-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
- BD OMICS-One™ WTA Next Assay
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current location site or be switched to your location?

Intracellular Flow Cytometry
Intracellular flow cytometry is a powerful technique for the identification of cell types and the analysis of signaling and functional responses within cell lines and heterogeneous cell samples. For some cell types, such as Th17 and regulatory T cells (Tregs), definitive identification depends on the combined use of surface and intracellular markers such as cytokines or transcription factors. Intracellular flow cytometry also provides rich information concerning cellular function and signaling responses. Fluorescent antibodies specific for cell surface markers can be combined with markers of apoptosis, proliferation and protein phosphorylation to determine which cell subsets respond to various stimuli or treatments. The combined use of multiple markers decreases data acquisition time and conserves precious samples, since more parameters can be measured on a per-cell basis. While western blotting and other methods are useful for the examination of single proteins expressed by entire cell populations, flow cytometry allows the detection of multiple proteins simultaneously at the level of individual cells.
BD Biosciences provides fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies, buffers, kits and protocols to facilitate intracellular flow cytometry. Our antibodies are tested in biologically relevant model systems. These established tools enable new discoveries in fields such as immunology, inflammation and stem cell biology. Find the tools and techniques, including BD fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies, buffers, kits and protocols that support intracellular cytokine staining and phosphoprotein and transcription factor detection by intracellular flow cytometry.
Protocols for intracellular flow cytometry
Basic principles of intracellular staining
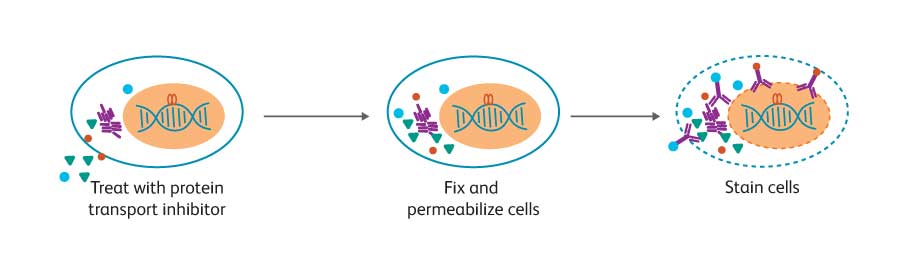
While techniques for cell surface staining are relatively standard, optimal staining for intracellular markers often depends on the biology of the target protein. Depending on the protein’s location inside the cell, association with other molecules, and its stability, different cell preparation and staining methods are recommended. Cytokines, for example, are typically secreted proteins.
However, if they are trapped inside the cell, they can be stained as intracellular proteins using protein transport inhibitors such as BD GolgiStop™ (containing monensin) or BD GolgiPlug™ (containing brefeldin A). Cytokines are relatively accessible using the gentle fixation and permeabilization afforded by BD Cytofix/ Cytoperm™ Fixation and Permeabilization Solution.
In contrast to cytokines, transcription factors often are localized inside the nucleus and bound to DNA and other proteins. Phosphorylation of some proteins, such as Stat5, results in dimer formation that masks the phosphorylated epitope of interest. Also, intracellular phosphatases can quickly dephosphorylate these proteins. Therefore, after treatment, cells must be quickly fixed and subjected to stronger permeabilization conditions to allow the antibody to enter the nucleus and access the epitope within disrupted molecular complexes.
Cells are fixed and permeabilized (symbolized by dashed line membrane), stained, and analyzed by flow cytometry. For studies on cytokine production, cells are first treated with a protein transport inhibitor to allow accumulation of the target protein inside the cell.
BD Biosciences provides tools to support intracellular flow cytometry
To facilitate intracellular flow cytometry assays, BD has developed several kits, buffers and protocols. In addition, many fluorescent antibodies specific for key cell surface markers have been tested in several buffer systems to save time, sample and money. Buffers are available for:
Detection of cytokines
BD Cytofix/Cytoperm™ Fixation/Permeabilization Solution (Cat. No. 554714) is suitable for staining most cytokines and cell surface markers. This buffer system can also be used to stain some transcription factors and other intracellular proteins. This buffer system contains mild detergents along with a formaldehyde-based fixative.
Transcription factors
The BD Pharmingen™ Transcription Factor Buffer Set (Cat. No. 562574/562725) is designed for the staining of transcription factors alone or in combination with cell surface markers and cytokines. This buffer system contains mild detergents along with a formaldehyde-based fixative.
Detection of phosphorylated protein
BD Phosflow™ Perm Buffer III (Cat. No. 558050) is the recommended permeabilization buffer for phosphoepitope detection by flow cytometry. Perm buffer III is a harsh alcohol-based buffer. Alternative permeabilization buffers also are available to accommodate particular experimental requirements. We also provide a convenient buffer compatibility tool, detailing many common clones and their compatibility with BD Phosflow™ Buffer protocols.
