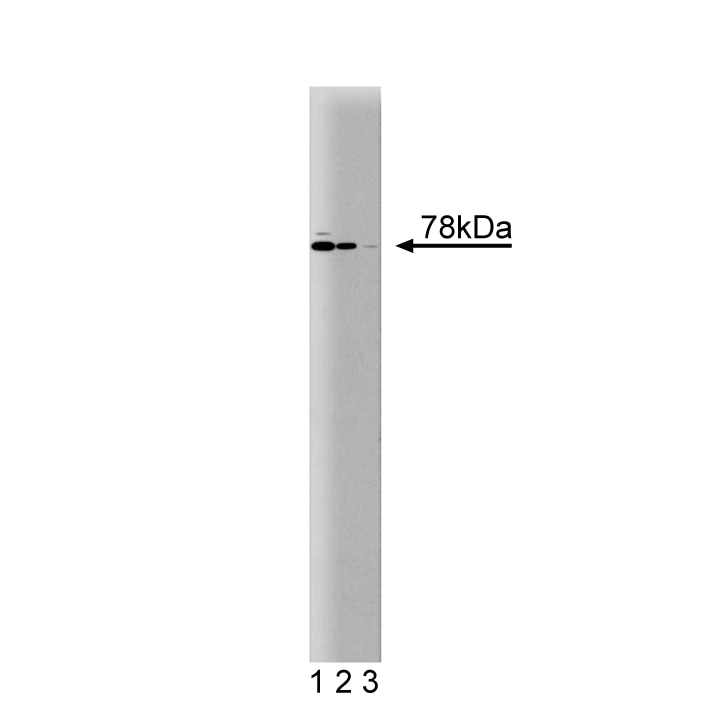




Western blot analysis of Moesin on a Jurkat cell lysate (Human T-cell leukemia; ATCC TIB-152). Lane 1: 1:5000, lane 2: 1:10,000, lane 3: 1:20,000 dilution of the mouse anti-Moesin antibody.

Western blot analysis of Moesin on a Jurkat cell lysate (Human T-cell leukemia; ATCC TIB-152). Lane 1: 1:5000, lane 2: 1:10,000, lane 3: 1:20,000 dilution of the mouse anti-Moesin antibody.

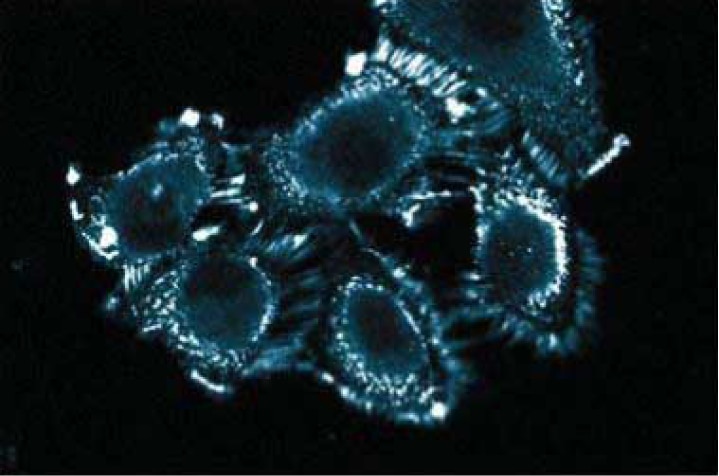
Immunofluorescence staining of A498 cells (Human kidney carcinoma; ATCC HTB-44).




Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
Western blot: Please refer to http://www.bdbiosciences.com/pharmingen/protocols/Western_Blotting.shtml
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
Companion Products



Moesin belongs to a family of proteins that includes ezrin and radixin. These proteins are co-expressed in a variety of cells. They localize to the cytoskeleton and modify interactions between cytoskeletal and membrane proteins. There is approximately 70% homology between moesin and ezrin and 80% homology between moesin and radixin. Moesin is intracellular and contains multiple conserved domains that are putative phosphorylation sites. It has a calculated molecular weight of 67.8 kDa, but migrates in SDS-PAGE at approximately 78 kDa. This discrepancy is likely due to a charged alpha-helical region within the protein.
Development References (5)
-
Lankes WT, Furthmayr H. Moesin: a member of the protein 4.1-talin-ezrin family of proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991; 88(19):8297-8301. (Biology). View Reference
-
Lankes WT, Schwartz-Albiez R, Furthmayr H. Cloning and sequencing of porcine moesin and radixin cDNA and identification of highly conserved domains. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993; 1216(3):479-482. (Biology). View Reference
-
Parlato S, Giammarioli AM, Logozzi M, et al. CD95 (APO-1/Fas) linkage to the actin cytoskeleton through ezrin in human T lymphocytes: a novel regulatory mechanism of the CD95 apoptotic pathway. EMBO J. 2000; 19(19):5123-5134. (Biology: Immunofluorescence, Western blot). View Reference
-
Poliak S, Matlis S, Ullmer C, Scherer SS, Peles E. Distinct claudins and associated PDZ proteins form different autotypic tight junctions in myelinating Schwann cells. J Cell Biol. 2002; 159(2):361-371. (Biology: Immunofluorescence). View Reference
-
Seveau S, Keller H, Maxfield FR, Piller F, Halbwachs-Mecarelli L. Neutrophil polarity and locomotion are associated with surface redistribution of leukosialin (CD43), an antiadhesive membrane molecule. Blood. 2000; 95(8):2462-2470. (Biology: Immunofluorescence, Western blot). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.