Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


.png)

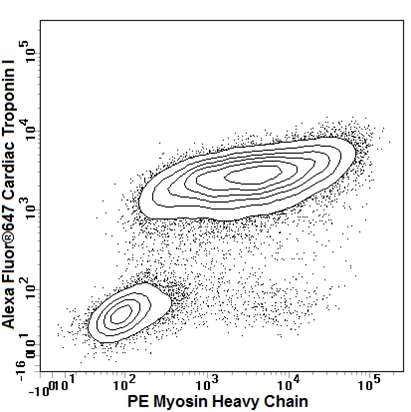
Analysis of Myosin Heavy Chain in human embryonic stem cell (hESC)-derived cardiomyocytes. hESC- derived cardiomyocytes (Evans laboratory, UC San Diego) were disassociated and fixed in BD Cytofix™ Fixation Buffer (Cat. No. 554655), permeabilized with BD Phosflow™ Perm/Wash Buffer I (Cat. No. 557885), and stained with PE Mouse Anti-Myosin Heavy Chain (MHC) and Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse Anti-Cardiac Troponin I (cTnI) (Cat. No. 554409). The cells were first gated on light scatter properties and then analyzed for MHC and cTnI expression. Flow cytometry was performed on a BD LSRFortessa™ flow cytometry system.

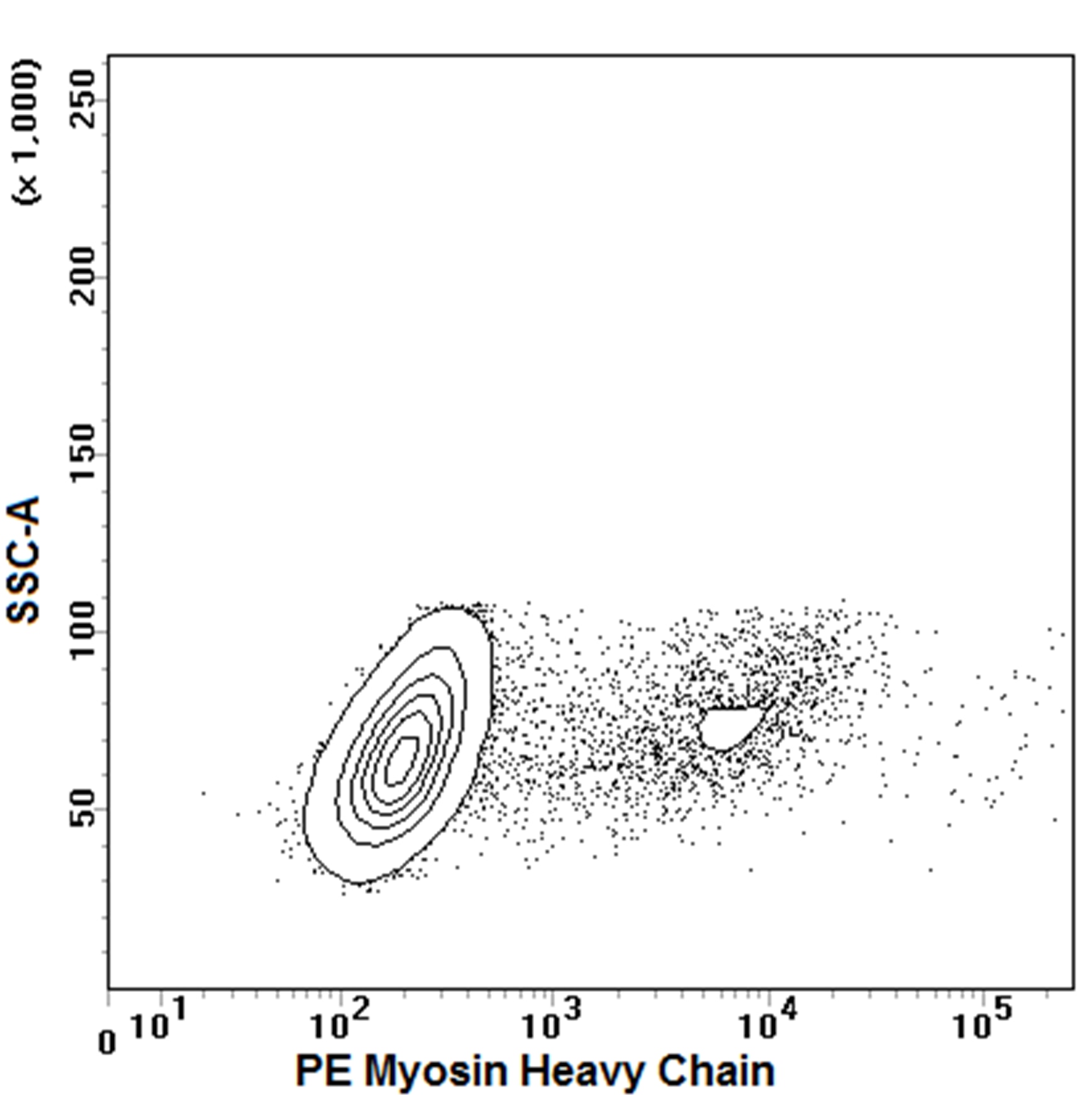
Analysis of Myosin Heavy Chain in differentiated C2C12 mouse myoblast cell line. C2C12 cells (ATCC: CRL-1772) that were differentiated for 3 days and then disassociated and fixed in BD Cytofix™ Fixation Buffer (Cat. No. 554655), permeabilized with BD Phosflow™ Perm/Wash buffer I (Cat. No. 557885), and stained with PE Mouse Anti-Myosin Heavy Chain (MHC). The cells were first gated on light scatter properties and then analyzed for MHC expression. Flow cytometry was performed on a BD LSRFortessa™ flow cytometry system.
.png)

