-
Reagents
- Flow Cytometry Reagents
-
Western Blotting and Molecular Reagents
- Immunoassay Reagents
-
Single-Cell Multiomics Reagents
- BD® OMICS-Guard Sample Preservation Buffer
- BD® AbSeq Assay
- BD® Single-Cell Multiplexing Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ ATAC-Seq Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Whole Transcriptome Analysis (WTA) Amplification Kit
- BD Rhapsody™ TCR/BCR Next Multiomic Assays
- BD Rhapsody™ Targeted mRNA Kits
- BD Rhapsody™ Accessory Kits
- BD® OMICS-One Protein Panels
- BD OMICS-One™ WTA Next Assay
-
Functional Assays
-
Microscopy and Imaging Reagents
-
Cell Preparation and Separation Reagents
Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current location site or be switched to your location?

BD Fc Block™ Reagents
Fcγ receptors belong to the immunoglobulin superfamily and are expressed at varying levels by multiple cell lineages, including myeloid and B cells. Different types of Fc receptors modulate a variety of primarily protective immune responses when aggregated by multivalent antigen-antibody complexes. Despite their important physiological role in the immune system, Fc receptors can also bind nonspecifically to detection antibodies in applications such as flow cytometry, causing a false-positive signal during analysis.
BD Biosciences offers a selection of isotype-specific purified recombinant Fc proteins that block nonspecific binding of Fc receptors to antibodies.
The Human BD Fc Block™ Reagent
.PCtif.tif)
.PCtif.tif)
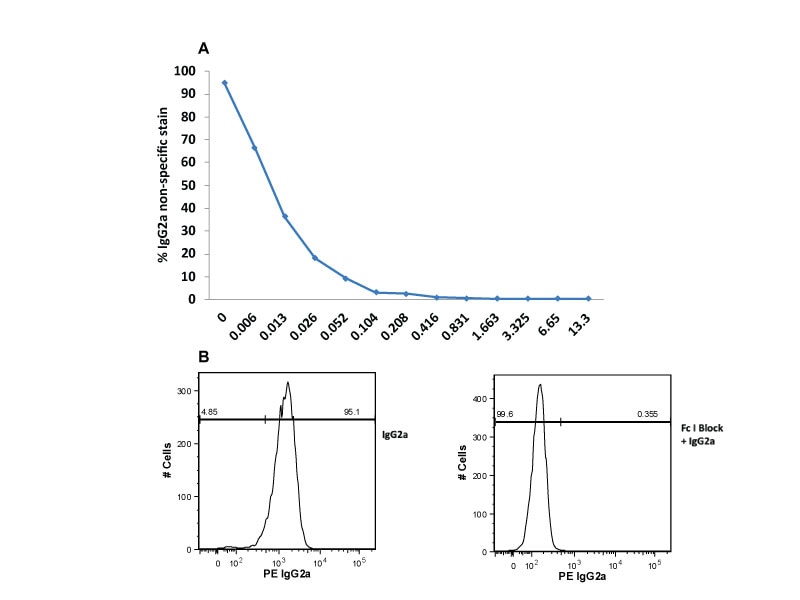
Single-color flow cytometric analysis of Ig Isotype control staining on THP-1 cells. THP-1 cells were incubated at room temperature with Human BD Fc Block™ Reagents and then stained with PE Mouse IgG2a, κ Isotype Control.
The Uses of BD Fc Block™ Reagent in Immunophenotyping of Mouse or Rat Leukocytes
FcγII and FcγIII low-affinity receptors for complexed IgG (Fc receptors or FcR) are designated CD32 and CD16, respectively, and expressed on many cell types, including B lymphocytes, NK cells, granulocytes, monocytes, macrophages and platelets. The Fc portions of antibodies may bind to FcR-bearing cells, resulting in nonspecific staining in applications such as flow cytometry.
Mouse BD Fc Block™ Reagent is a purified rat IgG2b anti-mouse CD16/CD32 monoclonal antibody,1 while Rat BD Fc Block™ Reagent is a purified mouse IgG1 anti-rat CD32 monoclonal antibody. Mouse and Rat BD Fc Block™ Reagents can be used to block the Fc-mediated binding of antibodies* to mouse or rat FcR, respectively. The Fc domain of the anti-mouse CD16/CD32 mAb 2.4G2 also binds and blocks the FcγI receptor (CD64).
