-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
- BD OMICS-One™ WTA Next Assay
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current location site or be switched to your location?
BD Pharmingen™ Purified Mouse Anti-Human Cyclin E
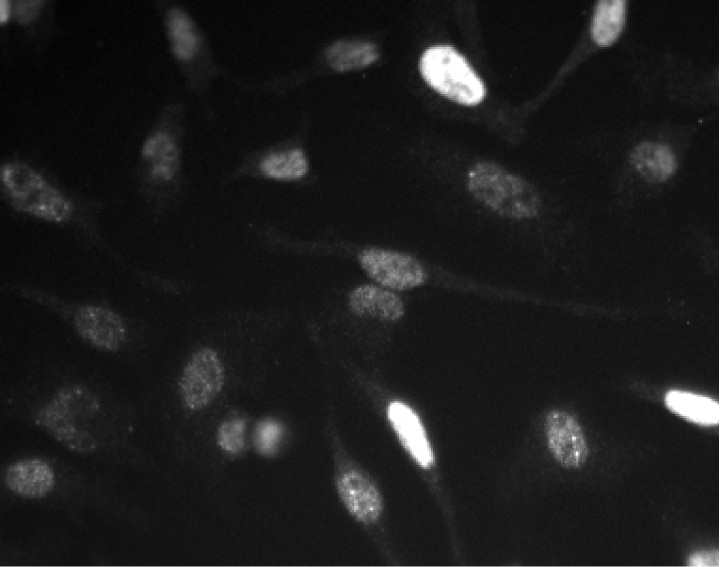
Left Figure: Western blot analysis of Cyclin E expression on HeLa cell lysate. Lysate from HeLa cells (ATCC CCL-2) was probed with Purified Mouse Anti-Human Cyclin E antibody (Cat. No. 551160/551159) at concentrations of 1.0 µg/mL (lane 1), 0.5 µg/mL (lane 2), and 0.25 µg/mL (lane 3). Cyclin E is identified as a band of 50 kDa. Right Figure: Immunofluorescent analysis of Cyclin E expression on HeLa cells. HeLa cells were seeded in a 96-well imaging plate at ~10,000 cells per well. After overnight incubation, cells were stained using the alcohol perm protocol and Purified Mouse Anti-Human Cyclin E antibody. The second step reagent was Alexa Fluor® 555 goat anti-mouse IgG (Invitrogen). The image was taken on a BD Pathway™ 855 Bioimager system using a 20x objective. This antibody also stained A549 (ATCC CCL-185) and U-2 OS (ATCC HTB-96) cells and worked with both the Triton™ X-100 and alcohol perm protocols (see Recommended Assay Procedure).

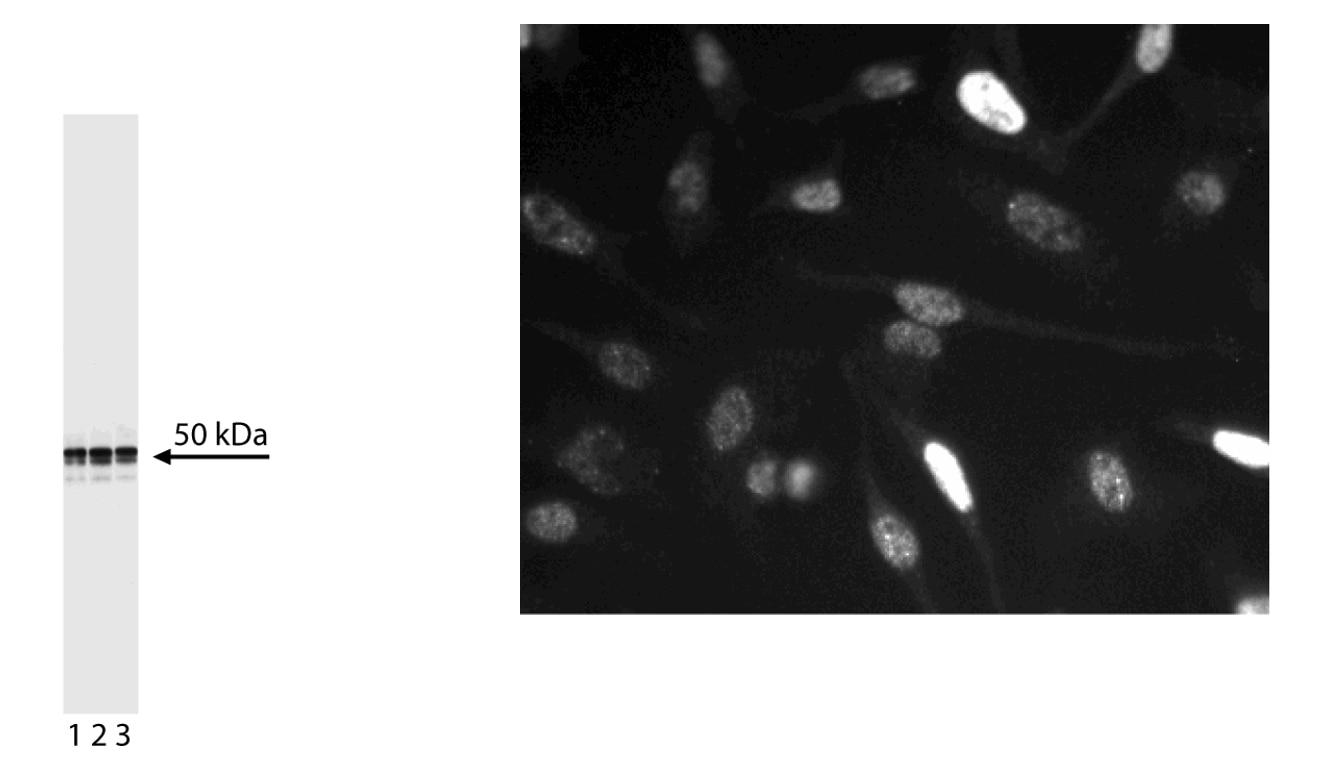
Left Figure: Western blot analysis of Cyclin E expression on HeLa cell lysate. Lysate from HeLa cells (ATCC CCL-2) was probed with Purified Mouse Anti-Human Cyclin E antibody (Cat. No. 551160/551159) at concentrations of 1.0 µg/mL (lane 1), 0.5 µg/mL (lane 2), and 0.25 µg/mL (lane 3). Cyclin E is identified as a band of 50 kDa. Right Figure: Immunofluorescent analysis of Cyclin E expression on HeLa cells. HeLa cells were seeded in a 96-well imaging plate at ~10,000 cells per well. After overnight incubation, cells were stained using the alcohol perm protocol and Purified Mouse Anti-Human Cyclin E antibody. The second step reagent was Alexa Fluor® 555 goat anti-mouse IgG (Invitrogen). The image was taken on a BD Pathway™ 855 Bioimager system using a 20x objective. This antibody also stained A549 (ATCC CCL-185) and U-2 OS (ATCC HTB-96) cells and worked with both the Triton™ X-100 and alcohol perm protocols (see Recommended Assay Procedure).

