Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?



.png)

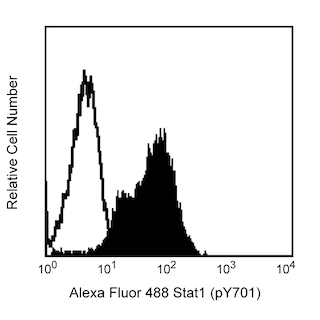
Flow cytometric analysis of NF-κB p65 (pS529) expression by TNF-treated HeLa S3 cells. Cultured cells from the human HeLa S3 (Cervical adenocarcinoma, ATCC CCL 2.2) cell line were starved overnight in Dulbecco's Minimal Eagle's Medium. The cells were harvested and washed with Dulbecco's Phosphate Buffered Saline. They were either left untreated (dashed line histogram) or treated (37°C, 10 min) with Recombinant Human TNF protein (20 ng/mL; Cat. No. 554618; solid line histogram) and Calyculin A (50 nM; Calbiochem Cat. No. 208851). The cells were fixed (10 min; 37°C) with pre-warmed BD Cytofix™ Fixation Buffer (Cat. No. 554655), permeabilized (30 min on ice) with BD Phosflow™ Perm Buffer III (Cat. No. 558050), and washed twice with BD Pharmingen™ Stain Buffer (FBS) (Cat. No. 554656). The cells were then stained with BD Horizon™ PE-CF594 Mouse Anti-Human NF-κB p65 (pS529) antibody (Cat. No. 565447). The fluorescence histograms showing NF-κB p65 (pS529) expression were derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of intact HeLa S3 cells. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using a BD™ LSR II Flow Cytometer System.

.png)

BD Phosflow™ PE-CF594 Mouse Anti-Human NF-κB p65 (pS529)

BD Phosflow™ PE-CF594 Mouse Anti-Human NF-κB p65 (pS529)
.png)
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test).
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- When excited by the yellow-green (561-nm) laser, the fluorescence may be brighter than when excited by the blue (488-nm) laser.
- Because of the broad absorption spectrum of the tandem fluorochrome, extra care must be taken when using multi-laser cytometers, which may directly excite both PE and CF™594.
- Please observe the following precautions: Absorption of visible light can significantly alter the energy transfer occurring in any tandem fluorochrome conjugate; therefore, we recommend that special precautions be taken (such as wrapping vials, tubes, or racks in aluminum foil) to prevent exposure of conjugated reagents, including cells stained with those reagents, to room illumination.
- CF™ is a trademark of Biotium, Inc.
- This product is provided under an Agreement between BIOTIUM and BD Biosciences. The manufacture, use, sale, offer for sale, or import of this product is subject to one or more patents or pending applications owned or licensed by Biotium, Inc. This product, and only in the amount purchased by buyer, may be used solely for buyer’s own internal research, in a manner consistent with the accompanying product literature. No other right to use, sell or otherwise transfer (a) this product, or (b) its components is hereby granted expressly, by implication or by estoppel. This product is for research use only. Diagnostic uses require a separate license from Biotium, Inc. For information on purchasing a license to this product including for purposes other than research, contact Biotium, Inc., 3159 Corporate Place, Hayward, CA 94545, Tel: (510) 265-1027. Fax: (510) 265-1352. Email: btinfo@biotium.com.
- Texas Red is a registered trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, OR.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products



The K10-895.12.50 monoclonal antibody recognizes the phosphorylated serine 529 (pS529) in the transactivation domain of the human NF-κB p65 subunit. Nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) is a ubiquitously expressed transcription factor that regulates the expression of many other genes. It is crucial for cellular responses to a variety of stimuli including stress and microbial pathogens that lead to immunity, inflammation, proliferation, differentiation, survival, apoptosis, and tumorigenesis. The most studied NF-κB complex consists of the p50 (also known as NF-κB1) and p65 (also known as REL-A) subunits, both containing a 300-amino acid region with homology to the Rel proto-oncogene product (RH domain). The RH domain contains motifs for dimerization, nuclear localization, and binding to specific DNA sequences. In addition to the RH domain, the p65 subunit contains the transactivation domain, which is responsible for the interaction with the inhibitor IκB and which contains phosphorylation sites. In most cell types, the p50/p65 heterodimer is located within the cytoplasm complexed to IκB. This complex prevents nuclear translocation and activity of NF-κB. In response to stimuli such as cytokines, LPS, DNA damage, and microbial infections, IκB is phosphorylated at critical residues. This phosphorylation induces dissociation of the IκB/NF-κB complex, allowing the free heterodimeric NF-κB to translocate to the nucleus. Furthermore, optimal activation of NF-κB requires phosphorylation in the transactivation domain of p65. In the nucleus, activated NF-κB dimers bind to the κB sites within promoters and enhancers and function as transcriptional regulators.
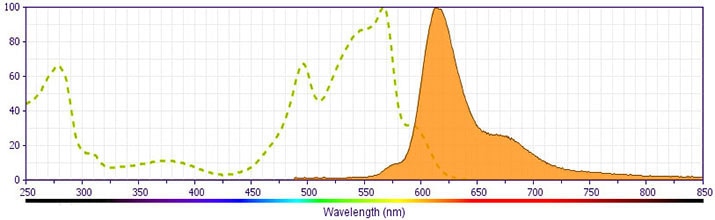
This antibody is conjugated to BD Horizon PE-CF594, which has been developed exclusively by BD Biosciences as a better alternative to PE-Texas Red®. PE-CF594 excites and emits at similar wavelengths to PE-Texas Red® yet exhibits improved brightness and spectral characteristics. Due to PE having maximal absorption peaks at 496 nm and 564 nm, PE-CF594 can be excited by the blue (488-nm), green (532-nm) and yellow-green (561-nm) lasers and can be detected with the same filter set as PE-Texas Red® (eg, 610/20-nm filter).
Development References (8)
-
Dominguez-Villar M, Gautron AS, de Marcken M, Keller MJ, Hafler DA. TLR7 induces anergy in human CD4+ T cells. Nat Immunol. 2015; 16(1):118-128. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Feasibility study: phospho-specific flow cytometry enabling rapid functional analysis of bone marrow samples from patients with multiple myeloma. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2014; 86B:139-144. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Mingueneau M, Kreslavsky T, Gray D, . The transcriptional landscape of alphabeta T cell differentiation. Nat Immunol. 2013; 14(6):619-632. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Natoli G, Saccani S, Bosisio D, Marazzi I. Interactions of NF-kappaB with chromatin: the art of being at the right place at the right time. Nat Immunol. 2005; 6(5):439-445. (Biology). View Reference
-
Siebenlist U, Brown K, Claudio E. Control of lymphocyte development by nuclear factor-kappaB. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005; 5:435-445. (Biology). View Reference
-
Suni MA, Maino VC. Flow cytometric analysis of cell signaling proteins. Methods Mol Biol. 2011; 717:155-169. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Viatour P, Merville M-P, Bours V, Chariot A. Phosphorylation of NF-kappaB and IkappaB proteins: implications in cancer and inflammation. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005; 30(1):43-52. (Biology). View Reference
-
van de Laar L, van den Bosch A, Boonstra A, et al. PI3K-PKB hyperactivation augments human plasmacytoid dendritic cell development and function. Blood. 2012; 120(25):4982-4991. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.