Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?
.png)
.png)
Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Product Notices
- Since applications vary, each investigator should titrate the reagent to obtain optimal results.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products


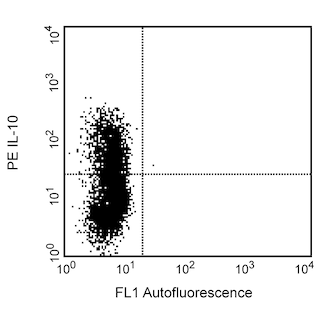



The FR70 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to mouse CD70, a 30-33-kDa type-II transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the TNF/NGF superfamily. CD70 is the ligand for CD27 and is expressed primarily on activated B cells. CD70 expression can be induced by activation of splenocytes with lipopolysaccharide and stimulatory antibodies specific for IgM, CD40 or both. mRNA coding for CD70 is transiently expressed after Concanavalin A stimulation of splenocytes or thymocytes. CD70 has been observed to be expressed on dendritic cells of Leishmania major-infected mice. The CD27-CD70 interaction delivers costimulatory signals to T cells and NK cells. It has been reported that FR70 antibody blocks binding of mCD27-Ig fusion protein to mouse Cd70-transfected cells and inhibits some in vitro T-cell- and NK-cell-dependent responses.
Development References (7)
-
Akiba H, Miyahira Y, Atsuta M. Critical contribution of OX40 ligand to T helper cell type 2 differentiation in experimental leishmaniasis. J Exp Med. 2000; 191(2):375-382. (Biology). View Reference
-
Akiba H, Oshima H, Takeda K, et al. CD28-independent costimulation of T cells by OX40 ligand and CD70 on activated B cells. J Immunol. 1999; 162(12):7058-7066. (Biology). View Reference
-
Hartwig UF, Karlsson L, Peterson PA, Webb SR. CD40 and IL-4 regulate murine CD27L expression. J Immunol. 1997; 159(12):6000-6008. (Biology). View Reference
-
Oshima H, Nakano H, Nohara C. Characterization of murine CD70 by molecular cloning and mAb. Int Immunol. 1998; 10(4):517-526. (Immunogen). View Reference
-
Takeda K, Oshima H, Hayakawa Y, et al. CD27-mediated activation of murine NK cells. J Immunol. 2000; 164(4):1741-1745. (Biology). View Reference
-
Taraban VY, Martin S, Attfield KE, et al. Invariant NKT cells promote CD8+ cytotoxic T cell responses by inducing CD70 expression on dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2008; 180(7):4615-4620. (Clone-specific). View Reference
-
Tesselaar K, Gravestein LA, van Schijndel GM, Borst J, van Lier RA. Characterization of murine CD70, the ligand of the TNF receptor family member CD27. J Immunol. 1997; 159(10):4959-4965. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.