Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


.png)

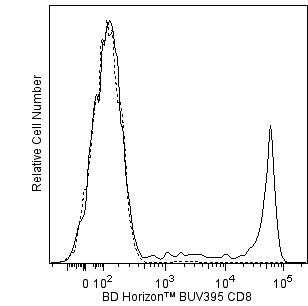
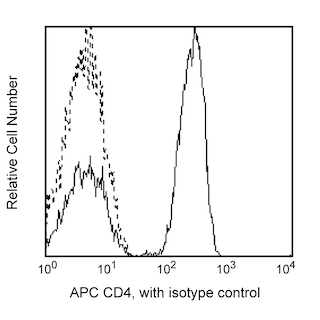
Multicolor flow cytometric analysis of CCR7 (CD197) on Human peripheral blood leucocytes and lymphocytes. Human whole blood was stained with APC Mouse Anti-Human CD4 (Cat. No. 561841), BD Horizon™ BUV395 Mouse Anti-Human CD8 (Cat. No. 563795/563796), BD Horizon™ BV421 Mouse Anti-Human CD45RA (Cat. No. 562885) antibodies, and with either BD Horizon™ RB780 Mouse IgG1, κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 568532) or BD Horizon™ RB780 Mouse Anti-Human CCR7 (CD197) antibody [Cat. No. 568748/568749]. The erythrocytes were lysed with BD PharmLyse™ Lysing Buffer (Cat. No. 555899). Flow cytometry and data analysis were performed using a BD FACS LSRFortessa™ Flow Cytometer and FlowJo™ software. Plots 1 and 2: The bivariate pseudocolor density plots showing the correlated expression of CCR7 (CD197) [or Isotype control staining] versus side light-scatter (SSC-A) signals were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable leucocytes. Plot 3: The two-parameter pseudocolor density plot showing the correlated expression of CCR7 (CD197) versus CD45RA was derived from CD4-positive T cell gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable lymphocytes. Please note that we have observed considerable donor-to-donor variation in the proportion of CCR7 (CD197)-negative CD4-positive lymphocytes. Plot 4: The two-parameter pseudocolor density plot showing CCR7 (CD197) staining versus CD45RA was derived from CD8-positive T cell gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable lymphocytes.
.png)

BD Horizon™ RB780 Mouse Anti-Human CCR7 (CD197)
.png)
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
BD® CompBeads can be used as surrogates to assess fluorescence spillover (compensation). When fluorochrome conjugated antibodies are bound to BD® CompBeads, they have spectral properties very similar to cells. However, for some fluorochromes there can be small differences in spectral emissions compared to cells, resulting in spillover values that differ when compared to biological controls. It is strongly recommended that when using a reagent for the first time, users compare the spillover on cells and BD® CompBeads to ensure that BD® CompBeads are appropriate for your specific cellular application.
Product Notices
- When using high concentrations of antibody, background binding of this dye to erythroid fragments produced by ammonium chloride-based lysis, such as with BD Pharm Lyse™ Lysing Buffer (Cat. No. 555899), has been observed when the antibody conjugate was present during the lysis procedure. This may cause nonspecific staining of target cells, such as leukocytes, which have bound the resulting erythroid fragments. This background can be mitigated by any of the following: titrating the antibody conjugate to a lower concentration, fixing samples with formaldehyde, or removing erythrocytes before staining (eg, gradient centrifugation or pre-lysis with wash). This background has not been observed when cells were lysed with BD FACS™ Lysing Solution (Cat. No. 349202) after staining.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test).
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Please observe the following precautions: Absorption of visible light can significantly alter the energy transfer occurring in any tandem fluorochrome conjugate; therefore, we recommend that special precautions be taken (such as wrapping vials, tubes, or racks in aluminum foil) to prevent exposure of conjugated reagents, including cells stained with those reagents, to room illumination.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
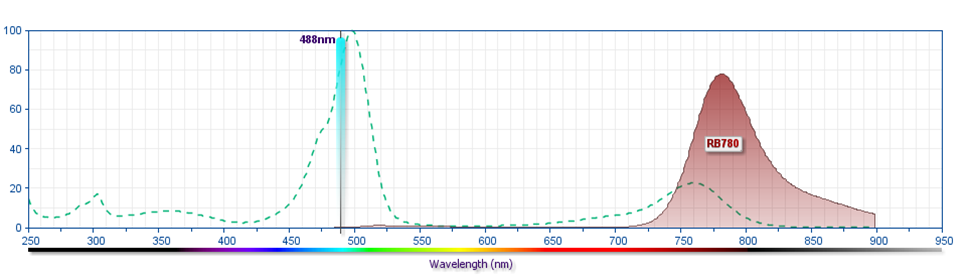
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Human donor specific background has been observed in relation to the presence of anti-polyethylene glycol (PEG) antibodies, developed as a result of certain vaccines containing PEG, including some COVID-19 vaccines. We recommend use of BD Horizon Brilliant™ Stain Buffer in your experiments to help mitigate potential background. For more information visit https://www.bdbiosciences.com/en-us/support/product-notices.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
- Cy is a trademark of Global Life Sciences Solutions Germany GmbH or an affiliate doing business as Cytiva.
Companion Products


