Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




αβ TCR expression in spleen and thymus. C57BL/6 splenocytes were simultaneously stained with FITC-conjugated anti-mouse CD4 mAb RM4-5 (Cat. No. 553046/553047, left panels), FITC-conjugated anti-mouse CD8a mAb 53-6.7 (Cat. No. 553030/553031, left panels), and purified H57-597 (bottom left panel) monoclonal antibodies, followed by PE-conjugated anti-hamster IgG (Cat. No. 554056, left panels). C57BL/6 thymocytes were stained with purified mAb H57-597 (bottom right panel), followed by PE-conjugated anti-hamster IgG (Cat. No. 554056, right panels). Flow cytometry was performed on a BD FACScan™ flow cytometry system.


BD Pharmingen™ Purified Hamster Anti-Mouse TCR β Chain

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
It has been observed that pre-incubation of thymus cell suspensions at 37°C for 2 to 4 hours prior to staining enhances the ability of anti-CD3e and anti-TCR β chain mAbs to detect that T cell receptor on immature thymocytes.
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Sodium azide is a reversible inhibitor of oxidative metabolism; therefore, antibody preparations containing this preservative agent must not be used in cell cultures nor injected into animals. Sodium azide may be removed by washing stained cells or plate-bound antibody or dialyzing soluble antibody in sodium azide-free buffer. Since endotoxin may also affect the results of functional studies, we recommend the NA/LE (No Azide/Low Endotoxin) antibody format, if available, for in vitro and in vivo use.
Companion Products

.png?imwidth=320)
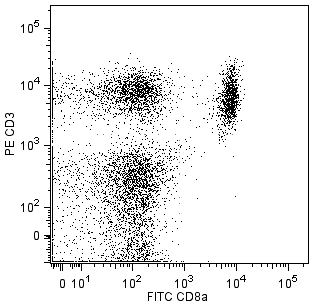

The H57-597 antibody reacts with a common epitope of the β chain of the T-cell Receptor (TCR) complex on αβ TCR-expressing thymocytes, peripheral T lymphocytes, NK1.1+ thymocytes, and NK-T cells of all mouse strains tested. It does not react with γδ TCR-bearing T cells. In the fetal and adult thymus, the TCR β-chain may form homodimers or pair with the pre-TCR α-chain on the surface of immature thymocytes before TCR α-chain expression. Plate-bound or soluble H57-597 antibody activates αβ TCR-bearing T cells, and plate-bound mAb can induce apoptotic death.
This antibody is routinely tested by flow cytometric analysis. Other applications were tested at BD Biosciences Pharmingen during antibody development only or reported in the literature.
Development References (17)
-
Atsuta N, Nishimura H, Nakamura N, Emoto M, Iwatsuki T, Yoshikai Y. Diversity of V gamma gene segments rearranged to the J gamma 4 gene in mice. J Immunol. 1995; 154(2):676-684. (Clone-specific: Depletion). View Reference
-
Bendelac A, Killeen N, Littman DR, Schwartz RH. A subset of CD4+ thymocytes selected by MHC class I molecules. Science. 1994; 263(5154):1774-1778. (Biology). View Reference
-
Bonneville M, Itohara S, Krecko EG, et al. Transgenic mice demonstrate that epithelial homing of gamma/delta T cells is determined by cell lineages independent of T cell receptor specificity. J Exp Med. 1990; 171(4):1015-1026. (Clone-specific: Immunohistochemistry). View Reference
-
Davenport C, Kumar V, Bennett M. Rapid rejection of H2k and H2k/b bone marrow cell grafts by CD8+ T cells and NK cells in irradiated mice. J Immunol. 1995; 155(8):3742-3749. (Clone-specific: Depletion). View Reference
-
Duke RC, Cohen JJ, Boehme SA, et al. Morphological, biochemical, and flow cytometric assays of apoptosis. In: Coligan J, Kruisbeek AM, Margulies D, Shevach EM, Strober W, ed. Current Protocols in Immunology. New York: John Wiley and Sons; 1995:3.17.1-3.17.33.
-
Gascoigne NR. Transport and secretion of truncated T cell receptor beta-chain occurs in the absence of association with CD3. J Biol Chem. 1990; 265(16):9296-9301. (Clone-specific: Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Groettrup M, von Boehmer H. T cell receptor beta chain dimers on immature thymocytes from normal mice. Eur J Immunol. 1993; 23(6):1393-1396. (Biology). View Reference
-
Kruisbeek AM, Shevach EM. Proliferative assays for T cell function. Curr Protoc Immunol. 2004; 3:3.12.1-3.12.14. (Clone-specific: Stimulation). View Reference
-
Kubo RT, Born W, Kappler JW, Marrack P, Pigeon M. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody which detects all murine alpha beta T cell receptors. J Immunol. 1989; 142(8):2736-2742. (Immunogen: Flow cytometry). View Reference
-
Lefrancois L. Phenotypic complexity of intraepithelial lymphocytes of the small intestine. J Immunol. 1991; 147(6):1746-1751. (Biology). View Reference
-
Ohno H, Ono S, Hirayama N, Shimada S, Saito T. Preferential usage of the Fc receptor gamma chain in the T cell antigen receptor complex by gamma/delta T cells localized in epithelia. J Exp Med. 1994; 179(1):365-369. (Clone-specific: Immunoprecipitation, Western blot). View Reference
-
Saint-Ruf C, Panigada M, Azogui O, Debey P, von Boehmer H, Grassi F. Different initiation of pre-TCR and gammadeltaTCR signalling. Nature. 2000; 406(6795):524-527. (Clone-specific: Immunoprecipitation, Western blot). View Reference
-
Saint-Ruf C, Ungewiss K, Groettrup M, Bruno L, Fehling HJ, von Boehmer H. Analysis and expression of a cloned pre-T cell receptor gene. Science. 1994; 266(5188):1208-1212. (Clone-specific: Stimulation). View Reference
-
Skeen MJ, Ziegler HK. Induction of murine peritoneal gamma/delta T cells and their role in resistance to bacterial infection. J Exp Med. 1993; 178(3):971-984. (Clone-specific: Depletion). View Reference
-
Vicari AP, Zlotnik A. Mouse NK1.1+ T cells: a new family of T cells. Immunol Today. 1996; 17(2):71-76. (Biology). View Reference
-
Wagner DH Jr, Hagman J, Linsley PS, Hodsdon W, Freed JH, Newell MK. Rescue of thymocytes from glucocorticoid-induced cell death mediated by CD28/CTLA-4 costimulatory interactions with B7-1/B7-2. J Exp Med. 1996; 184(5):1631-1638. (Clone-specific: Cytotoxicity, Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
van der Heyde HC, Elloso MM, Chang WL, Kaplan M, Manning DD, Weidanz WP. Gamma delta T cells function in cell-mediated immunity to acute blood-stage Plasmodium chabaudi adami malaria. J Immunol. 1995; 154(8):3985-3990. (Clone-specific: Depletion). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.