The permeabilization technique used can negatively impact the detection of cell surface and other intracellular antigens. The same techniques that allow access to the nucleus and open up DNA/protein or protein/protein complexes can often denature cell surface antigens, preventing their detection by antibodies. While detection of different intracellular proteins might require different conditions, the basic principles are the same: cells are fixed and permeabilized and then stained intracellularly with fluorescent antibodies.
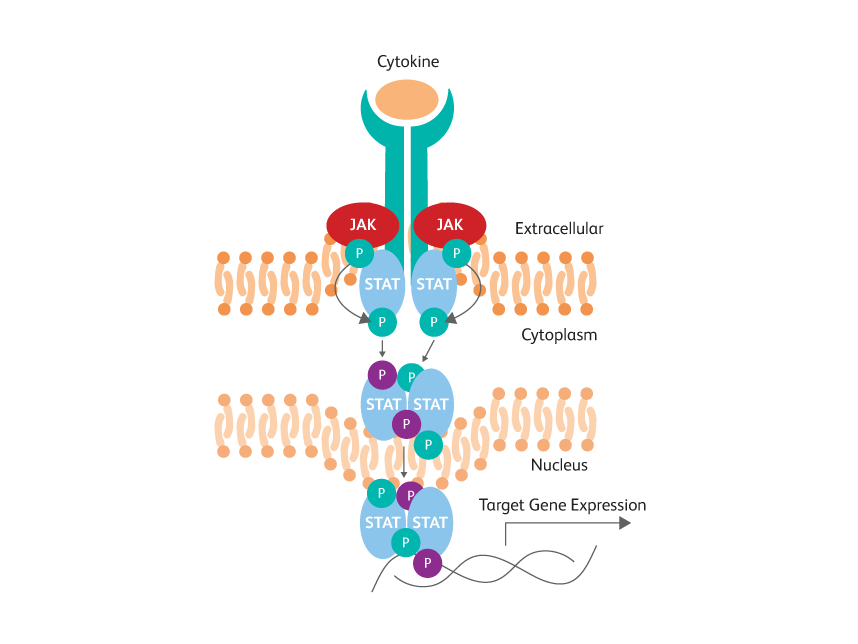
STAT phosphotyrosine epitopes are obscured by dimerization within activated cells.
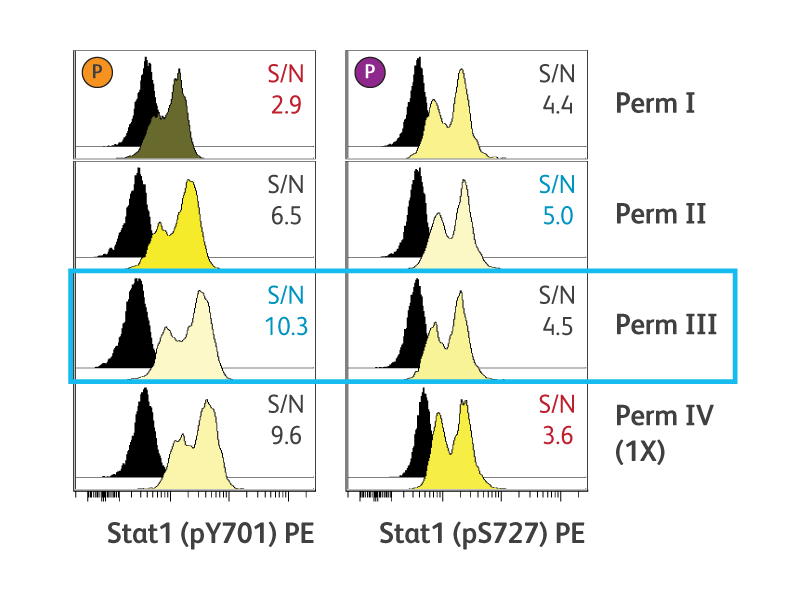
Optimal cell permeabilization conditions vary by epitope location.
Cytokine detection
Various activated cell types can secrete cytokines, chemokines and other inflammatory mediators such as perforin and granzymes as part of an immune or inflammatory response.
Methods such as ELISA and BD® Cytometric Bead Array (CBA) measure secreted proteins produced by entire cell populations. In contrast, intracellular flow cytometry allows the analysis of cytokines and other inflammatory mediators produced by individual, phenotypically identified cell types within cell populations of interest.
Intracellular flow cytometry makes it possible to easily determine if the cytokine production by an activated cell population is the result of a few cells producing large amounts of cytokine or a large population of cells producing small quantities of cytokine per cell. Moreover, intracellular flow cytometry makes it possible to easily measure multiple cytokines simultaneously, to identify polyfunctional cells.1 Intracellular cytokine staining is also useful for a variety of studies including B- and T-cell differentiation and plasticity.