.png?imwidth=320)
The 2-L1-A monoclonal antibody specifically binds to the human CC chemokine receptor CCR7, also known as CD197, on the cell surface. CCR7 (previously known as BLR2, EBI1 and CMKBR7) is a seven-transmembrane, G-protein-coupled receptor specific for two CC chemokines: CCL19 (also known as MIP-3β, Exodus-3, and ELC) and CCL21 (also known as 6Ckine, Exodus-2 SLC, TCA4, and SCYA21). CCR7 mRNA is expressed mainly in lymphoid tissues including the spleen, lymph nodes and tonsil, in bone marrow, and on peripheral T and B lymphocytes, cord blood CD34-positive cells, and mature dendritic cells. In response to its cognate chemokines, CCR7 (CD197) mediates homing of leucocytes to secondary lymphoid tissues. Differential CCR7 (CD197) expression can be used to distinguish naive, central memory, and effector memory T cell subsets. The human CCR7 gene, unlike other CC chemokine receptor genes, has been mapped to chromosome 17 (region 17q12). Because the extracellular region of CCR2 (CD192) has significant sequence homology with CCR7 (CD197), BD Biosciences has confirmed that mAb 2-L1-A does not cross-react with CCR2 on the surface of transfected cells.
Development References (8)
-
Birkenbach M, Josefsen K, Yalamanchili R, Lenoir G, Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus-induced genes: first lymphocyte-specific G protein-coupled peptide receptors. Nature. 1993; 67(4):2209-2220. (Biology). View Reference
-
Burgstahler R, Kempkes B, Steube K, Lipp M. Expression of the chemokine receptor BLR2/EBI1 is specifically transactivated by Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995; 215(2):737-743. (Biology). View Reference
-
Kim CH, Pelus LM, White JR, Broxmeyer HE. Macrophage-inflammatory protein-3 beta/EBI1-ligand chemokine/CK beta-11, a CC chemokine, is a chemoattractant with a specificity for macrophage progenitors among myeloid progenitor cells. J Immunol. 1998; 161(5):2580-2585. (Biology). View Reference
-
Schweickart VL, Raport CJ, Godiska R, et al. Cloning of human and mouse EBI1, a lymphoid-specific G-protein-coupled receptor encoded on human chromosome 17q12-q21.2. Genomics. 1994; 23(3):643-650. (Biology). View Reference
-
Yanagihara S, Komura E, Nagafune J, Watarai H, Yamaguchi Y. EBI1/CCR7 is a new member of dendritic cell chemokine receptor that is up-regulated upon maturation. J Immunol. 1998; 161(6):3096-3102. (Biology). View Reference
-
Yoshida R, Imai T, Hieshima K, et al. Molecular cloning of a novel human CC chemokine EBI1-ligand chemokine that is a specific functional ligand for EBI1, CCR7. J Biol Chem. 1997; 272(21):13803-13809. (Biology). View Reference
-
Yoshida R, Nagira M, Imai T, et al. EBI1-ligand chemokine (ELC) attracts a broad spectrum of lymphocytes: activated T cells strongly up-regulate CCR7 and efficiently migrate toward ELC. Int Immunol. 1998; 10(7):901-910. (Biology). View Reference
-
Yoshida R, Nagira M, Kitaura M, Imagawa N, Imai T, Yoshie O. Secondary lymphoid-tissue chemokine is a functional ligand for the CC chemokine receptor CCR7. J Biol Chem. 1998; 273(12):7118-7122. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.