Left Figure: Western blot analysis of Cyclin E expression on HeLa cell lysate. Lysate from HeLa cells (ATCC CCL-2) was probed with Purified Mouse Anti-Human Cyclin E antibody (Cat. No. 551160/551159) at concentrations of 1.0 µg/mL (lane 1), 0.5 µg/mL (lane 2), and 0.25 µg/mL (lane 3). Cyclin E is identified as a band of 50 kDa. Right Figure: Immunofluorescent analysis of Cyclin E expression on HeLa cells. HeLa cells were seeded in a 96-well imaging plate at ~10,000 cells per well. After overnight incubation, cells were stained using the alcohol perm protocol and Purified Mouse Anti-Human Cyclin E antibody. The second step reagent was Alexa Fluor® 555 goat anti-mouse IgG (Invitrogen). The image was taken on a BD Pathway™ 855 Bioimager system using a 20x objective. This antibody also stained A549 (ATCC CCL-185) and U-2 OS (ATCC HTB-96) cells and worked with both the Triton™ X-100 and alcohol perm protocols (see Recommended Assay Procedure).



Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Description
Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (cdks) are evolutionarily conserved proteins that are essential for cell-cycle control in eukaryotes. Cyclins (regulatory subunits) bind to cdks (catalytic subunits) to form complexes that regulate the progression of the cell cycle. These complexes are regulated by activating and inhibitory phosphorylation events, as well as by interactions with small proteins that bind to cyclins, cdks, or cyclin-cdk complexes, e.g., p21 and p27 [Kip1]. Cyclin E is expressed in G1 and associates with cdk2 to form an active kinase where it plays an important role in the regulation of the G1/S restriction checkpoint in the cell cycle. Abberant expression of cyclin E has been reported to be associated with the oncogenic transformation of cells. This antibody has been reported not to cross-react with mouse cyclin E.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
Bioimaging
1. Seed the cells in appropriate culture medium at ~10,000 cells per well in a 96-well Imaging Plate and culture overnight.
2. Remove the culture medium from the wells, and fix the cells by adding 100 μl of BD Cytofix™ Fixation Buffer (Cat. No. 554655) to each well. Incubate for 10 minutes at room temperature (RT).
3. Remove the fixative from the wells, and permeabilize the cells using either BD Perm Buffer III or Triton™ X-100:
a. Add 100 μl of -20°C Perm Buffer III (Cat. No. 558050) to each well and incubate for 5 minutes at RT.
OR
b. Add 100 μl of 0.1% Triton™ X-100 to each well and incubate for 5 minutes at RT.
4. Remove the permeabilization buffer, and wash the wells twice with 100 μl of 1× PBS.
5. Remove the PBS, and block the cells by adding 100 μl of BD Pharmingen™ Stain Buffer (FBS) (Cat. No. 554656) to each well. Incubate for 30 minutes at RT.
6. Remove the blocking buffer and add 50 μl of the optimally titrated primary antibody (diluted in Stain Buffer) to each well, and incubate for 1 hour at RT.
7. Remove the primary antibody, and wash the wells three times with 100 μl of 1× PBS.
8. Remove the PBS, and add the second step reagent at its optimally titrated concentration in 50 μl to each well, and incubate in the dark for 1 hour at RT.
9. Remove the second step reagent, and wash the wells three times with 100 μl of 1× PBS.
10. Remove the PBS, and counter-stain the nuclei by adding 200 μl per well of 2 μg/ml Hoechst 33342 (e.g., Sigma-Aldrich Cat. No. B2261) in 1× PBS to each well at least 15 minutes before imaging.
11. View and analyze the cells on an appropriate imaging instrument.
Bioimaging: For more detailed information please refer to "Cellular Imaging" at our website: http://www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources
Western blot: For more detailed information please refer to "Cell biology (WB, IP, IHC, IF)" at our website: http://www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- This antibody has been developed and certified for the bioimaging application. However, a routine bioimaging test is not performed on every lot. Researchers are encouraged to titrate the reagent for optimal performance.
- Triton is a trademark of the Dow Chemical Company.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Please refer to http://regdocs.bd.com to access safety data sheets (SDS).
Companion Products





| Description | Quantity/Size | Part Number | EntrezGene ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| N/A | 50.0 | N/A | N/A |
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.