Since cytokines typically are secreted proteins, they must first be trapped inside the cell by using a protein transport inhibitor. The two most commonly used protein transport inhibitors are monensin (BD GolgiStop™ Inhibitor) and brefeldin A (BD GolgiPlug™ Inhibitor). Monensin prevents protein secretion by interacting with the Golgi transmembrane Na++/H+ transport, while brefeldin A redistributes intracellularly produced proteins from the cis/medial Golgi complex to the endoplasmic reticulum.2 As a result, the best choice of protein transport inhibitor varies by cytokine and by species (see table below).
| Species | Cytokines | Transport Inhibitor |
|---|---|---|
| Human | IL-1α, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α | Monensin |
| Human | IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-10, IL-12, MCP-1, MCP-3, MIG, MIP-1α, RANTES | Either Monensin or Brefeldin A |
| Mouse | IL-6, IL-12, TNF-α | Brefeldin A |
| Mouse | GM-CSF, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-10 | Monensin |
| Mouse | IFN-γ, IL-2 | Either Monensin or Brefeldin A |
IFN-γ and IL-2 production in CD8+ cells
PBMCs were stimulated with staphylococcal enterotoxin B for 6 hours in the presence of brefeldin A. After stimulation, cells were fixed and permeabilized using the BD Cytofix/Cytoperm™ Buffer System. Cells were stained with the following fluorescent antibodies: CD3 FITC, CD4 PerCP-Cy5.5, CD8 BD Horizon Brilliant Violet™ 421, IFN-γ PE and IL-2 APC. Cells were then washed and analyzed using the BD FACSVerse™ Flow Cytometer.
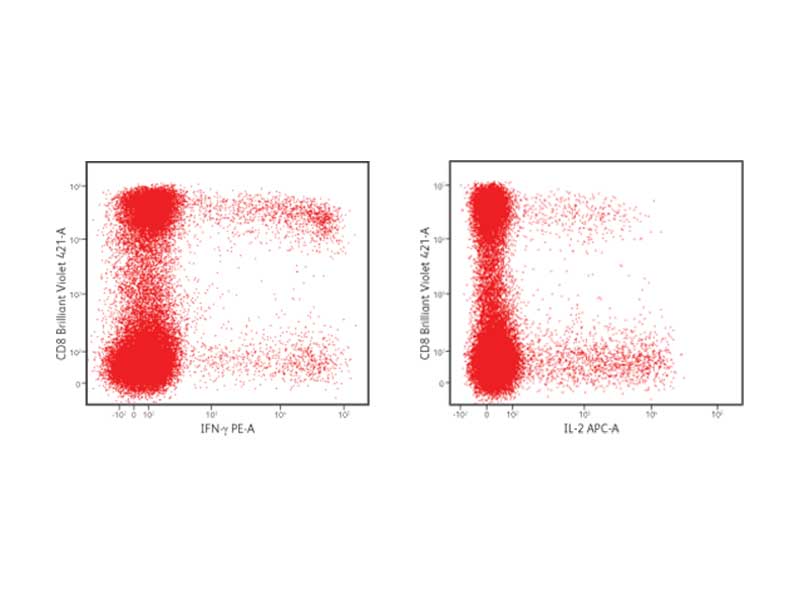
BD Biosciences has simplified the detection of cytokines and cell surface markers with kits, buffer systems and rich panels of fluorescent antibodies. Antibodies to surface markers and cytokines conjugated to a variety of fluorochromes are available. This allows for flexibility in staining panel design, supporting high content multicolor flow cytometric analyses to gain the most data from precious cell samples.
BD FastImmune™ Kits contain tested cocktails of fluorescent antibodies, an appropriate protein transport inhibitor, compatible buffers and a detailed protocol for the optimal preparation, staining and detection of cytokine-producing cells from whole blood. Onboard assays on the BD FACSVerse™ Flow Cytometer System further simplify the process.
BD Cytofix/Cytoperm™ Buffer has been cited in thousands of publications for the analysis of cytokine-producing cells by flow cytometry. Researchers select the protein transport inhibitor best suited to their cytokine of interest and use the BD Cytofix/Cytoperm™ Buffer System to fix, permeabilize and stain their cells for flow cytometric analysis.
