Old Browser
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


Anti-Human IFN-γ APC
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
The anti-Hu–IFN-γ antibody, clone 25723.11, is derived from the hybridization of mouse P3X-63-Ag8.653 myeloma cells with lymph node cells from BALB/c mice immunized with recombinant human IFN-γ.
The anti-human interferon-γ (anti-Hu–IFN-γ) antibody recognizes a 20- to 25-kilodalton (kDa) glycoprotein, which is a type II interferon. It is also known as immune interferon.
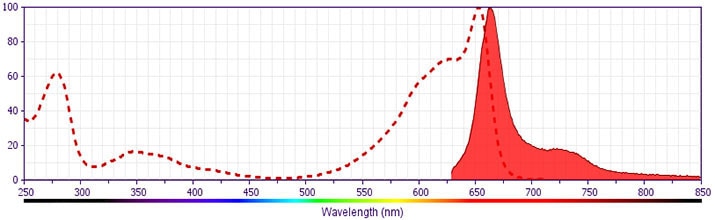
Development References (16)
-
Aggarwal B, Puri R. Human Cytokines: Their Role in Disease and Therapy. Cambridge, MA: Blackwell Science; 1995:3-24.
-
Buhtoiarov IN, Lum H, Berke G, Paulnock DM, Sondel PM, Rakhmilevich AL. CD40 ligation activates murine macrophages via an IFN-γ-dependent mechanism resulting in tumor cell destruction in vitro. J Immunol. 2005; 174:6013-6022. (Biology).
-
Centers for Disease Control. Update: universal precautions for prevention of transmission of human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis B virus, and other bloodborne pathogens in healthcare settings. MMWR. 1988; 37:377-388. (Biology).
-
Chan ED, Winston BW, Uh ST, Wynes MW, Rose DM, Riches DW. Evaluation of the role of mitogen-activated protein kinases in the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase by IFN-γ and TNF-α in mouse macrophages. J Immunol. 1999; 162:415-422. (Biology).
-
ElGhazali GEB, Paulie S, Andersson G, et al. Number of interleukin-4– and interferon- γ –secreting human T cells reactive with tetanus toxoid and the mycobacterial antigen PPD or phytohemagglutindistinct response profiles depending on the type of antigen used for activation. Eur J Immunol. 1993; 23:2740-2745. (Biology).
-
Hardy KJ, Sawada T. Human γ interferon strongly upregulates its own gene expression in peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1989; 170:1021-1026. (Biology).
-
Jarasch N, Martin U, Kamphausen E, Zell R, Wutzler P, Henke A. Interferon-γ-induced activation of nitric oxide-mediated antiviral activity of macrophages caused by a recombinant coxsackievirus B3. Viral Immunol. 2005; 18:355-364. (Biology).
-
Johnson HM, Bazer FW, Szente BE, Jarpe MA. How interferons fight disease. Scientific American. 1994; May:68-75. (Biology).
-
Murray HW, Spitalny GL, Nathan CF. Activation of mouse peritoneal macrophages in vitro and in vivo by interferon-γ. J Immunol. 1990; 13:411-421. (Biology).
-
Murray HW. γ interferon, cytokine-induced macrophage activation, and antimicrobial host defense. In vitro, in animal models, and in humans. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990; 13:411-421. (Biology).
-
Openshaw P, Murphy EE, Hosken NA, et al. Heterogeneity of intracellular cytokine synthesis at the single-cell level in polarized T helper 1 and T helper 2 populations. J Exp Med. 1995; 182(5):1357-1367. (Biology). View Reference
-
Paliard X, Malefijt RDW, Yssel H, et al. Simultaneous production of IL-2, IL-4, and IFN-γ by activated human CD4+ and CD8+ T cell clones. J Immunol. 1988; 141:849-855. (Biology).
-
Powrie F, Coffman RL. Cytokine regulation of T-cell function: potential for therapeutic intervention. Immunol Today. 1993; 14:270-274. (Biology).
-
Protection of Laboratory Workers from Occupationally Acquired Infections. Approved Guideline. 2005; M29-A3. (Biology).
-
Romagnani S. Human TH1 and TH2 subsets: regulation of differentiation and role in protection and immunopathology. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1992; 98:279-285. (Biology).
-
Street NE, Mosmann TR. Functional diversity of T lymphocytes due to secretion of different cytokine patterns. FASEB J. 1991; 5:171-176. (Biology).
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
Analyte Specific Reagent. Analytical and performance characteristics are not established.
Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical Data Sheets before using this product as described.
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.