Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




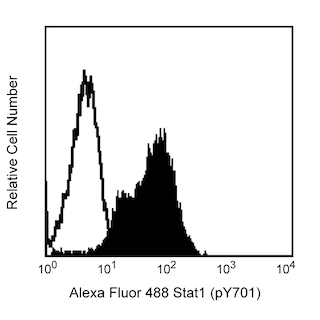
Analysis of IRF-7 (pS477/pS479) in transfected human epithelial cells. The 293 fetal kidney cell line was either co-transfected with TBK1 and IRF-7 expression vectors (dashed histogram) or un-transfected (solid line). After 24 hours, the cells were fixed (BD Cytofix™ buffer, Cat. No. 554655) for 10 minutes at 37°C, then permeabilized (BD Phosflow™ Perm Buffer III, Cat. No. 558050) on ice for at least 30 minutes, and then stained with Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse anti-IRF-7 (pS477/pS479). Flow cytometry was performed on a BD FACSCalibur™ flow cytometry system.


BD™ Phosflow Alexa Fluor® 647 Mouse anti-IRF-7 (pS477/pS479)

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test).
- Alexa Fluor® 647 fluorochrome emission is collected at the same instrument settings as for allophycocyanin (APC).
- Alexa Fluor® is a registered trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, OR.
- The Alexa Fluor®, Pacific Blue™, and Cascade Blue® dye antibody conjugates in this product are sold under license from Molecular Probes, Inc. for research use only, excluding use in combination with microarrays, or as analyte specific reagents. The Alexa Fluor® dyes (except for Alexa Fluor® 430), Pacific Blue™ dye, and Cascade Blue® dye are covered by pending and issued patents.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
Companion Products

Interferon regulatory factor 7 (IRF-7) is a transcription factor that regulates anti-viral defenses by controlling the induction of type-I interferon (IFN) responses. IRF-7 expression is induced in lymphoid cells by virus infection, as well as by IFN, lipopolysaccharide, and TNF-α. IRF-7 responses are initiated by Toll-like receptors (TLR) or the cytoplasmic protein retinoic acid inducible gene I (RIG-I). Upon TLR activation, it forms cytoplasmic complexes with MyD88, an adaptor in the TLR signaling pathways. The TLR-dependent and RIG-I-dependent pathways activate kinases, such as IKK-ε and TBK1, that phosphorylate IRF-7 and induce movement of IRF-7-containing complexes to the nucleus, where it preferentially activates IFN-α promoters.
The K47-671 monoclonal antibody recognizes human IRF-7 phosphorylated at serines 477 and 479 (pS477/pS479). Our in-house testing is performed on a cell line that has been co-transfected with TBK1 and IRF-7. Phosphorylation of IRF-7 in the transfectants requires virus infection or over-expression of a signaling molecule of the RIG-I pathway, such as TBK1. Phosphorylation of endogenous IRF-7 in untransfected cells has not yet been detected. We confirmed that mAb K47-671 does not cross-react with TBK1 by Western blot analysis using the purified antibody.
Development References (8)
-
Honda K, Yanai H, Mizutani T, et al. Role of a transductional–tanscriptional processor complex involving MyD88 and IRF-7 in Toll-like receptor signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004; 101(43):15416-15421. (Biology). View Reference
-
Honda K, Yanai H, Negishi H, et al. IRF-7 is the master regulator of type-I interferon-dependent immune responses. Nature. 2005; 434:772-777. (Biology). View Reference
-
Hoshino K, Sugiyama T, Matsumoto M, et al. IκB kinase-α is critical for interferon-α production induced by Toll-like receptors 7 and 9. Nature. 2006; 440(7086):949-953. (Biology). View Reference
-
Kawai T, Sato S, Ishii KJ, et al. Interferon-α induction through Toll-like receptors involves a direct interaction of IRF7 with MyD88 and TRAF6. Nat Immunol. 2004; 5(10):1061-1068. (Biology). View Reference
-
Lin R, Mamane Y, Hiscott J. Multiple regulatory domains control IRF-7 activity in response to virus infection. J Biol Chem. 2000; 275(44):34320-34327. (Biology). View Reference
-
Matikainen S, Sirén J, Tissari J, et al. Tumor necrosis factor alpha enhances influenza A virus-induced expression of antiviral cytokines by activating RIG-I gene expression. J Virol. 2006; 80(7):3515-3522. (Biology). View Reference
-
Paz S, Sun Q, Nakhaei P, et al. Induction of IRF-3 and IRF-7 phosphorylation following activation of the RIG-I pathway. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2006; 52(1):17-28. (Clone-specific). View Reference
-
Sharma S, tenOever BR, Grandvaux N, Zhou G-P, Lin R, Hiscott J. Triggering the interferon antiviral response through an IKK-related pathway. Science. 2003; 300:1148-1151. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.