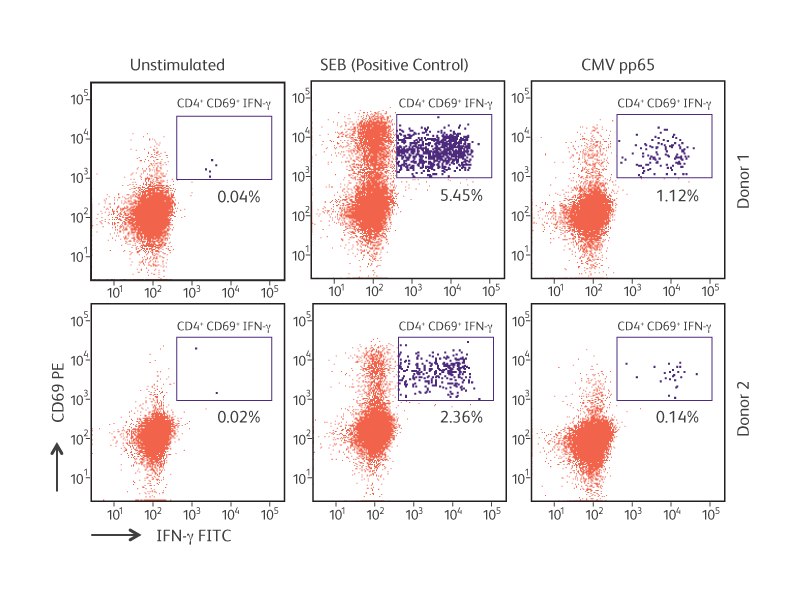
Antigen-specific IFN-γ production by cytomegalovirus (CMV) pp65-stimulated CD4+CD69+ T lymphocytes.
References
- Seder RA, Darrah PA, Roederer M. T-cell quality in memory and protection: implications for vaccine design. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(4):247-258. doi: 10.1038/nri2274
- Schuerwegh AJ, Stevens WJ, Bridts CH, De Clerck LS. Evaluation of monensin and brefeldin A for flow cytometric determination of interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factoralpha in monocytes. Cytometry. 2001;46(3):172-176. doi: 10.1002/cyto.1102
Transcription factors
Intracellular flow cytometry enables the detection of transcription factors and associated proteins within heterogeneous cell populations.
The simultaneous analysis of multiple markers allows for the determination of critical time points, markers and frequencies of cells moving along a particular differentiation pathway.
Transcription factors are proteins that bind to DNA and other proteins to regulate gene expression. They play key roles in cellular development and differentiation. Examples include FoxP3 for Treg differentiation and Sox17 for definitive endoderm differentiation.
FoxP3 is considered to be the master regulator of Tregs. Like many transcription factors, FoxP3 binds to thousands of genes, resulting in the up- or down-regulation of gene expression necessary for Treg function.1 SATB1, a genome organizer, is repressed by FoxP3, preventing the induction of T-effector cytokines, including IL-4 and IFN-γ.2
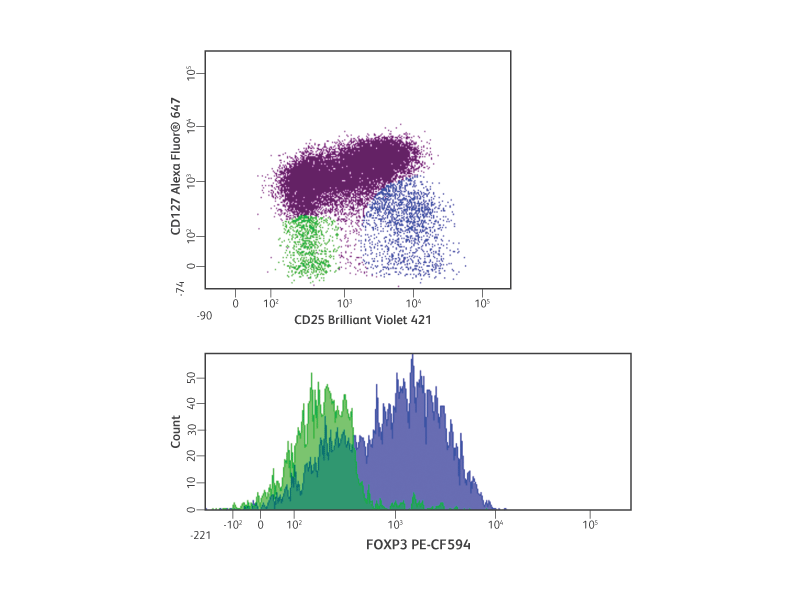
Detection of human Tregs by intracellular flow cytometry.
Similar to intracellular cytokine staining, transcription factor detection using flow cytometry requires cellular fixation and permeabilization. Transcription factors are typically located in the nucleus bound to DNA and other proteins. Depending on the nature of the target molecule epitopes, different fixation and permeabilization buffers might be necessary.
The fixation and permeabilization of cells can compromise cell surface marker staining, which makes the choice of compatible buffers even more critical. To further enable easy transcription factor detection, BD Biosciences has developed the BD Pharmingen™ Transcription Factor Buffer Set. This buffer permeabilizes cells sufficiently to allow exposure of intranuclear epitopes and is compatible with many cell types, cell surface staining and tandem dyes.
