Old Browser
This page has been recently translated and is available in French now.
Looks like you're visiting us from {countryName}.
Would you like to stay on the current country site or be switched to your country?




Flow cytometric analysis of CD3 expression on human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Human whole blood was stained with either BD Horizon™ BUV805 Mouse IgG1, κ Isotype Control (Cat. No. 612897; dashed line histogram) or BD Horizon BUV805 Mouse Anti-Human CD3 antibody (Cat. No. 612893/612894; solid line histogram). The erythrocytes were lysed with BD FACS™ Lysing Solution (Cat. No. 349202). The fluorescence histogram showing CD3 expression (or Ig Isotype control staining) was derived from gated events with the forward and side light-scatter characteristics of intact lymphocytes. Flow cytometry and data analysis were performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ X-20 Cell Analyzer System and FlowJo™ software.


BD Horizon™ BUV805 Mouse Anti-Human CD3

Regulatory Status Legend
Any use of products other than the permitted use without the express written authorization of Becton, Dickinson and Company is strictly prohibited.
Preparation And Storage
Recommended Assay Procedures
BD™ CompBeads can be used as surrogates to assess fluorescence spillover (Compensation). When fluorochrome-conjugated antibodies are bound to BD CompBeads, they have spectral properties very similar to cells. However, for some fluorochromes there can be small differences in spectral emissions compared to cells, resulting in spillover values that differ when compared to biological controls. It is strongly recommended that when using a reagent for the first time, users compare the spillover on cells and BD CompBeads. This will ensure that BD CompBeads are appropriate for your specific cellular application.
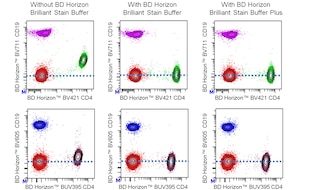
For optimal and reproducible results, BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer should be used anytime two or more BD Horizon Brilliant dyes are used in the same experiment. Fluorescent dye interactions may cause staining artifacts which may affect data interpretation. The BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer was designed to minimize these interactions. More information can be found in the Technical Data Sheet of the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer (Cat. No. 563794/566349) or the BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer Plus (Cat. No. 566385).
Note: When using high concentrations of antibody, background binding of this dye to erythroid cell subsets (mature erythrocytes and precursors) has been observed. For researchers studying these cell populations, or in cases where light scatter gating does not adequately exclude these cells from the analysis, this background may be an important factor to consider when selecting reagents for panel(s).
Product Notices
- This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test).
- An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest.
- Caution: Sodium azide yields highly toxic hydrazoic acid under acidic conditions. Dilute azide compounds in running water before discarding to avoid accumulation of potentially explosive deposits in plumbing.
- For fluorochrome spectra and suitable instrument settings, please refer to our Multicolor Flow Cytometry web page at www.bdbiosciences.com/colors.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Ultraviolet 805 is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673, 8,158,444; 8,227,187; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- BD Horizon Brilliant Stain Buffer is covered by one or more of the following US patents: 8,110,673; 8,158,444; 8,575,303; 8,354,239.
- Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/us/s/resources for technical protocols.
Companion Products





