Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?


Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
For optimal and reproducible results, BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer should be used anytime two or more BD Horizon Brilliant dyes (including BD OptiBuild Brilliant reagents) are used in the same experiment. Fluorescent dye interactions may cause staining artifacts which may affect data interpretation. The BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer was designed to minimize these interactions. More information can be found in the Technical Data Sheet of the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer (Cat. No. 563794).
Product Notices
- This antibody was developed for use in flow cytometry.
- The production process underwent stringent testing and validation to assure that it generates a high-quality conjugate with consistent performance and specific binding activity. However, verification testing has not been performed on all conjugate lots.
- Researchers should determine the optimal concentration of this reagent for their individual applications.
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Ultraviolet 661 is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,227,187; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
Companion Products
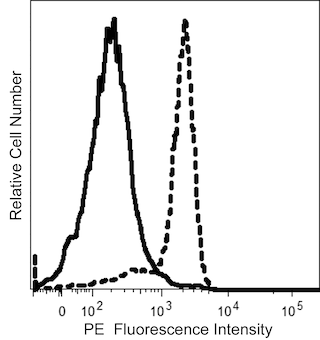





The IA10 monoclonal antibody specifically binds to CD55, which is also known as complement decay-accelerating factor (DAF). CD55 is a glycophosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored, single chain membrane glycoprotein of approximately 70 kDa that belongs to the regulators of complement activation (RCA) gene family which includes CD21, CD35, and CD46. CD55 is widely expressed on hematopoietic cells including platelets and erythrocytes, as well as on many non-hematopoietic cells, such as, endothelial cells and epithelial cells. CD55 is involved in protecting cells from damage by autologous activated complement complexes. CD55 prevents the amplification steps of the complement cascade by interfering with the assembly of the C3-convertases, C4b2a and C3bBb, and the C5-convertases, C4b2a3b and C3bBb3b.
The antibody was conjugated to BD Horizon™ BUV661 which is part of the BD Horizon Brilliant™ Ultraviolet family of dyes. This dye is a tandem fluorochrome of BD Horizon BUV395 with an Ex Max of 348-nm and an acceptor dye with an Em Max at 661-nm. BD Horizon Brilliant BUV661 can be excited by the ultraviolet laser (355 nm) and detected with a 670/25 filter and a 630 nm LP. Due to cross laser excitation of this dye, there may be significant spillover into channels detecting APC-like emissions (eg, 670/25-nm filter).
Due to spectral differences between labeled cells and beads, using BD™ CompBeads can result in incorrect spillover values when used with BD Horizon BUV661 reagents. Therefore, the use of BD CompBeads or BD CompBeads Plus to determine spillover values for these reagents is not recommended. Different BUV661 reagents (eg, CD4 vs. CD45) can have slightly different fluorescence spillover therefore, it may also be necessary to use clone-specific compensation controls when using these reagents.
Development References (5)
-
Coyne KE, Hall SE, Thompson S, et al. Mapping of epitopes, glycosylation sites, and complement regulatory domains in human decay accelerating factor. J Immunol. 1992; 149(9):2906-2913. (Clone-specific: Blocking, Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Kinoshita T, Medof ME, Silber R, Nussenzweig V. Distribution of decay-accelerating factor in the peripheral blood of normal individuals and patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. J Exp Med. 1985; 162(1):75-92. (Immunogen: Blocking, Flow cytometry, Functional assay, Inhibition, Western blot). View Reference
-
Klickstein LB, Springer TA. CD55 cluster report. In: Schlossman SF. Stuart F. Schlossman .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing V : white cell differentiation antigens : proceedings of the fifth international workshop and conference held in Boston, USA, 3-7 November, 1993. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1995:1473-1474.
-
Loveland BE, Szokolai K, Johnstone RW, McKenzie IF. Coordinate functions of multiple complement regulating molecules, CD46, CD55, and CD59. Transplant Proc. 1994; 26(3):1070-1071. (Biology). View Reference
-
Membrane cofactor protein (MCP or CD46): newest member of the regulators of complement activation gene cluster. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991; 9:431-455. (Biology). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.