Convenient kits for the study of stem cell differentiation
As pluripotent stem cells differentiate into different cell types, expression of transcription factors and other proteins changes. In mammalian embryonic development, the definitive endoderm generates the liver, pancreas and
intestine.3-5 During specification into definitive endoderm, levels of the transcription factors Sox17 and FoxA2 and the cell surface marker CD184 (CXCR4) increase, while pluripotency markers such as Nanog and Sox2 decrease.6
Multicolor flow cytometry is an excellent method for determining the relative numbers of cells expressing markers of interest. This is useful for the study of cell differentiation pathways and specifically for the optimization, quantification and comparison of differentiation protocols and the differentiation potentials of different cells.
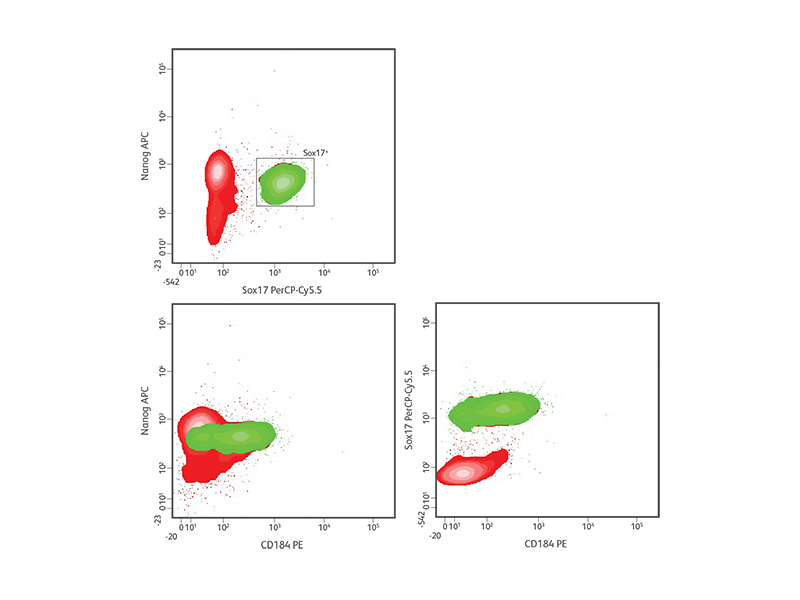
Definitive endoderm differentiation of H9 hESCs.
To facilitate the study of transcription factors in stem cells, BD has developed several kits for the detection of key stem cell–specific transcription factors including the BD Stemflow™ Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Transcription Factor Analysis Kit (Cat. No. 560589), the BD Stemflow™ Mouse Pluripotent Stem Cell Transcription Factor Analysis Kit (Cat. No. 560585), the BD Stemflow™ Human Neural Cell Lineage Analysis Kit (Cat. No. 561526), and the BD Stemflow™ Human Definitive and Pancreatic Endoderm Analysis Kit (Cat. No. 562496). These kits contain antibodies and buffer systems to characterize pluripotent stem cells and track the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into respective lineages.
References
- Birzele F, Fauti T, Stahl H, et al. Next-generation insights into regulatory T cells: expression profiling and FoxP3 occupancy in Human. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39(18):7946-7960. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr444
- Beyer M, Thabet Y, Müller RU, et al. Repression of the genome organizer SATB1 in regulatory T cells is required for suppressive function and inhibition of effector differentiation. Nat Immunol. 2011;12(9):898-907. doi: 10.1038/ni.2084
- Wang P, McKnight KD, Wong DJ, et al. A molecular signature for purified definitive endoderm guides differentiation and isolation of endoderm from mouse and human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(12):2273-2287. doi: 10.1089/scd.2011.0416
- Takayama K, Inamura M, Kawabata K, et al. Efficient and directive generation of two distinct endoderm lineages from human ESCs and iPSCs by differentiation stage-specific SOX17 transduction. PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e21780. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021780
- Murry CE, Keller G. Differentiation of embryonic stem cells to clinically relevant populations: lessons from embryonic development. Cell. 2008;132(4):661-680. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.02.008
- D’Amour KA, Agulnick AD, Eliazer S, Kelly OG, Kroon E, Baetge EE. Efficient differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to definitive endoderm. Nat Biotechnol. 2005;23(12):1534-1541. doi: 10.1038/nbt1163
Phosphorylation
With the ability to collect data at the level of individual cells, flow cytometry offers several advantages for cell signaling studies.
Unlike lysate-based approaches, flow cytometry facilitates the detection and analysis of heterogeneous signaling responses. Thus, it is possible to distinguish between a robust protein phosphorylation response within a small population of cells versus a smaller but more homogeneous response. With the addition of fluorescent antibodies specific for cell surface markers to cell subsets within complex cell mixtures such as whole blood, signaling responses mediated by protein phosphorylation can be detected. Moreover, rare cell populations can be uncovered without pre-enrichment of the cells. As a result, rich data are obtained from limited cell samples.
