Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




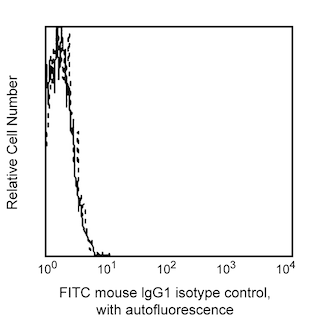
Profile of anti-PD-L1 (clone MIH1) reactivity on MIT76 transfected cells analyzed by flow cytometry.


BD Pharmingen™ FITC Mouse Anti-Human CD274

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test).
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
The MIH1 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to CD274, which is also known as, B7 homolog 1 (B7-H1), Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PDCD1 ligand, PDCD1L1, PDCD1LG1), or Programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1, PDL1). CD274 and PD-L2 (CD273) are type I transmembrane glycoproteins that belong to the B7 family and serve as ligands for CD279 (Program Death 1/PD-1). CD274 is expressed on antigen-presenting cells including activated monocytes/macrophages and dendritic cells, as well as, activated T cells, and keratinocytes. CD274 is also expressed on placental trophoblasts, myocardial endothelium, cortical thymic epithelial cells, and on most carcinomas. CD274 plays an important role in regulating T cell responses. The MIH1 antibody blocks CD279 binding to CD274 and can enhance the proliferation and cytokine production of activated T cells.
Development References (5)
-
Brown JA, Dorfman DM, Ma FR, et al. Blockade of programmed death-1 ligand on dendritic cells enhances T cell activation and cytokine production. J Immunol. 2003; 170:1257-1266. (Biology). View Reference
-
Carreno BM, Bennett F, Chau TA, et al. CTLA-4 (CD152) can inhibit T cell activation by two different mechanisms depending on its level of cell surface expression.. J Immunol. 2000; 165(3):1352-6. (Biology). View Reference
-
Carter L, Fouser LA, Jussif J, et al. PD-1:PD-L inhibitory pathway affects both CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells and is overcome by IL-2. Eur J Immunol. 2002; 32:634-643. (Biology). View Reference
-
Freeman GJ, Long AJ, Iwai Y, et al. Engagement of PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte activation. J Exp Med. 2000; 192:1027-1034. (Biology). View Reference
-
Latchman Y, Wood CR, Chernova T, et al. PD-L2 is a second ligand for PD-1 and inhibits T cell activation. Nat Immunol. 2001; 2(3):261-268. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical Data Sheets before using this product as described.
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.