-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
- BD OMICS-One™ WTA Next Assay
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current location site or be switched to your location?
BD OptEIA™ Mouse GM-CSF ELISA Set


Serial dilutions within the plate may also be performed by pipetting 100µL of Assay Diluent into each standard well except the highest (1000 pg/mL), then adding 100 µL of the 1000 pg/mL standard to both that well and the 500 pg/mL well, mixing the well contents by rinsing the pipette tip, and adding 100 µL of the 500 pg/mL standard to the 250 pg/mL well. Continue these dilutions to the 15.6 pg/mL standard well, out of which the extra 100 µL should be discarded.



This standard curve is for demonstration only. A standard curve must be run with each assay. Typical Standard Curve and 20-plate yield were obtained in the BD Biosciences Pharmingen laboratory, using the recommended procedure and manual plate washing.
Serial dilutions within the plate may also be performed by pipetting 100µL of Assay Diluent into each standard well except the highest (1000 pg/mL), then adding 100 µL of the 1000 pg/mL standard to both that well and the 500 pg/mL well, mixing the well contents by rinsing the pipette tip, and adding 100 µL of the 500 pg/mL standard to the 250 pg/mL well. Continue these dilutions to the 15.6 pg/mL standard well, out of which the extra 100 µL should be discarded.

This standard curve is for demonstration only. A standard curve must be run with each assay. Typical Standard Curve and 20-plate yield were obtained in the BD Biosciences Pharmingen laboratory, using the recommended procedure and manual plate washing.

Serial dilutions within the plate may also be performed by pipetting 100µL of Assay Diluent into each standard well except the highest (1000 pg/mL), then adding 100 µL of the 1000 pg/mL standard to both that well and the 500 pg/mL well, mixing the well contents by rinsing the pipette tip, and adding 100 µL of the 500 pg/mL standard to the 250 pg/mL well. Continue these dilutions to the 15.6 pg/mL standard well, out of which the extra 100 µL should be discarded.








Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Description
The OptEIA™ Set for mouse granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) contains the components necessary to develop enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) for natural or recombinant mouse GM-CSF in serum, plasma, and cell culture supernatants. Sufficient materials are provided to yield approximately 20 plates of 96-wells if the recommended storage, materials, buffer preparation, and assay procedure are followed as specified in this package.
Assay Optimization
BD OptEIA™ Sets allow flexible assay design to fit individual laboratory needs. To design an immunoassay with different sensitivity and dynamic range, the following parameters can be varied: Capture, Detection Antibody titers, Incubation time, Incubation temperature, Assay Diluent formulation, Buffer pH, ionic strength, protein concentration, Type of substrate, Washing technique (i.e., number of wash repetitions and soak times)
Standardization: This immunoassay is calibrated against purified Baculovirus-expressed recombinant mouse GM-CSF.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
Recommended buffers, solutions
Note: Do not use sodium azide in these preparations. Sodium azide inactivates the horseradish peroxidase enzyme.
The BD OptEIA™ Reagent Set B (Cat. No 550534) containing Coating Buffer, Assay Diluent, Substrate Reagents A and B, Stop Solution and 20X Wash Buffer Concentrate is recommended.
1. Coating Buffer - 0.1 M Sodium Carbonate, pH 9.5; 7.13 g NaHCO3, 1.59 g Na2CO3; q.s. to 1.0 L; pH to 9.5 with 10 N NaOH.
Freshly prepare or use within 7 days of preparation, stored at 2-8°C.
2. Assay Diluent- PBS* with 10% FBS#, pH 7.0. The BD Pharmingen™ Assay Diluent (Cat. No. 555213) is recommended.
*Phosphate-Buffered Saline: 80.0 g NaCl, 11.6 g Na2HPO4, 2.0 g KH2PO4, 2.0 g KCL, q.s. to 10 L; pH to 7.0.
#Fetal Bovine Serum: Hyclone Cat. No. SH30088 (heatinactivated) recommended.
Freshly prepare or use within 3 days of preparation, with 2-8°C storage.
3. Wash Buffer - PBS* with 0.05% Tween-20. Freshly prepare or use within 3 days of preparation, stored at 2-8°C.
4. Substrate Solution - Tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) and Hydrogen Peroxide. The BD Pharmingen™ TMB Substrate Reagent Set (Cat. No. 555214) is recommended.
5. Stop Solution - 1 M H3PO4 or 2 N H2SO4
Additional Materials Required
1. 96-well BD Falcon™ ELISA plates (Cat. No. 353279) are recommended
2. Microplate reader capable of measuring absorbance at 450 nm
3. Precision pipettes
4. Graduated cylinder, one liter
5. Deionized or distilled water
6. Wash bottle or automated washer
7. Log-log graph paper or automated data reduction
8. Tubes to prepare standard dilutions
9. Laboratory timer
10. Plate sealers or parafilm
Specimen Collection and Handling:Specimens should be clear, non-hemolyzed and non-lipemic.
Cell culture supernatants: Remove any particulate material by centrifugation and assay immediately or store samples at ≤-20°C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Serum: Use a serum separator tube and allow samples to clot for 30 minutes, then centrifuge for 10 minutes at 1000 x g. Remove serum and assay immediately or store samples at ≤ -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Plasma: Collect plasma using citrate, EDTA, or heparin as anticoagulant. Centrifuge for 10 minutes at 1000 x g within 30 minutes of collection. Assay immediately or store samples at ≤-20°C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Standards Preparation and Handling
1. Reconstitution: After warming lyophilized standard to room temperature, carefully open vial to avoid loss of material. Reconstitute lyophilized standard with 1.0 mL of deionized water to yield a stock standard. Allow the standard to equilibrate for at least 15 minutes before making dilutions. Vortex gently to mix.
2. Storage/ handling of reconstituted standard: After reconstitution, immediately aliquot standard stock in polypropylene vials at 50 µl per vial and freeze at -80°C for up to 6 months. If necessary, store at 2-8°C for up to 8 hours prior to aliquotting/freezing. Do not leave reconstituted standard at room temperature.
3. Standards Preparation for Assay:
a. Prepare a 1000 pg/mL standard from the stock standard. Vortex to mix. (See dilution instructions on Instruction/Analysis Certificate.)
b. Add 300 µL Assay Diluent to 6 tubes. Label as 500 pg/mL, 250 pg/mL, 125 pg/mL, 62.5 pg/mL, 31.3 pg/mL, and 15.6 pg/mL.
c. Perform serial dilutions by adding 300 µL of each standard to the next tube and vortexing between each transfer. Assay Diluent serves as the zero standard (0 pg/mL).
Working Detector Preparation
(Note: One-step incubation of Biotin/SAv reagents.) Add required volume of Detection Antibody to Assay Diluent. Within 15 minutes prior to use, add required quantity of Enzyme Reagent, vortex or mix well. For recommended dilutions, see lot-specific Instruction/Analysis Certificate. For a full 96-well plate, prepare 12 mL of Working Detector. Discard any remaining Working Detector after use.
Detailed Assay Procedure