BD Phosflow™ products consist of a system of buffers and fluorescent monoclonal antibodies optimized for the flow cytometric detection of intracellular signaling molecules and specific posttranslational modifications. To detect specific phosphorylated epitopes by flow cytometry, cells are fixed to maintain the phosphorylated state of signaling proteins and then permeabilized to allow antibodies to enter cells and specifically bind to target proteins. Flow cytometric analysis of stained cells can then capture a snapshot of intracellular signaling and protein phosphorylation.
Protein phosphorylation is transient by nature and heavily regulated by protein phosphatases. Appropriate stimulation time points and prompt inactivation of phosphatases are required for most methods of phosphoprotein detection, including western blot analysis. Likewise, cell samples for flow cytometric analysis must be quickly fixed to maintain phosphoepitopes. Another important consideration is the level of phosphoprotein expression. Certain protein phosphorylation events can be difficult to detect at the single-cell level, particularly when cells express low levels of a particular signaling protein or exhibit incomplete phosphorylation of the site of interest. BD offers high-quality antibodies directly conjugated to bright fluorochromes to greatly improve the intracellular detection of phosphoprotein.
Multiparameter flow cytometry offers key advantages for the detection and analysis of intracellular signaling within cells and cell subsets in complex mixtures. Since cell signaling studies often examine cellular responses to treatment with stimulatory or inhibitory molecules, unstimulated or untreated cells often provide the best controls for evaluating background staining. Unlike an immunoglobulin isotype control, an unstimulated cell control accounts for the unique background characteristics of each antibody as well as the basal phosphoprotein expression levels within the cells of interest. Cellular permeabilization is required to expose phosphorylated epitopes. Although multiple buffer systems are available, BD Phosflow™ Perm Buffer III is recommended for most applications. The BD Biosciences website contains useful information about the performance of various BD cell surface marker and intracellular antibodies in different buffer conditions and staining protocols.
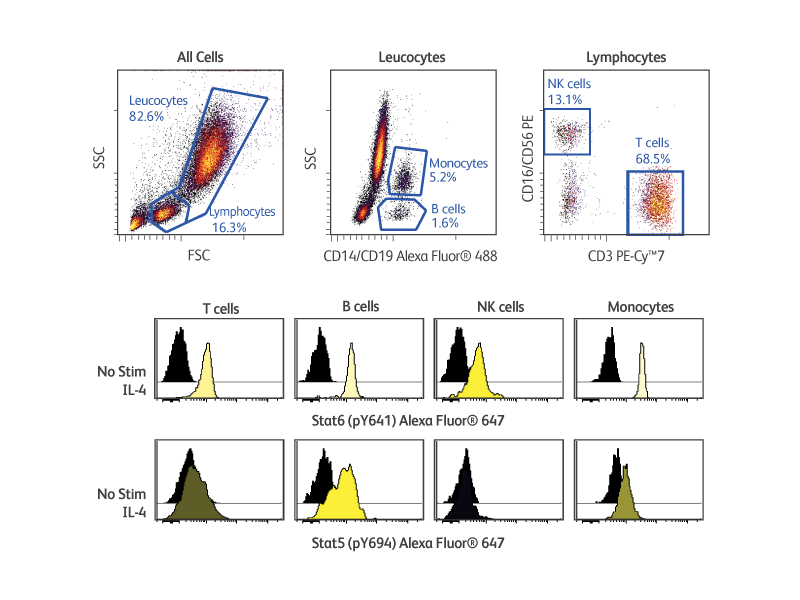
BD Phosflow™ Kits provide useful tools for analyzing the signaling responses elicited by cells of the adaptive and innate immune systems. These kits include fluorescent antibody cocktails specific for cell surface markers to identify specific leucocyte subsets as well as fluorescent antibodies to key phosphoproteins. In addition, the kits provide compatible buffers, positive and negative control cells, and detailed protocols. The BD Phosflow™ Human Monocyte/NK Cell Activation Kit (Cat. No. 562089) allows the simultaneous study of protein phosphorylation in B cells, T cells, monocytes and NK cells from human whole blood, while the BD Phosflow™ Human T-Cell Activation Kit (Cat. No. 560750) is useful for the study of phosphoprotein responses in CD4 versus CD8 T cells.
