Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?

.png)

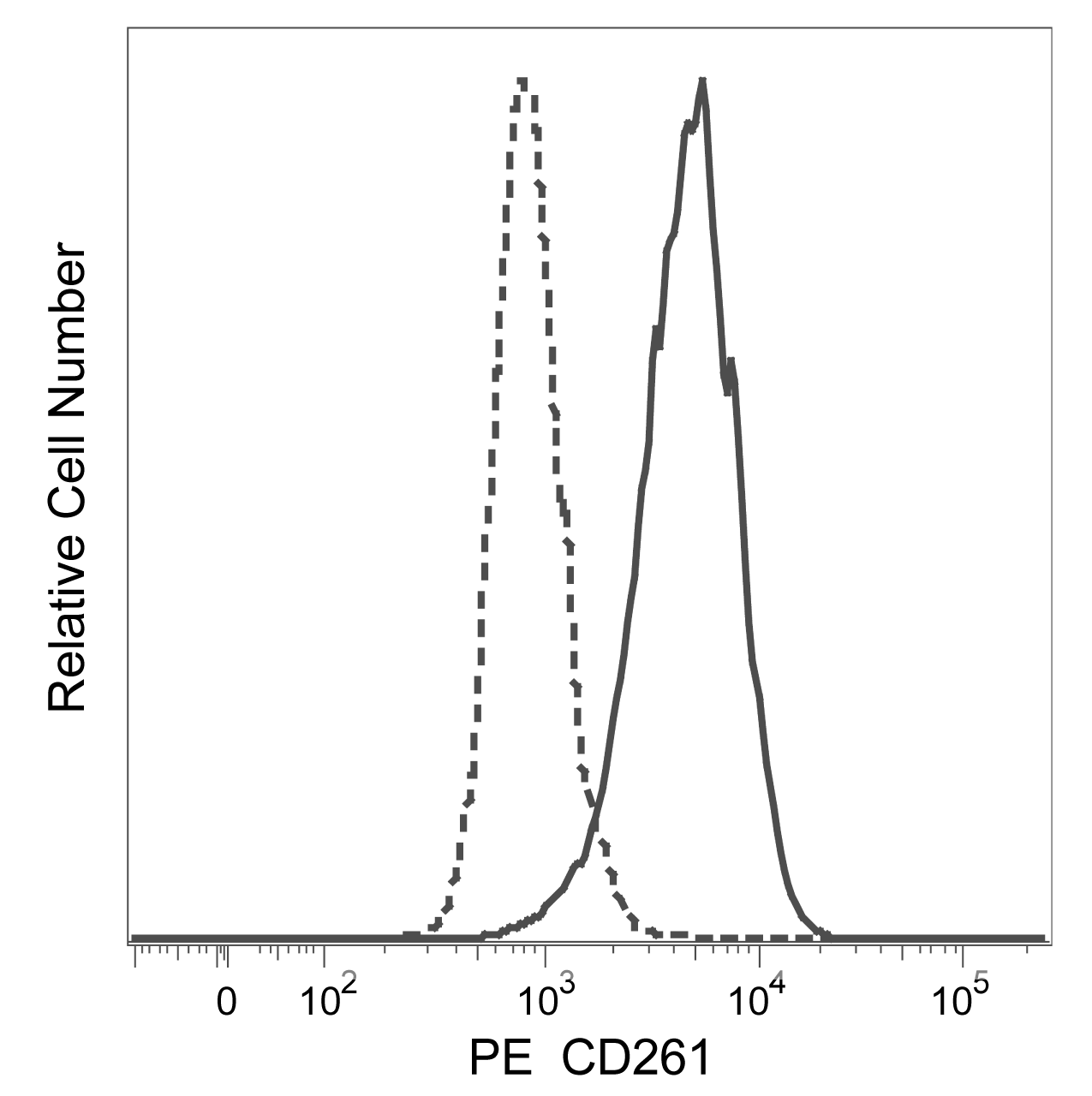
Flow cytometric analysis of CD261 expression on human erythroleukemia cells. Cells from the human Hel 92.1.7 (Erythroleukemia, ATCC TIB-180) cell line were stained with either PE Mouse IgG1, κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 554680; dashed line histogram) or PE Mouse Anti-Human CD261 antibody (Cat. No. 564180; solid line histogram). The fluorescence histograms were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of viable cells. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using a BD FACSCanto™ II Flow Cytometer System.
.png)

BD Pharmingen™ PE Mouse Anti-Human TRAIL-R1 (CD261)
.png)
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
Staining cells at 37°C with PE Mouse Anti-Human CD261 antibody may improve the fluorescence intensity of positively stained cells upon flow cytometric analysis.
Product Notices
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test).
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
Companion Products


The S35-934 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand receptor 1 (TRAIL-R1/TRAIL Receptor 1). TRAIL-R1 is also known as CD261, Death Receptor 4 (DR4) and APO2. TRAIL-R1 is a type I transmembrane protein that is encoded by TNFRSF10A (tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 10a). It serves as a receptor for TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) which is also known as CD253 and TNFSF10. TRAIL-R1 is expressed by a variety of tumor-derived cell lines. It is generally expressed at very low levels by most leucocytes. When bound by TRAIL, TRAIL-R1 can promote recruitment and subsequent activation of caspase-8, ultimately triggering the activation of effector caspases within cells that lead to apoptosis. Many transformed cell types are susceptible to TRAIL:TRAIL-R1-mediated cell death whereas normal cells are typically resistant.
Development References (8)
-
Dickens LS, Boyd RS, Jukes-Jones R, et al. A death effector domain chain DISC model reveals a crucial role for caspase-8 chain assembly in mediating apoptotic cell death. Mol Cell. 2012; 47(2):291-305. (Biology). View Reference
-
Falschlehner C, Schaefer U, Walczak H. Following TRAIL's path in the immune system. Immunology. 2009; 127(2):145-154. (Biology). View Reference
-
Florian S, Sonneck K, Czerny M, et al. Detection of novel leukocyte differentiation antigens on basophils and mast cells by HLDA8 antibodies. Allergy. 2006; 61(9):1054-1062. (Biology). View Reference
-
Grewal IS. Overview of TNF superfamily: a chest full of potential therapeutic targets. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009; 647:1-7. (Biology). View Reference
-
Johnstone RW, Frew AJ, Smyth MJ. The TRAIL apoptotic pathway in cancer onset,progression and therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008; 8(10):782-798. (Biology). View Reference
-
Pan G, O'Rourke K, Chinnaiyan AM, et al. The receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL. Science. 1997; 276(5309):111-113. (Biology). View Reference
-
Spierings DC, de Vries EG, Vellenga E, et al. Tissue distribution of the death ligand 2 TRAIL and its receptors. J Histochem Cytochem. 2004; 52(6):821-831. (Biology). View Reference
-
Wiley SR, Schooley K, Smolak PJ, et al. Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity. 1995; 3(6):673-682. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.