1. Coat microwells with 100 µL per well of Capture Antibody diluted in Coating Buffer. For recommended antibody coating dilution, see lot-specific Instruction/Analysis Certificate. Seal plate and incubate overnight at 4°C.
2. Aspirate wells and wash 3 times with ≥ 300 µL/well Wash Buffer. After last wash, invert plate and blot on absorbent paper to remove any residual buffer.
3. Block plates with ≥ 200 µL/well Assay Diluent. Incubate at RT for 1 hour.
4. Aspirate/wash as in step 2.
5. Prepare standard and sample dilutions in Assay Diluent. See "Standards Preparation and Handling".
6. Pipette 100 µL of each standard, sample, and control into appropriate wells. Seal plate and incubate for 2 hours at RT.
7. Aspirate/ wash as in step 2, but with 5 total washes.
8. Add 100 µL of Working Detector (Detection Antibody + SAv-HRP reagent) to each well. Seal plate and incubate for 1 hour at RT.
9. Aspirate/ wash as in step 2, but with 7 total washes. NOTE: In this final wash step, soak wells in wash buffer for 30 seconds to 1 minute for each wash.
10. Add 100 µL of Substrate Solution to each well. Incubate plate (without plate sealer) for 30 minutes at room temperature in the dark.
11. Add 50 µL of Stop Solution to each well.
12. Read absorbance at 450 nm within 30 minutes of stopping reaction. If wavelength correction is available, subtract absorbance at 570 nm from absorbance 450 nm.
Assay Procedure Summary
1. Add 100 µL diluted Capture Ab to each well. Incubate overnight at 4°C.
2. Aspirate and wash 3 times.
3. Block plates: 200 µL Assay Diluent to each well. Incubate 1 hr RT
4. Aspirate and wash 3 times.
5. Add 100 µL standard or sample to each well. Incubate 2 hr RT.
6. Aspirate and wash 5 times.
7. Add 100 µL Working Detector (Detection Ab + SAv-HRP) to each well. Incubate 1 hr RT
8. Aspirate and wash 7 times (with 30 sec to 1 min soaks)
9. Add 100 µL Substrate Solution to each well. Incubate 30 min RT in dark
10. Add 50 µL Stop Solution to each well. Read at 450 nm within 30 min with λ correction 570 nm.
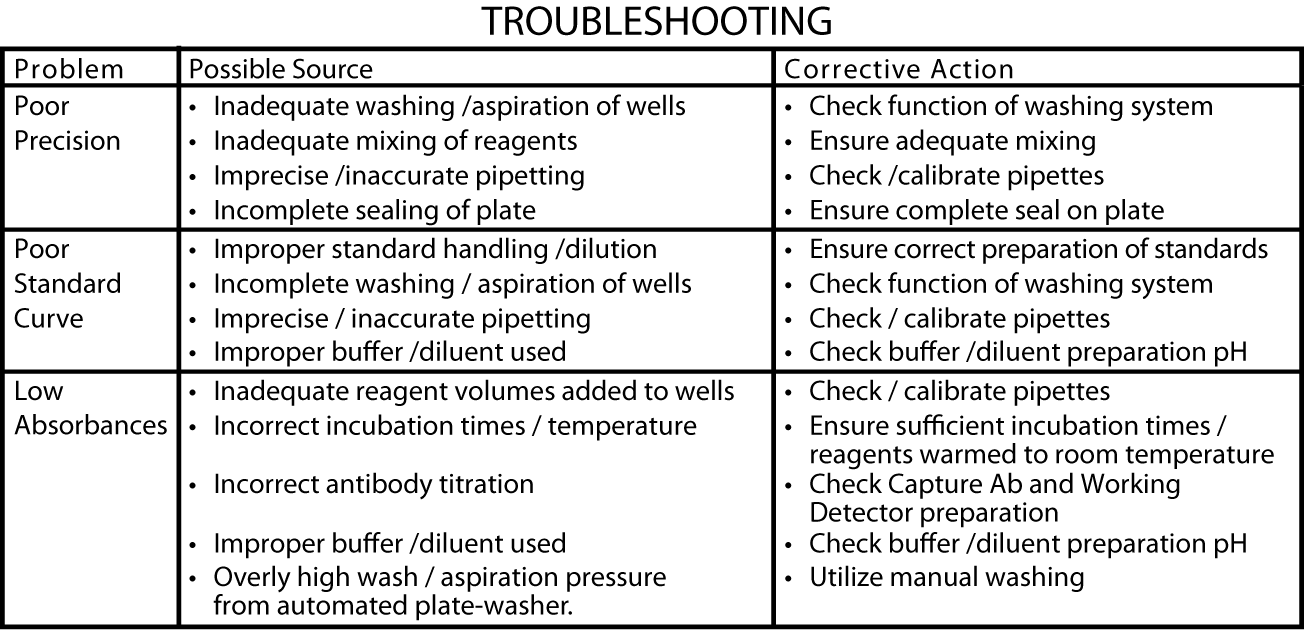
Calculation of Results
Calculate the mean absorbance for each set of duplicate standards, controls and samples. Subtract the mean zero standard absorbance from each.
Plot the standard curve on log-log graph paper, with GM-CSF concentration on the x-axis and absorbance on the y-axis. Draw the best fit curve through the standard points.
To determine the GM-CSF concentration of the unknowns, find the unknown's mean absorbance value on the y-axis and draw a horizontal line to the standard curve. At the point of intersection, draw a vertical line to the x-axis and read the GM-CSF concentration. If samples were diluted, multiply the GM-CSF concentration by the dilution factor.
Computer data reduction may also be employed, utilizing log-log regression analysis.
Specificity
Cross Reactivity: The following factors were tested in the BD OptEIA™ assay at ≥ 10 ng/mL and no cross-reactivity (value ≥ 4 pg/mL) was identified.
Recombinant Human: IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-7, IL-8, IL-9, IL-10, IL-11, IL-12 (p40), IL-12 (p70), IL-13, IL-15, G-CSF, GM-CSF, IFN-γ, CD23, Lymphotactin, MIP-1α, MIP-1β, MCP-1, MCP-2, NT-3, PDGF-AA, SCF, TNF, LT-α (TNF-β), VEGF
Recombinant Mouse: IL-1β, IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-7, IL-9, IL-10, IL-12 (p70), IL-15, IFN-γ, MCP-1, TCA3, TNF
Recombinant Rat: IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, GM-CSF, IFN-γ, TNF
Other: Viral IL-10 (1 ng/mL), Rabbit TNF
Limitations of the Procedure
· Samples that generate absorbance values higher than the standard curve should be diluted with Standard Diluent and re-assayed.
· Interference by drug metabolites, soluble receptors, or other binding proteins in specimens has not been thoroughly investigated. The possibility
of interference cannot be excluded.
· BD OptEIA™ Sets are intended for use as an integral unit. Do not mix reagents from different Set batches. Reagents from other manufacturers
are not recommended for use in this Set.
Product Notices
- For online training for BD OptEIA™ Set ELISA Techniques, please refer to http://www.bdbiosciences.com/OptEIA/downloads.shtml
- Samples that generate absorbance values higher than the standard curve should be diluted with Standard Diluent and re-assayed.
- Interference by drug metabolites, soluble receptors, or other binding proteins in specimens has not been thoroughly investigated. The possibility of interference cannot be excluded.
- BD OptEIA™ Sets are intended for use as an integral unit. Do not mix reagents from different Set batches. Reagents from other manufacturers are not recommended for use in this Set.
- Reagents which contain preservatives may be toxic if ingested, inhaled, or in contact with skin.
- Handle all serum and plasma specimens in accordance with NCCLS guidelines for preventing transmission of blood-borne infections.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- Source of all serum proteins is from USDA inspected abattoirs located in the United States.
- ProClin is a trademark of Rohm and Haas Company.
| Description | Quantity/Size | Part Number | EntrezGene ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| N/A | null | N/A | N/A |
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.