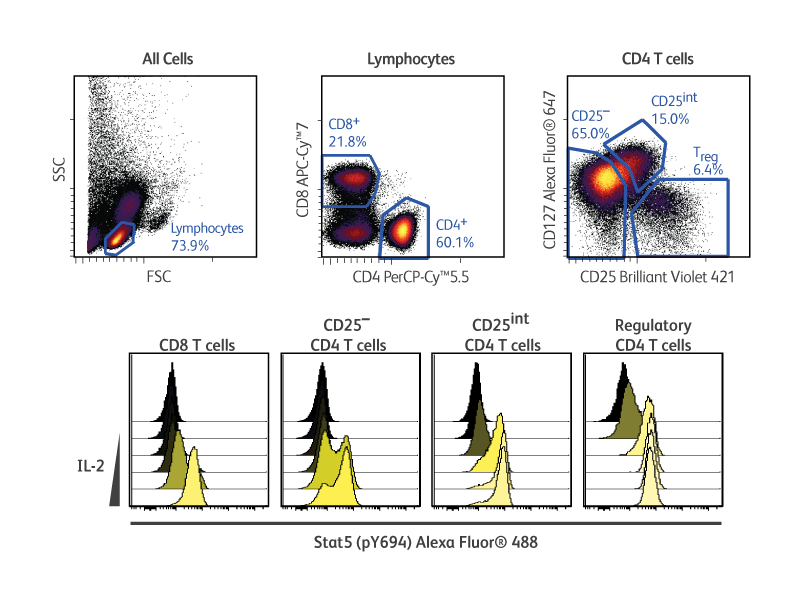
Multiplexing
While other techniques can measure either cytokines, transcription factors or phosphorylated proteins separately, intracellular flow cytometry enables the measurement of multiple intracellular markers simultaneously at the single-cell level.
This method provides data on signaling responses, differentiation states and other cellular events. The combined use of fluorescent antibodies specific for cell surface and intracellular markers enables high-resolution comparative analyses of the phenotypic and functional differences within multiple cell types across samples.
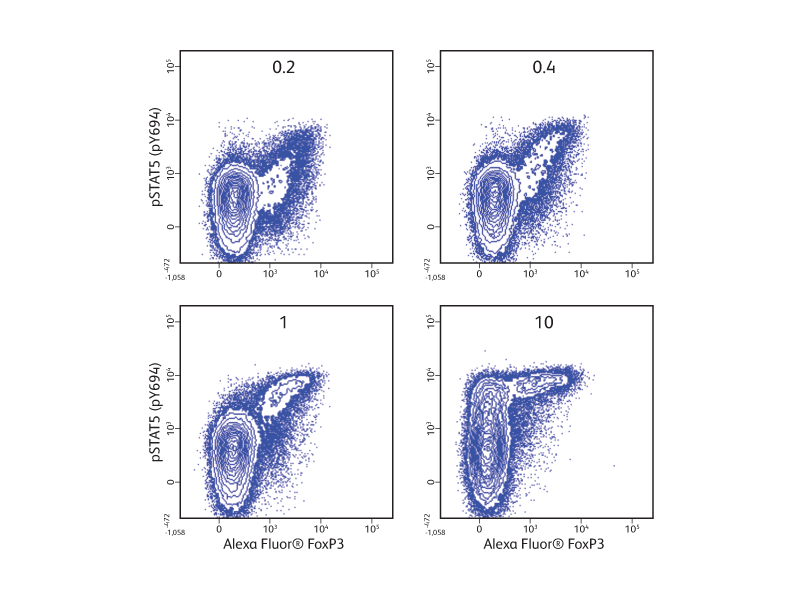
In the example shown (right), cryopreserved PBMCs were stimulated with increasing concentrations of human recombinant IL-2 prior to fixation, permeabilization and staining with surface and intracellular markers. The use of the BD Pharmingen™ Transcription Factor Phospho Buffer Set enabled the otherwise challenging simultaneous detection of phosphorylated STAT5 and transcription factor FoxP3 in regulatory T cells in response to IL-2.
The simultaneous measurement of the expressed levels of multiple transcription factors, cytokines and surface markers by cells within the same sample is very useful for the study of T helper (Th) cell differentiation and function. RORγt is the signature transcription factor for Th17 cells. It is important for the secretion of IL-17 and the maintenance of CD4+CD8+ double-positive thymocytes.1,2
In the experimental results shown (right), cells were isolated from BALB/c mouse thymus and spleen. Thymocytes or splenocytes were surface stained with fluorescent antibodies specific for CD44, CD62L, CD196 or appropriate immunoglobulin isotype controls. Cells were fixed and permeabilized with the BD Pharmingen™ Transcription Factor Buffer Set and then intracellularly stained with fluorescent antibodies specific for RORγt, Foxp3, IL-17A and IFN-γ.
In the top panel, the cellular expression of IL-17A is compared with the expression of RORγt, Foxp3 (Treg transcription factor) and IFN-γ (Th1 cytokine). As expected in thymocytes, there were many IL-17A+ RORγt+ double-positive cells, while there was essentially no co-expression of IL-17A with Foxp3 or IFN-γ. Splenocytes expressed very little IL-17A.
