Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?





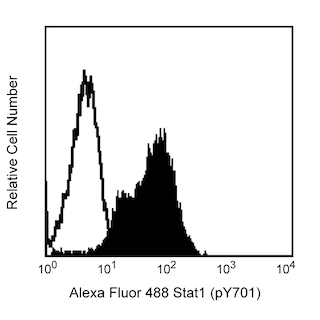
Analyses of Bcl-2 (pS70) expression. Panel 1: Western blot analysis of Bcl-2 (pS70) expressed by human Jurkat cells. Lysates (15 µg total cell protein/lane) from untreated (C) and Taxol-treated (T) (Paclitaxel, Sigma, Cat. No. T7191; 100 nM, 24 h) Jurkat cells were blotted using Purified Mouse Anti-Bcl-2 (pS70) antibody (Cat. No. 562529; 0.125, 0.063, and 0.032 µg/ml for Lanes 1, 2, and 3, respectively), HRP Goat Anti-Mouse Ig (Cat. No. 554002) and a chemiluminescent detection system. Panel 2a: Western blot analysis of Bcl-2 (pS70) expressed by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). Phytohemagglutinin-stimulated (PHA, 20 μg/ml for 3 days; Sigma Cat. No. L1668) PBMC were cultured with or without Taxol (100 nM, 24 hr, 37°C). Lysates from 1 million untreated (C) and Taxol-treated (T) PBMC were blotted using Purified Mouse Anti-Bcl-2 (pS70) antibody (2.0 µg/ml) as described above. Panel 2b: Flow cytometric analysis of Bcl-2 (pS70) expressed by human PBMC. PHA-stimulated (20 μg/ml for 3 days) PBMC were cultured with (solid line histogram) or without (dashed line histogram) Taxol (100 nM, 24 hr, 37°C). Cells were fixed in BD Phosflow™ Cytofix Buffer (Cat. No. 554655; 10 min, 37˚C) and permeabilized in BD Phosflow™ Perm Buffer III (Cat. No. 558050; 30 min, on ice) prior to staining with BD Phosflow™ PE Mouse Anti-Bcl-2 (pS70) (Cat. No. 562532) antibody. Fluorescence histograms showing Bcl-2 (pS70) expression were generated for gated events with the forward and side-light scatter characteristics of intact lymphocytes. Panel 3: Immunohistochemical staining for Bcl-2 (pS70). A citrate-pretreated, formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue section of human tonsil was stained with isotype control (Cat. No. 550878; Left) or Purified Mouse Anti-Bcl-2 (pS70) antibody (Right) (20X original magnification). Note: Bcl-2 (pS70) was identified as a ~28 kDa band in the cell lysates by Western blotting.



BD™ Phosflow Purified Mouse anti-Human Bcl-2 (pS70)

BD™ Phosflow Purified Mouse anti-Human Bcl-2 (pS70)

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
Companion Products



The N46-467 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to Bcl-2 (pS70), ie, the Bcl-2 protein phosphorylated at the Ser70 site. Bcl-2 is a ~ 26 kDa intracellular, integral membrane protein found primarily in the nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum and outer mitochondrial membrane. Bcl-2 is encoded by the BCL2 (B-cell CLL/lymphoma 2) gene and is also known as Apoptosis regulator Bcl-2. Members of the Bcl-2 family play a major role in regulating the response of cells to apoptotic signals. Bcl-2 is one of the anti-apoptotic members of the Bcl-2 family. Bcl-2 knockout mice showed pronounced lymphoid apoptosis and other apoptosis related lesions later in life. Bcl-2 is a proto-oncogene because it blocks apoptosis and provides a selective survival advantage in many cell types and thus contributes to tumorigenesis. It has been implicated in several types of cancers, such as breast, prostate, and melanoma . Bcl-2 contains multiple phosphorylation sites including Thr56, Ser70, Thr74 and Ser87. Phosphorylation of Bcl-2 Ser70 has been shown to be a mitotic marker. Phosphorylation at this site regulates Bcl-2's anti-apoptotic activity and has recently been implicated in promoting autophagy. Several studies have shown that Bcl-2 phosphorylation is caused by c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK).
Development References (6)
-
Deng X, Xiao L, Lang W, et al. Novel role for JNK as a stress-activated Bcl2 kinase. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276(26):23681-23688. (Biology). View Reference
-
Geng F, Tang L, Li Y, et al. Allyl isothiocyanate arrests cancer cells in mitosis, and mitotic arrest in turn leads to apoptosis via Bcl-2 protein phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 2011; 286(37):32259-32267. (Biology). View Reference
-
Ling YH, Tornos C, Perez-Soler R. Phosphorylation of Bcl-2 is a marker of M phase events and not a determinant of apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1998; 273(30):18984-18991. (Biology). View Reference
-
Maundrell K, Antonsson B, Magnenat E, et al. Bcl-2 undergoes phosphorylation by c-Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinases in the presence of the constitutively active GTP-binding protein Rac1. J Biol Chem. 1997; 272(40):25238-42. (Biology). View Reference
-
Pattingre S, Bauvy C, Carpentier S, Levade T, Levine B, Codogno P.. Role of JNK1-dependent Bcl-2 phosphorylation in ceramide-induced macroautophagy. J Biol Chem. 2009; 284(5):2719-2728. (Biology). View Reference
-
Sarkar S, Korolchuk VI, Renna M, et al. Complex inhibitory effects of nitric oxide on autophagy. Mol Cell. 2011; 43(1):19-32. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.