BD Pharmingen™ PE Mouse Anti-Myosin Heavy Chain

BD Pharmingen™ PE Mouse Anti-Myosin Heavy Chain
.png)
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
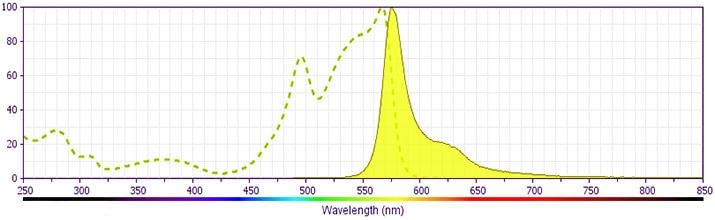
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Alexa Fluor® is a registered trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, OR.
Companion Products





The MF20 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to the heavy chain component of skeletal muscle myosin or myosin II. Skeletal muscle myosin is composed of 2 heavy chains and 4 light chains. Myosin Heavy chain is a 220-kDa protein that interacts with actin in the ATP-dependent mechanism of muscle contraction. This antibody is reported to cross react with human, mouse, rat, chicken, dog, frog, and zebrafish.
Development References (5)
-
Bader D, Masaki T, Fischman DA. Immunochemical analysis of myosin heavy chain during avian myogenesis in vivo and in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1982; 95(3):763-770. (Immunogen). View Reference
-
Dambrot C, Passier R, Atsma D, Mummery CL. Cardiomyocyte differentiation of pluripotent stem cells and their use as cardiac disease models. Biochem J. 2011; 434(1):25-35. (Biology). View Reference
-
Lian X, Hsiao C, Wilson G, et al. Robust cardiomyocyte differentiation from human pluripotent stem cells via temporal modulation of canonical Wnt signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012; 109(27):E1848-E1857. (Biology). View Reference
-
López JE, Myagmar BE, Swigart PM, et al. β-myosin heavy chain is induced by pressure overload in a minor subpopulation of smaller mouse cardiac myocytes. Circ Res. 2011; 109(6):629-638. (Clone-specific). View Reference
-
Travaglione S, Messina G, Fabbri A. Cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 hinders skeletal muscle differentiation in vitro by perturbing the activation/deactivation balance of Rho GTPases. Cell Death Differ. 2005; 12(1):78-86. (Clone-specific). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.