In the bottom panel, further analysis revealed that IL-17A– producing cells from spleen expressed the surface markers CD44 and CD196 (CCR6) but not CD62L, providing additional information on the phenotype of IL-17A+ cells.
BD Biosciences also provides several protocols for intracellular flow cytometry.
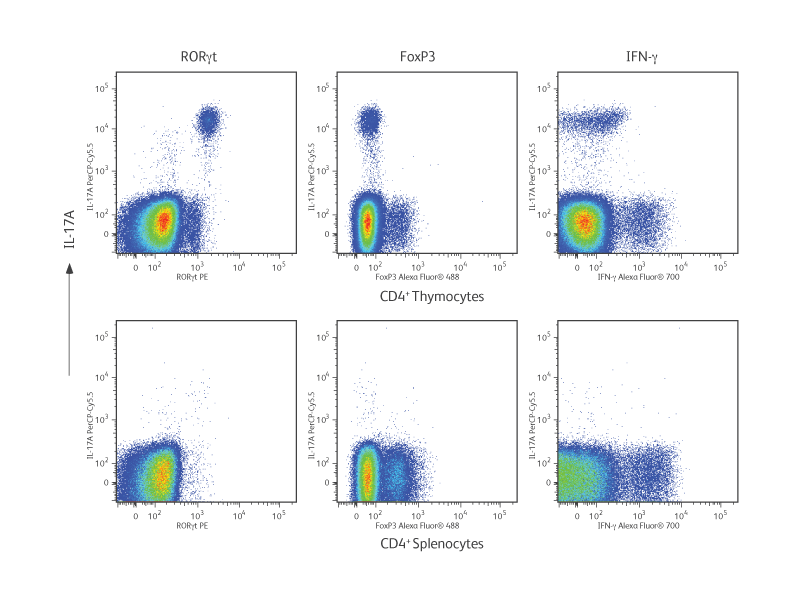
Phenotypic analysis of Th17 cells from BALB/c thymus and spleen.
References
- Ghoreschi K, Laurence A, Yang XP, Hirahara K, O’Shea JJ. T helper 17 cell heterogeneity and pathogenicity in autoimmune disease. Trends Immunol. 2011;32(9):395-401. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2011.06.007
- Ivanov II, McKenzie BS, Zhou L, et al. The orphan nuclear receptor RORgammat directs the differentiation program of proinflammatory IL-17+ T helper cells. Cell. 2006;126(6):1121-1133. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.07.035
-
Brochures
-
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Product Information Sheets
-
BD Pharmingen™ Transcription Factor Buffer Set
-
BD Pharmingen™ Transcription Factor PhosphoPlus Buffer Set
-
BD FACSelect™ Buffer Compatibility Resource
-
BD Phosflow™ Human CrkL (pY207) Monoclonal Antibodies
-
BD Phosflow™ Human Monocyte/NK Cell Activation Kit
-
BD Phosflow™ Smad Monoclonal Antibodies
-
BD Phosflow™ T Cell Activation Kit (Human)
-
Protocols
-
96 Deep-Well BD Phosflow™ Staining with Cytokine Stimulation
-
BD Phosflow™ 96-Well Deep-Well Plate Protocol
-
BD Phosflow™ Alternative Protocol 1: Fix–Stain–Perm
-
BD Phosflow™ Alternative Protocol 2: Stain–Fix–Perm
-
BD Phosflow™ Protocol for Adherent Cells
-
BD Phosflow™ Protocols for Human PBMCs
-
BD Phosflow™ Protocols for Human Whole Blood Samples
-
BD Phosflow™ Protocols for Mouse Splenocytes or Thymocytes
-
BD Phosflow™ Protocols for TCR Stimulation: Human
-
Intracelluar Flow and Phosflow FAQ
-
Live Cell Discrimination and Simultaneous Measurement of Phosphorylation and Cell Surface Markers in Thawed and Activated Human PBMCs Using BD Horizon™ Fixable Viability Stain 450, BD Cytofix™ Fixation Buffer and BD Phosflow™ Perm Buffer III
-
Simultaneous Measurement of Cell Surface Markers with Cellular Proliferation and Protein Phosphorylation
-
Simultaneous Measurement of Cell Surface Markers with T-bet and Stat5 (pY694) in IL-2–Stimulated Human Whole Blood using BD Phosflow™ Lyse/Fix Buffer and BD Phosflow™ Perm Buffer III
-
Suggested Stimulation Conditions for Phosphoprotein Detection
-
Tools
-
Webinars
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Alexa Fluor is a trademark of Life Technologies Corporation.
CF is a trademark of Biotium, Inc.
Cy is a trademark of Global Life Sciences Solutions Germany GmbH or an affiliate doing business as Cytiva.
Cytobank is a trademark of Beckman Coulter, Inc.