Protocol for Immunofluorescent Staining of Mouse and Rat Leukocytes
I. Procedure
- Harvest cells from tissue, preparing a single-cell suspension. Red blood cells may be removed by lysis or density gradient. Red blood cells from murine peripheral blood or a spleen cell suspension can be lysed using BD Pharm Lyse™ Lysing Buffer. Add 2.0 mL of 1X lysing buffer to the spleen cell suspension or per 200 μL of murine peripheral blood. Gently vortex immediately after adding the lysing solution. Incubate at room temperature, protected from light, for 15 min. Centrifuge 200 x g for 5 min. Carefully aspirate and dispose of supernatant, without disturbing the pellet. Resuspend pellet in 1X cold wash buffer (PBS/0.1% NaN3/1.0% fetal bovine serum). Centrifuge at 350 x g for 5 min. Finally, resuspend cell pellet to a concentration of 2 x 107 cells/mL (i.e., 106 cells per 50 μL).
- Dilute primary mAbs (e.g., unconjugated, biotinylated, or fluorochrome-conjugated mAbs) to predetermined optimal concentrations (see Staining Tips) in wash buffer and deliver to the wells of a U-bottom microtiter plate in a volume of 50 μL.
- Deliver 106 cells in 50 μL to each well already containing 50 μL of mAb (or 50 μL wash buffer for negative controls). Mix by gently vortexing or tapping.
- Incubate at 4 °C for 20–40 min in the dark.
- Wash 2X with 200 μL wash buffer (or 3X if a biotin-conjugated primary antibody is used). After each centrifugation, 350 x g for 5 min, aspirate wells or flick plate to remove supernatant. Vortex gently or tap plate to loosen pellet prior to adding next wash or diluted secondary reagent.
- If a second-step reagent is needed, resuspend cell pellet in 100 μL of appropriately diluted secondary reagent (e.g., fluorochrome-conjugated avidin, streptavidin, anti-Ig allotype, anti-Ig isotype, polyclonal anti-Ig). For example, dilute antibody to ~1 μg per 100 μL in wash buffer and add this to each well containing the loosened cell pellet.
- Incubate at 4 °C for 20–40 min in the dark.
- Wash 2X with 200 μL wash buffer, as in Step 5. Use 100 μL wash buffer to transfer cell pellets to 0.4 mL aliquots of wash buffer (final concentration ~106 cells in 0.5 mL) in tubes appropriate for flow cytometer. Acquire sample data on flow cytometer as soon as possible after staining. (see Staining Tip 5.)
II. Staining Tips
- Determine optimal concentrations (brightest staining/lowest background) of each primary and secondary antibody by titrating between 1.0 μg and 0.1 μg antibody per 100 μL wash buffer for 106 cells in a preliminary experiment.
- When performing multicolor labeling, directly conjugated mAbs can be added simultaneously, rather than sequentially. For instrument setup, please see description in “Procedure for Setting Compensation for Multicolor Flow Cytometric Analysis.”
- To reduce FcgII/IIIR-mediated antibody binding (or binding of Sav-PE or Sav-Cy-chrome), which could contribute to background, the use of Purified Rat Anti-Mouse CD16/CD32 (Mouse BD Fc Block™) or Purified Mouse Anti-Rat CD32 is recommended. BD Fc Block™ Reagent can be added to cells (<1 μg per million cells, 3–5 min, 4 °C) and does not need to be washed out prior to addition of primary mAb. Verify that the secondary reagent will not bind the BD Fc Block™ Reagent. See figure legend in “The Uses of BD Fc Block™ Reagent in Immunophenotyping of Mouse and Rat Leukocytes.”
- For very low-density cell surface markers (e.g., cytokine receptors), a three-step protocol may amplify the staining. Use purified primary antibody (steps 2–4 of above procedure), biotinylated anti-Ig for the second step (steps 6–7 above), and fluorochrome-conjugated avidin or streptavidin as the third step (repeat steps 6–7).
- We have found that freshly isolated leukocytes and cell lines may wait for analysis in wash buffer at 4 °C, without fixation, for up to 18 h post-staining without loss of viability. Activated lymphocytes may lose viability rapidly, and data should be collected within 5 h of staining. To preserve cell integrity beyond these time limits, paraformaldehyde fixation may be necessary. However, it is possible that the quality of staining may be diminished by such fixation. We do not recommend fixation of stained cells, except when the possibility of exposure to biohazardous material exists.
- Every experiment must include controls. Negative controls are samples of the same cell population treated exactly as the test sample but with the omission or modification of one of the staining steps. Examples of negative controls are unstained cells, cells exposed to the second-step reagent alone or cells exposed to isotype controls that are the same isotype and format (e.g., purified, biotin or fluorochrome) as the primary antibody and titrated in parallel. For multicolor staining, single-color stained controls should be included. To identify markers on an unknown or novel cell type, positive controls (i.e., cells which are known to express the antigen of interest) should be included in each experiment and should be handled exactly as the test samples.
1. Unkeless JC. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody directed against mouse macrophage and lymphocyte Fc receptors. J Exp Med. 1979;150(3):580-596. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.580
Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.