The SK7 (Leu-4) monoclonal antibody specifically binds to the epsilon chain of the CD3 antigen/T-cell antigen receptor (TCR) complex. This complex is composed of at least six proteins that range in molecular weight from 20 to 30 kDa. The antigen recognized by CD3 antibodies is noncovalently associated with either α/β or γ/δ TCR (70 to 90 kDa). The CD3 antigen is present on 61% to 85% of normal peripheral blood lymphocytes 60% to 85% of thymocytes and on Purkinje cells in the cerebellum. The soluble form of this antibody has a mitogenic effect on most peripheral blood T lymphocytes, provided appropriate functional monocytes are present.
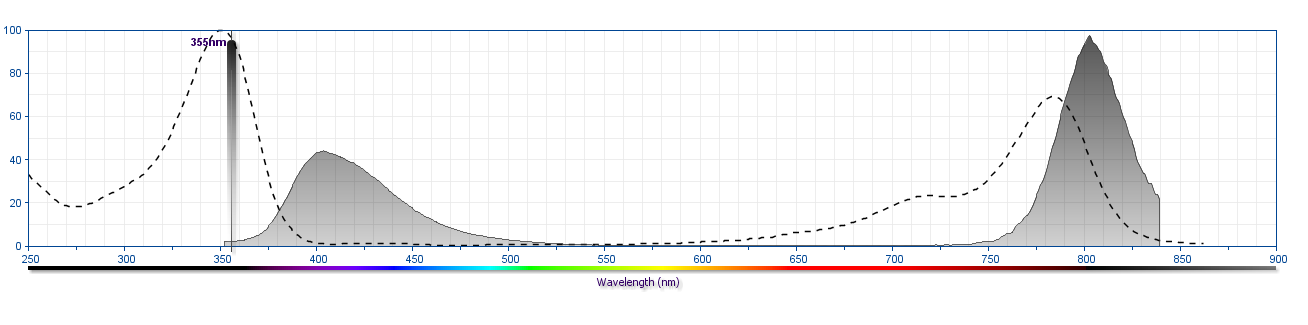
The antibody was conjugated to BD Horizon BUV805 which is part of the BD Horizon Brilliant™ Ultraviolet family of dyes. This dye is a tandem fluorochrome with an Ex Max near 350 nm and an Em Max near 805 nm. BD Horizon Brilliant BUV805 can be excited by the ultraviolet laser (355 nm) and detected with a 820/60 nm filter and a 770 nm LP.
Development References (13)
-
Ernst DN, Shih CC. CD3 complex. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2000; 14(3):226-229. (Biology). View Reference
-
Kan EA, Wang CY, Wang LC, Evans RL. Noncovalently bonded subunits of 22 and 28 kd are rapidly internalized by T cells reacted with anti-Leu-4 antibody. J Immunol. 1983; 131(2):536-539. (Clone-specific: Flow cytometry, Functional assay, Immunofluorescence, Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Kaneoka H, Perez-Rojas G, Sasasuki T, Benike CJ, Engleman EG. Human T lymphocyte proliferation induced by a pan-T monoclonal antibody (anti-Leu 4): heterogeneity of response is a function of monocytes. J Immunol. 1983; 131(1):158-164. (Clone-specific: Activation, Functional assay, Stimulation). View Reference
-
Knapp W. W. Knapp .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing IV : white cell differentiation antigens. Oxford New York: Oxford University Press; 1989:1-1182.
-
Knowles RW. Immunochemical analysis of the T-cell–specific antigens. In: Reinherz EL. Ellis L. Reinherz .. et al., ed. Leukocyte typing II. New York: Springer-Verlag; 1986:259-288.
-
Kurrle R, Seyfert W, Trautwein A, Seiler FR. T cell activation by CD3 antibodies. In: Reinherz EL. Ellis L. Reinherz .. et al., ed. Leukocyte typing II. New York: Springer-Verlag; 1986:137-146.
-
Lanier LL, Allison JP, Phillips JH. Correlation of cell surface antigen expression on human thymocytes by multi-color flow cytometric analysis: implications for differentiation. J Immunol. 1986; 137(8):2501-2507. (Clone-specific: Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Ledbetter JA, Evans RL, Lipinski M, Cunningham-Rundles C, Good RA, Herzenberg LA. Evolutionary conservation of surface molecules that distinguish T lymphocyte helper/inducer and cytotoxic/suppressor subpopulations in mouse and man. J Exp Med. 1981; 153(2):310-323. (Clone-specific: Immunoprecipitation). View Reference
-
Ledbetter JA, Frankel AE, Herzenberg. Human Leu T-cell differentiation antigens: quantitative expression on normal lymphoid cells and cell lines. In: Hammerling G, Hammerling U, Kearney J, ed. Monoclonal Antibodies and T Cell Hybridomas: Perspectives and Technical News. New York: Elsevier/North Holland Biomedical Press; 1981:16-22.
-
McMichael AJ. A.J. McMichael .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing III : white cell differentiation antigens. Oxford New York: Oxford University Press; 1987:1-1050.
-
Schlossman SF. Stuart F. Schlossman .. et al., ed. Leucocyte typing V : white cell differentiation antigens : proceedings of the fifth international workshop and conference held in Boston, USA, 3-7 November, 1993. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1995.
-
Zola H. Leukocyte and stromal cell molecules : the CD markers. Hoboken, N.J.: Wiley-Liss; 2007.
-
van Dongen JJM, Krissansen GW, Wolvers-Tettero ILM, et al. Cytoplasmic expression of the CD3 antigen as a diagnostic marker for immature T-cell malignanacies. Blood. 1988; 71(3):603-612. (Clone-specific: Immunofluorescence, Western blot). View Reference
Please refer to Support Documents for Quality Certificates
Global - Refer to manufacturer's instructions for use and related User Manuals and Technical data sheets before using this products as described
Comparisons, where applicable, are made against older BD Technology, manual methods or are general performance claims. Comparisons are not made against non-BD technologies, unless otherwise noted.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Report a Site Issue
This form is intended to help us improve our website experience. For other support, please visit our Contact Us page.